AP Microeconomics
... • Marginal Revenue: extra revenue gained with each additional unit of output; MR = ΔTR • P = d = MR: Price Takers, each firm takes market price (or market demand) so P and MR are constant (perfectly elastic & horizontal) ...
... • Marginal Revenue: extra revenue gained with each additional unit of output; MR = ΔTR • P = d = MR: Price Takers, each firm takes market price (or market demand) so P and MR are constant (perfectly elastic & horizontal) ...
Chapter 7
... 3. The industry is a constant-cost industry, which means that the entry and exit of firms will not affect resource prices or location of unit-cost schedules for individual firms. B. Basic conclusion to be explained is that after long-run equilibrium is achieved, the product price will be exactly equ ...
... 3. The industry is a constant-cost industry, which means that the entry and exit of firms will not affect resource prices or location of unit-cost schedules for individual firms. B. Basic conclusion to be explained is that after long-run equilibrium is achieved, the product price will be exactly equ ...
Document
... demand curve shifts up (db); economic profit, which attracts new firms. Input prices go up, MC and ATC curves shift up. Market S increases to S’; new price pc, firm’s demand curve shifts ...
... demand curve shifts up (db); economic profit, which attracts new firms. Input prices go up, MC and ATC curves shift up. Market S increases to S’; new price pc, firm’s demand curve shifts ...
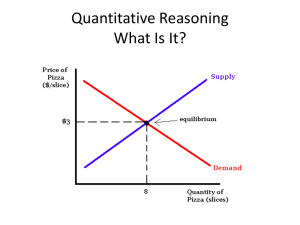
Quantitative Reasoning What Is It?
... • Expressing a solution so that an audience understands what the solution means • In class discussion or presentations, can you (for instance) explain the concept of wage elasticity of demand, apply it to the question of teenage employment in fast food restaurants and explain the effect of an increa ...
... • Expressing a solution so that an audience understands what the solution means • In class discussion or presentations, can you (for instance) explain the concept of wage elasticity of demand, apply it to the question of teenage employment in fast food restaurants and explain the effect of an increa ...
worksheet - Econedlink
... food choices, which tend to continue into adulthood. McDonald's hoped that by introducing the dolls, more girls would be enticed to eat at McDonald's, increasing the company's customer base long into the future. 1. Is McDonald’s attempting to change the demand for or the supply of Happy Meals? Is Mc ...
... food choices, which tend to continue into adulthood. McDonald's hoped that by introducing the dolls, more girls would be enticed to eat at McDonald's, increasing the company's customer base long into the future. 1. Is McDonald’s attempting to change the demand for or the supply of Happy Meals? Is Mc ...
Chapter 11 - Barren County Schools
... Ex: spring, summer, and fall are busy seasons for farm workers – however, they may lose their job during the winter months. ...
... Ex: spring, summer, and fall are busy seasons for farm workers – however, they may lose their job during the winter months. ...
Potential Benefits of Production Information to Cattle Producers
... – Usually sell for a higher price ...
... – Usually sell for a higher price ...
Elasticity Demand
... What is the difference in price between week 1 and week 2? What is the percentage change? (Difference ÷ Original) She then sold 75. What is the difference in quantity demanded (sold) between wk 1 and wk 2? What is the percentage change? (Difference ÷ Original) % change quantity demanded (balls sold) ...
... What is the difference in price between week 1 and week 2? What is the percentage change? (Difference ÷ Original) She then sold 75. What is the difference in quantity demanded (sold) between wk 1 and wk 2? What is the percentage change? (Difference ÷ Original) % change quantity demanded (balls sold) ...
File
... • If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that consumers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? ...
... • If you were running a business, what would you do if you discovered that consumers were suddenly willing to pay twice as much for your product? ...
Demand and Supply
... The greater the number of sellers in a market, the larger is supply. Productivity Productivity is output per unit of input. An increase in productivity lowers costs and increases supply. ...
... The greater the number of sellers in a market, the larger is supply. Productivity Productivity is output per unit of input. An increase in productivity lowers costs and increases supply. ...
Teacher`s name: Amanda Plummer
... The SWBAT accurately draw a graph with curves and an equilibrium point. (Ap) The SWBAT analyze a graph of supply and demand. (An) Content Outline: Supply: The amount of output available in a market. It is a quantity of goods that sellers are willing to sell. The main determinant of supply is the m ...
... The SWBAT accurately draw a graph with curves and an equilibrium point. (Ap) The SWBAT analyze a graph of supply and demand. (An) Content Outline: Supply: The amount of output available in a market. It is a quantity of goods that sellers are willing to sell. The main determinant of supply is the m ...
PDF
... represents the market’s expectation of the price once the harvest is complete. These contracts trade near‐continuously, and their prices change as traders update their own expectations based on new fundamental information, such as revisions to USDA crop forecasts (e.g., Adjemian, 2012). ...
... represents the market’s expectation of the price once the harvest is complete. These contracts trade near‐continuously, and their prices change as traders update their own expectations based on new fundamental information, such as revisions to USDA crop forecasts (e.g., Adjemian, 2012). ...
Supply and Demand
... WHAT we produce is determined by the equilibrium of the markets. HOW we produce is determined by profit seeking behavior and using resources ...
... WHAT we produce is determined by the equilibrium of the markets. HOW we produce is determined by profit seeking behavior and using resources ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.