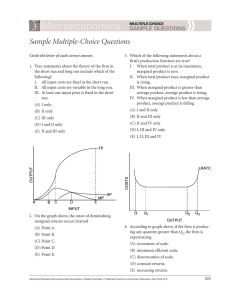
Practice problems on Chapter 8
... 4. The benefit to buyers of participating in a market is measured by a. the price elasticity of demand. b. consumer surplus. c. the amount buyers are willing to pay for the good. d. the equilibrium price. 5. The benefit that government receives from a tax is measured by a. the change in the equilibr ...
... 4. The benefit to buyers of participating in a market is measured by a. the price elasticity of demand. b. consumer surplus. c. the amount buyers are willing to pay for the good. d. the equilibrium price. 5. The benefit that government receives from a tax is measured by a. the change in the equilibr ...
Lecture 4: Markets In Action
... because more cranberries will be produced. B. The supply of cranberries will increase as the marginal cost of production for farmers falls. C. The quantity of cranberries purchased will increase as the price falls. D. Both A and B are correct. E. Both B and C are correct. ...
... because more cranberries will be produced. B. The supply of cranberries will increase as the marginal cost of production for farmers falls. C. The quantity of cranberries purchased will increase as the price falls. D. Both A and B are correct. E. Both B and C are correct. ...
Factor Markets: Land, Labor, and Capital
... change in wealth shifts labor supply, but income effect from wage rate increase is a movement along labor supply. ...
... change in wealth shifts labor supply, but income effect from wage rate increase is a movement along labor supply. ...
An example of competitive equilibrium in production economy: U1
... Explanatory note: Is this way of computing CE is different from other previous questions, eg. when both agents have Cobb-Douglas? Or why in this question we have to bother about checking for demand side of good x when we have already cleared the market of good y? If you have noticed, in some of the ...
... Explanatory note: Is this way of computing CE is different from other previous questions, eg. when both agents have Cobb-Douglas? Or why in this question we have to bother about checking for demand side of good x when we have already cleared the market of good y? If you have noticed, in some of the ...
problem set 1 - Shepherd Webpages
... the product and the actual market price that is paid, summed over all units that are produced and sold. The lowest price at which someone is willing to supply the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using real world data, three ...
... the product and the actual market price that is paid, summed over all units that are produced and sold. The lowest price at which someone is willing to supply the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using real world data, three ...
AP Micro 3-4 Perfect Competition Long-Run
... What happens to P and Q in the industry? What happens to P and Q in the firm? ...
... What happens to P and Q in the industry? What happens to P and Q in the firm? ...
Lecture 4: Topic #1 Extent (How Much) Decisions Marginal Revenue
... • A US company, NNS, that produces potash fertilizer experienced an increase in input costs due to their use of petrochemicals. • NNS doubled the price of the generic fertilizer, and priced it’s branded fertilizer at a 35% premium above the generic price. • Costs increased rapidly over the first ...
... • A US company, NNS, that produces potash fertilizer experienced an increase in input costs due to their use of petrochemicals. • NNS doubled the price of the generic fertilizer, and priced it’s branded fertilizer at a 35% premium above the generic price. • Costs increased rapidly over the first ...
Pricing!!
... Price Sensitivity Measures from consumers Oral-B’s Cross Action toothbrush has three types of bristles that are set at different angles. It has a dense tip that cleans behind back teeth and an ergonomic rubberized handle. ...
... Price Sensitivity Measures from consumers Oral-B’s Cross Action toothbrush has three types of bristles that are set at different angles. It has a dense tip that cleans behind back teeth and an ergonomic rubberized handle. ...
EB Chapter 5 Market Conditions and Business Environments
... is the largest coffee and fresh-baked goods restaurant chain in Canada. Tim Horton, the popular Maple Leafs’ hockey star, opened the first Tim Hortons coffee and donut restaurant in Hamilton, Ontario, in 1964. Ron Joyce, a retired Canadian navy and police officer, became the first franchisee. After ...
... is the largest coffee and fresh-baked goods restaurant chain in Canada. Tim Horton, the popular Maple Leafs’ hockey star, opened the first Tim Hortons coffee and donut restaurant in Hamilton, Ontario, in 1964. Ron Joyce, a retired Canadian navy and police officer, became the first franchisee. After ...
Chapter four - Whitman People
... video rental franchise charges $3.50 per movie what will Bill’s consumer surplus be and why? Assume now that the video rental franchise now has a new package deal in which it offers to rent three movies to customers at a price of $9.00 would Bill be interested? How much consumer surplus would he enj ...
... video rental franchise charges $3.50 per movie what will Bill’s consumer surplus be and why? Assume now that the video rental franchise now has a new package deal in which it offers to rent three movies to customers at a price of $9.00 would Bill be interested? How much consumer surplus would he enj ...
Principles of Economics
... what proportions is the burden of the tax divided? How do the effects of taxes on sellers compare to those levied on buyers? The answers to these questions depend on the elasticity of demand and the elasticity of supply. ...
... what proportions is the burden of the tax divided? How do the effects of taxes on sellers compare to those levied on buyers? The answers to these questions depend on the elasticity of demand and the elasticity of supply. ...
Practice Quiz
... If a firm has no ability to select the price of its product, it: a. will go out of business due to losses. b. is a price-maker. c. cannot maximize profit. d. has a horizontal individual demand curve. Topic: Price taker, Difficulty: D, Type: RE, Answer: d A firm operating in a perfectly competitive m ...
... If a firm has no ability to select the price of its product, it: a. will go out of business due to losses. b. is a price-maker. c. cannot maximize profit. d. has a horizontal individual demand curve. Topic: Price taker, Difficulty: D, Type: RE, Answer: d A firm operating in a perfectly competitive m ...
Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair/Oster, 10e
... As illustrated in (a), some producers are willing to produce hamburgers for a price of $0.75 each. Since they are paid $2.50, they earn a producer surplus equal to $1.75. Other producers are willing to supply hamburgers at a price of $1.00; they receive a producer surplus equal to $1.50. Since the m ...
... As illustrated in (a), some producers are willing to produce hamburgers for a price of $0.75 each. Since they are paid $2.50, they earn a producer surplus equal to $1.75. Other producers are willing to supply hamburgers at a price of $1.00; they receive a producer surplus equal to $1.50. Since the m ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑