Imperfect Competition
... as much as a monopoly, so we expect an intermediate outcome. Model #1: Firms compete by simultaneously setting their quantities (Cournot model). Model #2: Firms compete by simultaneously setting their prices ...
... as much as a monopoly, so we expect an intermediate outcome. Model #1: Firms compete by simultaneously setting their quantities (Cournot model). Model #2: Firms compete by simultaneously setting their prices ...
Study Questions
... 1. Consider the following inverse demand curve faced by a monopolist: P= 100 -Q. a. Find the marginal revenue curve for the monopolist. b. At what quantity is total revenue maximized? c. If MC and AC are constant at $20, then what is the profit-maximizing output for a monopoly? What is the monopoly ...
... 1. Consider the following inverse demand curve faced by a monopolist: P= 100 -Q. a. Find the marginal revenue curve for the monopolist. b. At what quantity is total revenue maximized? c. If MC and AC are constant at $20, then what is the profit-maximizing output for a monopoly? What is the monopoly ...
The Prisoners` Dilemma
... attempts to prevent monopoly behavior. When monopolies are “created” rather than natural, governments should act to prevent them from forming and break up existing ones. The government policies used to prevent or eliminate monopolies are known as antitrust policy. ...
... attempts to prevent monopoly behavior. When monopolies are “created” rather than natural, governments should act to prevent them from forming and break up existing ones. The government policies used to prevent or eliminate monopolies are known as antitrust policy. ...
Price elasticity of Demand PowerPoint
... • Price elasticity of demand is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good. • Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded given a percent change in the price. ...
... • Price elasticity of demand is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good. • Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded given a percent change in the price. ...
print version
... many producers/sellers, very many consumers/buyers, and therefore no seller or buyer can dominate the market. Perfect competition can lead to sellers undercutting each other. Secondly, perfect monopoly is the extreme opposite to perfect competition where products are unique; there is only one produc ...
... many producers/sellers, very many consumers/buyers, and therefore no seller or buyer can dominate the market. Perfect competition can lead to sellers undercutting each other. Secondly, perfect monopoly is the extreme opposite to perfect competition where products are unique; there is only one produc ...
I. The Basic Economic Concepts
... increasing relative opportunity costs. Inflation if you try to be outside the PPF Zero opportunity cost to produce more if inside the PPF (like in today’s US economy) Shifts caused by losses and gains of resources Shifts caused by technological progress. Comparative Advantage and foreign trade ...
... increasing relative opportunity costs. Inflation if you try to be outside the PPF Zero opportunity cost to produce more if inside the PPF (like in today’s US economy) Shifts caused by losses and gains of resources Shifts caused by technological progress. Comparative Advantage and foreign trade ...
Monopoly
... – If monopolists are no greedier than perfect competitors because both maximize profit – What is the problem with monopoly? • Lower output • Higher price – Than perfect competition ...
... – If monopolists are no greedier than perfect competitors because both maximize profit – What is the problem with monopoly? • Lower output • Higher price – Than perfect competition ...
Presentation
... 3) We derive a formula for marginal revenue and marginal cost within this relevant range If MR>MC at our current price, our product is ...
... 3) We derive a formula for marginal revenue and marginal cost within this relevant range If MR>MC at our current price, our product is ...
Problem Set #6 - people.vcu.edu
... compensated demand curve is given by esX PX = -(1-sx) where sx is the share of income spent on good X and us the substitution elasticity. Use this result together with the elasticity interpretation of the Slutsky equation to show that: a. if =1 (the Cobb-Douglas case), eX PX + eY PY = -2 b. >1 ...
... compensated demand curve is given by esX PX = -(1-sx) where sx is the share of income spent on good X and us the substitution elasticity. Use this result together with the elasticity interpretation of the Slutsky equation to show that: a. if =1 (the Cobb-Douglas case), eX PX + eY PY = -2 b. >1 ...
Supply and Demand
... Demand – Inverse Relationship Other Factors that affect Quantity Demanded: ◦ Real Income Effect ◦ Substitute Effect ◦ Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility ...
... Demand – Inverse Relationship Other Factors that affect Quantity Demanded: ◦ Real Income Effect ◦ Substitute Effect ◦ Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility ...
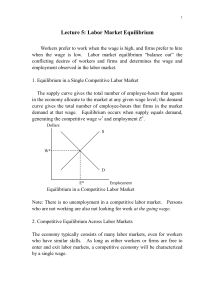
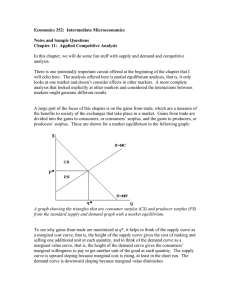
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.