Basic Economic Concept – Unit 1 – Homework Packet
... 6. If BB' represents a country’s current production possibilities curve, what can you say about a point like X? (Write a brief statement.) 7. If BB' represents a country’s current production possibilities curve, what can you say about a point like Y? (Write a brief statement.) 1.2 Opportunity Cost a ...
... 6. If BB' represents a country’s current production possibilities curve, what can you say about a point like X? (Write a brief statement.) 7. If BB' represents a country’s current production possibilities curve, what can you say about a point like Y? (Write a brief statement.) 1.2 Opportunity Cost a ...
price rationing
... the price (bid) will rise to eliminate excess demand until there is only one bidder willing to purchase the single available painting. Some estimate that the Mona Lisa would sell for $600 million if auctioned. ...
... the price (bid) will rise to eliminate excess demand until there is only one bidder willing to purchase the single available painting. Some estimate that the Mona Lisa would sell for $600 million if auctioned. ...
1 - Carlos Pitta
... Question # 9: Here you need to calculate two areas: the rectangle with an area (BASE*HEIGHT) equal to: (Height: 22-16=6, in the price axis) times (Base: 0 to 40=40, in the quantity axis)= 240 PLUS, the triangle Base (80 – 40=40, in the quantity axis) times (Height: 22-16=6, en the price axis) times ...
... Question # 9: Here you need to calculate two areas: the rectangle with an area (BASE*HEIGHT) equal to: (Height: 22-16=6, in the price axis) times (Base: 0 to 40=40, in the quantity axis)= 240 PLUS, the triangle Base (80 – 40=40, in the quantity axis) times (Height: 22-16=6, en the price axis) times ...
Chapter 11
... maximizes joint profits. b. maximizes the price received. c. maximizes profits given what the other firm produces. d. maximizes revenue given what the other firm produces. Product differentiation complicates the study of oligopolies because such markets may not a. be efficient. b. have prices equal ...
... maximizes joint profits. b. maximizes the price received. c. maximizes profits given what the other firm produces. d. maximizes revenue given what the other firm produces. Product differentiation complicates the study of oligopolies because such markets may not a. be efficient. b. have prices equal ...
Qs-ch7-9
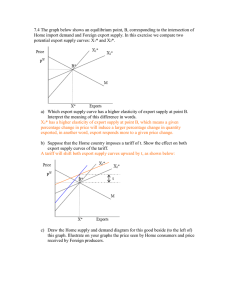
... e) Tariff, t, in a small country corresponding to the quantity of imports M. f) Tariff, t, in a large country corresponding to the same quantity of imports M. g) Tariff, t’, in a large country corresponding to the quantity of imports M’>M. h) Quota of M in a small country, but with Home monopoly. Fi ...
... e) Tariff, t, in a small country corresponding to the quantity of imports M. f) Tariff, t, in a large country corresponding to the same quantity of imports M. g) Tariff, t’, in a large country corresponding to the quantity of imports M’>M. h) Quota of M in a small country, but with Home monopoly. Fi ...
Chapter 2: The basics of Supply and Demand
... (c) the demand curve will shift to restore equilibrium (d) the supply curve will shift to restore equilibrium in the market (e) prices are expected to fall 12. Assume the market for bubble gum is competitive and current conditions yield an equilibrium at a price of 25 cents and a quantity of 100,000 ...
... (c) the demand curve will shift to restore equilibrium (d) the supply curve will shift to restore equilibrium in the market (e) prices are expected to fall 12. Assume the market for bubble gum is competitive and current conditions yield an equilibrium at a price of 25 cents and a quantity of 100,000 ...
Monopolistic Competition
... Potential entrants must be able to serve the same market as existing firms. New firms may use the same production techniques and produce at the same per unit cost as existing firms Potential entrants incur zero sunk costs. Potential entrants estimate profits based on existing industry prices (i.e., ...
... Potential entrants must be able to serve the same market as existing firms. New firms may use the same production techniques and produce at the same per unit cost as existing firms Potential entrants incur zero sunk costs. Potential entrants estimate profits based on existing industry prices (i.e., ...
Study Guide: Sample Chapter 3
... 19. A change in any influence on supply—except for the good’s price—causes the supply curve to ____________________. We call this a ____________________. 20. A rise in the price of an input causes a ____________________ in supply, shifting the supply curve to the ____________________. 21. A rise in ...
... 19. A change in any influence on supply—except for the good’s price—causes the supply curve to ____________________. We call this a ____________________. 20. A rise in the price of an input causes a ____________________ in supply, shifting the supply curve to the ____________________. 21. A rise in ...
profit and loss presentation
... • Value added may be tangible – additional features or intangible – brand image, style, etc. • Value Chain – value adding activities in a product or service ...
... • Value added may be tangible – additional features or intangible – brand image, style, etc. • Value Chain – value adding activities in a product or service ...
File - ECONOMICS @ Isleworth
... good responds to a change in price of the other good. Substitutes – have a positive cross elasticity (the change in the price of good B causes a similar change in the quantity demanded of good a e.g. B goes up, A goes up). The bigger the number, the closer they are substitutes. Complements – have a ...
... good responds to a change in price of the other good. Substitutes – have a positive cross elasticity (the change in the price of good B causes a similar change in the quantity demanded of good a e.g. B goes up, A goes up). The bigger the number, the closer they are substitutes. Complements – have a ...
EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY
... sector is unionized than if the labor market is supplied perfectly competitive. 3. The elasticity of demand for a factor of production will be larger if the prices of all other factors of production are held constant rather than if the quantities of all other factors are held constant. 4. Consider a ...
... sector is unionized than if the labor market is supplied perfectly competitive. 3. The elasticity of demand for a factor of production will be larger if the prices of all other factors of production are held constant rather than if the quantities of all other factors are held constant. 4. Consider a ...
Economics, by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick
... A situation in which economies of scale are so large that one firm can supply the entire market at a lower average total cost than can two or more firms. ...
... A situation in which economies of scale are so large that one firm can supply the entire market at a lower average total cost than can two or more firms. ...
demand
... direct competition that the increased consumption of one will probably result in a decrease in demand for the other. Similarly, an increase in the price of one will actually cause an increase in demand for the other. For example, if the prices of private single-family homes are high, then more peopl ...
... direct competition that the increased consumption of one will probably result in a decrease in demand for the other. Similarly, an increase in the price of one will actually cause an increase in demand for the other. For example, if the prices of private single-family homes are high, then more peopl ...
1st Midterm F11
... Answer: Producing 105 units of cider, so X = (105,10). Dan produces 60 units of cider (he has the lowest opportunity cost of producing cider), Jake produces 40 units of cider (he has the next lowest opportunity cost of producing cider), Kyle produces 5 units of cider and the 10 units of pretzels. Po ...
... Answer: Producing 105 units of cider, so X = (105,10). Dan produces 60 units of cider (he has the lowest opportunity cost of producing cider), Jake produces 40 units of cider (he has the next lowest opportunity cost of producing cider), Kyle produces 5 units of cider and the 10 units of pretzels. Po ...
law of demand
... Understand how the behavior of buyers and sellers can be characterized through demand and supply curves. Explain how equilibrium price and quantity are determined in a market for a good or service. Analyze how a market equilibrium is affected by changes in demand or supply. Explore the effects of go ...
... Understand how the behavior of buyers and sellers can be characterized through demand and supply curves. Explain how equilibrium price and quantity are determined in a market for a good or service. Analyze how a market equilibrium is affected by changes in demand or supply. Explore the effects of go ...
Izmir University of Economics Name & Surname: Department of Economics, Fall 2014
... Note: The duration of the exam is 90 minutes. Good luck! Part1: Each multiple choice questions is worth 2 points. The whole section is worth 30 points. 1) Which of the following best defines economics? A) Economics teaches how to limit our wants. B) Economics studies how to choose the best alternati ...
... Note: The duration of the exam is 90 minutes. Good luck! Part1: Each multiple choice questions is worth 2 points. The whole section is worth 30 points. 1) Which of the following best defines economics? A) Economics teaches how to limit our wants. B) Economics studies how to choose the best alternati ...
Midterm Exam #2 Multiple choice questions 1
... 42.A local store noticed that when it increased the price of milk from $2.50 per gallon to $3.50 per gallon, it sold the same amount of milk per week (165 gallons). Since everything else remained the same, we would say the ( c ) a. demand for milk is perfectly elastic b. demand for milk is elastic c ...
... 42.A local store noticed that when it increased the price of milk from $2.50 per gallon to $3.50 per gallon, it sold the same amount of milk per week (165 gallons). Since everything else remained the same, we would say the ( c ) a. demand for milk is perfectly elastic b. demand for milk is elastic c ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑