Micro Exam
... 3. Assume that the government increases the unit excise tax on gasoline suppliers and also that people commute longer distances to work as more houses are built in city suburbs. As a result, the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline will most likely change in which of the following ways? (A) (B ...
... 3. Assume that the government increases the unit excise tax on gasoline suppliers and also that people commute longer distances to work as more houses are built in city suburbs. As a result, the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline will most likely change in which of the following ways? (A) (B ...
PP - Personal.kent.edu
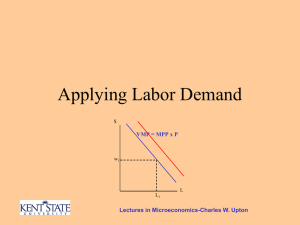
... Let’s see what happens when in the long run when the price of a product changes. Initially the firm is employing L* workers. ...
... Let’s see what happens when in the long run when the price of a product changes. Initially the firm is employing L* workers. ...
Introduction to Agricultural Economics
... Drawing graphs for substitution and income effects: Steps - Draw original budget constraint. Mark point of “consumer equilibrium” - Once price changes, draw new budget constraint. Identify new “consumer equilibrium”. - Identify substitution effect. It is the movement on the original indifference cu ...
... Drawing graphs for substitution and income effects: Steps - Draw original budget constraint. Mark point of “consumer equilibrium” - Once price changes, draw new budget constraint. Identify new “consumer equilibrium”. - Identify substitution effect. It is the movement on the original indifference cu ...
CHAPTER 2 Demand and Supply
... schedule like the one in Figure 2.1. Expressing the schedule on a graph, as shown on the right in Figure 2.1, gives us the consumer’s demand curve (D) for strawberries. The demand curve is drawn by placing the price of strawberries on the vertical axis and the quantity demanded per month on the hori ...
... schedule like the one in Figure 2.1. Expressing the schedule on a graph, as shown on the right in Figure 2.1, gives us the consumer’s demand curve (D) for strawberries. The demand curve is drawn by placing the price of strawberries on the vertical axis and the quantity demanded per month on the hori ...
GRAPHING A LINEAR EQUATION
... a linear relationship, write an equation that will give the price of the house in any year, and use this equation to predict the price of a similar house in the year 2010. 23) The population of Argentina in 1987 was 31.5 million and in 1997 it was 42.5 million. Assuming a linear relationship, write ...
... a linear relationship, write an equation that will give the price of the house in any year, and use this equation to predict the price of a similar house in the year 2010. 23) The population of Argentina in 1987 was 31.5 million and in 1997 it was 42.5 million. Assuming a linear relationship, write ...
Factor Markets and Income Distribution
... product – like people of different races, sexes who get different wages. 2. In the real world some resources are not fully employed and seem to have prices higher than their value of marginal product or their market clearing levels. 3. It leads to the belief that the existing distribution of income ...
... product – like people of different races, sexes who get different wages. 2. In the real world some resources are not fully employed and seem to have prices higher than their value of marginal product or their market clearing levels. 3. It leads to the belief that the existing distribution of income ...
The Price System, Demand and Supply, and Elasticity Chapter 4
... the way that markets and market price work to allocate scarce resources. Recall that when we try to understand “how the system works,” we are ...
... the way that markets and market price work to allocate scarce resources. Recall that when we try to understand “how the system works,” we are ...
Spatial Variation of the Marginal Utility of Income
... preferences”), and both households will move to new equilibria at A’ and B’ on the same higher indifference curve. This shows, in accordance with (6) and (7), that both households are equally efficient at converting income into utility, even though facing different prices. In this case, the sum of u ...
... preferences”), and both households will move to new equilibria at A’ and B’ on the same higher indifference curve. This shows, in accordance with (6) and (7), that both households are equally efficient at converting income into utility, even though facing different prices. In this case, the sum of u ...
AP® Microeconomics
... 3. Assume that the government increases the unit excise tax on gasoline suppliers and also that people commute longer distances to work as more houses are built in city suburbs. As a result, the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline will most likely change in which of the following ways? (A) (B ...
... 3. Assume that the government increases the unit excise tax on gasoline suppliers and also that people commute longer distances to work as more houses are built in city suburbs. As a result, the equilibrium price and quantity of gasoline will most likely change in which of the following ways? (A) (B ...
Total Revenue Marginal Revenue
... The inefficiencies of monopoly may be effect OR lessened by economies of scale and less likely by technological progress but they may be intensified by the presence of X-inefficiency and rent-seeking expenditures. Price discrimination occurs when a firm sells a product at different price that a ...
... The inefficiencies of monopoly may be effect OR lessened by economies of scale and less likely by technological progress but they may be intensified by the presence of X-inefficiency and rent-seeking expenditures. Price discrimination occurs when a firm sells a product at different price that a ...
File
... price rises the evidence seems to suggest that smokers will continue to smoke with little change in their habit. However, even with this product it is probably the case that if price rose to $15 or $20 for a packet of 20 cigarettes there would be a greater impact on demand and demand would become mo ...
... price rises the evidence seems to suggest that smokers will continue to smoke with little change in their habit. However, even with this product it is probably the case that if price rose to $15 or $20 for a packet of 20 cigarettes there would be a greater impact on demand and demand would become mo ...
A. A consumer chooses between two goods, x and x
... The expected utility from a lottery with two outcomes is a point on the straight line connecting the utility levels at the two outcomes. When an individual’s utility function is concave, this line with always lie below the utility curve, indicating that the individual would prefer to have the expect ...
... The expected utility from a lottery with two outcomes is a point on the straight line connecting the utility levels at the two outcomes. When an individual’s utility function is concave, this line with always lie below the utility curve, indicating that the individual would prefer to have the expect ...
Answer on Question #54472, Economics / Economics of Enterprise
... thumb to help us determine the relationship between the two goods. If cross price elasticity > 0 then the two goods are substitutes; If cross price elasticity = 0 then the two goods are independent; If cross price elasticity < 0 then the two goods are complements. Since the cross elasticity of deman ...
... thumb to help us determine the relationship between the two goods. If cross price elasticity > 0 then the two goods are substitutes; If cross price elasticity = 0 then the two goods are independent; If cross price elasticity < 0 then the two goods are complements. Since the cross elasticity of deman ...
General Equilibrium
... In the partial equilibrium set up we assumed that all prices other than the price ...
... In the partial equilibrium set up we assumed that all prices other than the price ...
MONOPOLY A (pure) monopolist is a sole supplier of the output of
... When a firm gets into the market ahead of others, it might be able to expand and reap economies of scale. It would be able to charge a lower price than its rivals. It would eat into the market share of its competitors who are forced to cut back production and shut down plants. Not able to compete, ...
... When a firm gets into the market ahead of others, it might be able to expand and reap economies of scale. It would be able to charge a lower price than its rivals. It would eat into the market share of its competitors who are forced to cut back production and shut down plants. Not able to compete, ...
Demand and Supply - Tactic Publications
... • The income effect - when the price of a good rises, consumers are not willing to buy as much of the good because their real income or purchasing power has decreased. If you have $100 in income and the price of a pizza is $10 then your real income is 10 pizzas. If the price of pizzas increases to ...
... • The income effect - when the price of a good rises, consumers are not willing to buy as much of the good because their real income or purchasing power has decreased. If you have $100 in income and the price of a pizza is $10 then your real income is 10 pizzas. If the price of pizzas increases to ...
1. - faculty.bcitbusiness.org at 142.232.104.155
... when firms make decisions that explicitly take each other’s behavior into account is the same as the equilibrium in competitive and monopolistic markets: When a market is in equilibrium, firms are doing the best they can and have no reason to change their price or output. ...
... when firms make decisions that explicitly take each other’s behavior into account is the same as the equilibrium in competitive and monopolistic markets: When a market is in equilibrium, firms are doing the best they can and have no reason to change their price or output. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑