Handout for lecture 11
... • Gain from selling one more unit = 5 • But now have reduced price from 6 to 5 on the first ...
... • Gain from selling one more unit = 5 • But now have reduced price from 6 to 5 on the first ...
The “ideal” benchmark of perfect competition
... But the concept of perfect competition is important as a benchmark for assessing the different kinds of imperfect competition. ...
... But the concept of perfect competition is important as a benchmark for assessing the different kinds of imperfect competition. ...
Teacher`s name: Amanda Plummer
... The SWBAT accurately draw a graph with curves and an equilibrium point. (Ap) The SWBAT analyze a graph of supply and demand. (An) Content Outline: Supply: The amount of output available in a market. It is a quantity of goods that sellers are willing to sell. The main determinant of supply is the m ...
... The SWBAT accurately draw a graph with curves and an equilibrium point. (Ap) The SWBAT analyze a graph of supply and demand. (An) Content Outline: Supply: The amount of output available in a market. It is a quantity of goods that sellers are willing to sell. The main determinant of supply is the m ...
SL 151 Name ______ CM ______ Bremmer I May 12, 2006 3rd In
... According to the loanable funds model, an increase in the price level causes: the demand for loanable funds to shift to the right and the nominal interest rate will increase. the demand for loanable funds to shift to the left and the nominal interest rate will decrease. the supply of loanable funds ...
... According to the loanable funds model, an increase in the price level causes: the demand for loanable funds to shift to the right and the nominal interest rate will increase. the demand for loanable funds to shift to the left and the nominal interest rate will decrease. the supply of loanable funds ...
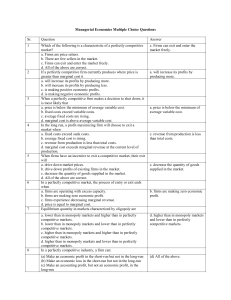
Managerial Economics Multiple Choice Questions Sr. Question
... (a) a negative strategic effect (b) a positive strategic effect (c) no strategic effect (e) no effect on profits at all. If price of substitutes of (X) increases then demand curve of X ...
... (a) a negative strategic effect (b) a positive strategic effect (c) no strategic effect (e) no effect on profits at all. If price of substitutes of (X) increases then demand curve of X ...
Demand
... the demand for another good, the two goods are called substitutes. EX.: milk and soya milk/ BMW and Audi. When a fall in the price of one good increases the demand for another good, the two goods are called complements. Ex: squash balls and squash racquets. ...
... the demand for another good, the two goods are called substitutes. EX.: milk and soya milk/ BMW and Audi. When a fall in the price of one good increases the demand for another good, the two goods are called complements. Ex: squash balls and squash racquets. ...
HW4 - QC Economics
... demanded for your product if you raise your price. While you do not know the exact demand curve for your product, you do know that in the first year you charged $45 and sold 1200 units and that in the second year you charged $30 and sold 1800 units. a. If you plan to raise your price by 10 percent, ...
... demanded for your product if you raise your price. While you do not know the exact demand curve for your product, you do know that in the first year you charged $45 and sold 1200 units and that in the second year you charged $30 and sold 1800 units. a. If you plan to raise your price by 10 percent, ...
Chapter 2
... • Three nonprice factors that shift the Aggregate Supply curve are – changes in resource costs: an increase (decrease) in resource costs shifts the AS curve to the left (right). – An advance in technology shifts the AS curve to the right. – An increase (decrease) in inflation expectations shifts the ...
... • Three nonprice factors that shift the Aggregate Supply curve are – changes in resource costs: an increase (decrease) in resource costs shifts the AS curve to the left (right). – An advance in technology shifts the AS curve to the right. – An increase (decrease) in inflation expectations shifts the ...
Economics 11 Fall 2008 Prof Woolf
... restaurant, where he makes $6/hr, next to Dr. Smith's office. Allen has to drive two hours everyday to get to work, but lives in a much nicer neighbor-hood than Dr. Smith does. The most likely explanation for this is that A) Allen doesn't like Dr. Smith. B) the opportunity cost of Dr. Smith's time i ...
... restaurant, where he makes $6/hr, next to Dr. Smith's office. Allen has to drive two hours everyday to get to work, but lives in a much nicer neighbor-hood than Dr. Smith does. The most likely explanation for this is that A) Allen doesn't like Dr. Smith. B) the opportunity cost of Dr. Smith's time i ...
SUPPLY
... able to produce at each and every price (the entire curve) Quantity supplied: amount producers are willing and able to produce at a certain price (a point on the curve) ...
... able to produce at each and every price (the entire curve) Quantity supplied: amount producers are willing and able to produce at a certain price (a point on the curve) ...
S2017 Makeup Prelim 1
... 2. Momma Bear, Poppa Bear and Baby Bear make two goods: beds and porridge. In a week’s time Poppa Bear can make 15 beds and no porridge, or 5 bowls of porridge and no beds, or any linear combination. Baby Bear can make 3 beds and no porridge, or 3 bowls of porridge and no beds, or any linear combin ...
... 2. Momma Bear, Poppa Bear and Baby Bear make two goods: beds and porridge. In a week’s time Poppa Bear can make 15 beds and no porridge, or 5 bowls of porridge and no beds, or any linear combination. Baby Bear can make 3 beds and no porridge, or 3 bowls of porridge and no beds, or any linear combin ...
Voc #3Vocabulary for Supply and Demand Lectures
... affect the quantity demanded for a product at a given price but we are going to assume that none of these change so that we look just at the price of the product and the quantity demanded for that product at that price. 13. The Law of downward sloping demand. For most products, you will observe that ...
... affect the quantity demanded for a product at a given price but we are going to assume that none of these change so that we look just at the price of the product and the quantity demanded for that product at that price. 13. The Law of downward sloping demand. For most products, you will observe that ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑