Answers to Homework #2
... unaffected by the tax-rebate program, because in this case the household pays 0.10*500=$50 in taxes and receives $50 as an annual tax rebate. The two effects would cancel each other out. To the extent that the household reduces its gas consumption through substitution, it must be better off. The new ...
... unaffected by the tax-rebate program, because in this case the household pays 0.10*500=$50 in taxes and receives $50 as an annual tax rebate. The two effects would cancel each other out. To the extent that the household reduces its gas consumption through substitution, it must be better off. The new ...
Name
... a. On a large graph, plot the MC, AFC, AVC, and ATC curves from this data (____/5) b. EXPLAIN what would happen to each of Cory’s per unit cost curves if the price of Styrofoam blanks (a variable input) increases. How would the cost curves change if there were an increase in his rent (a fixed input) ...
... a. On a large graph, plot the MC, AFC, AVC, and ATC curves from this data (____/5) b. EXPLAIN what would happen to each of Cory’s per unit cost curves if the price of Styrofoam blanks (a variable input) increases. How would the cost curves change if there were an increase in his rent (a fixed input) ...
ECON101 2015-16 Fall Midterm Answer Key
... For leisure travelers, the percentage change in the quantity of tickets demanded is the change in the quantity demanded, 400, divided by the average quantity, 600, multiplied by 100, or (400/600) × 100, which is 66.7 percent. So for leisure travelers, the percentage ch ...
... For leisure travelers, the percentage change in the quantity of tickets demanded is the change in the quantity demanded, 400, divided by the average quantity, 600, multiplied by 100, or (400/600) × 100, which is 66.7 percent. So for leisure travelers, the percentage ch ...
How? When? What? The economics of competitive advantage Why?
... costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary rate of return needed by a c ...
... costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary rate of return needed by a c ...
How? When? What? The economics of competitive advantage Why?
... costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary rate of return needed by a c ...
... costs and profits • Accountants focus on historical records of explicit costs • Economists consider explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs, especially the marginal cost (sunk costs are irrelevant as bygones are bygones) • Zero or normal profit is the minimum/necessary rate of return needed by a c ...
Demand curve
... Supply: the demand curve Quantity supplied - the amount of a good that firms want to sell at a given price, holding constant other factors that influence firms’ supply decisions, such as costs and government actions Supply curve - the quantity supplied at each possible price, holding constant t ...
... Supply: the demand curve Quantity supplied - the amount of a good that firms want to sell at a given price, holding constant other factors that influence firms’ supply decisions, such as costs and government actions Supply curve - the quantity supplied at each possible price, holding constant t ...
ch08, lecture
... 12. In Exhibit 15, the firm’s total revenue at a price of $10 per unit pays for a. a portion of total variable costs. b. a portion of total fixed costs. c. none of the total fixed costs. d. all of the total fixed costs. D. At a price of $10, the firm is making an economic profit - more than enough ...
... 12. In Exhibit 15, the firm’s total revenue at a price of $10 per unit pays for a. a portion of total variable costs. b. a portion of total fixed costs. c. none of the total fixed costs. d. all of the total fixed costs. D. At a price of $10, the firm is making an economic profit - more than enough ...
Chapter 4
... economy based on the market 2. A market demand schedule shows the quantities of products demanded at each price by all consumers in a market ...
... economy based on the market 2. A market demand schedule shows the quantities of products demanded at each price by all consumers in a market ...
Measles Vaccine Mania? The 1987-1989 epidemic and the demand
... dissuaded some parents from vaccinating their kids, illustrated as a movement up the demand curve from B to E. On the other side of the market, higher prices would have induced pharmaceutical companies to squeeze additional doses from their factories, illustrated as a movement up the supply curve fr ...
... dissuaded some parents from vaccinating their kids, illustrated as a movement up the demand curve from B to E. On the other side of the market, higher prices would have induced pharmaceutical companies to squeeze additional doses from their factories, illustrated as a movement up the supply curve fr ...
Economics Chapter 4
... Other factors, however, might also have an effect on the marketing of pizza. ...
... Other factors, however, might also have an effect on the marketing of pizza. ...
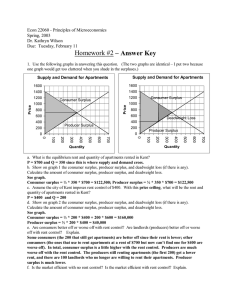
Homework #2 – Answer Key
... of $5.15 per hour? Substantiate your view using economic reasoning. Answers to this question will vary. The good point of raising the minimum wage is people who have a job will get paid more money. The bad points of raising the minimum wage are: some people will lose their jobs (with a price ceiling ...
... of $5.15 per hour? Substantiate your view using economic reasoning. Answers to this question will vary. The good point of raising the minimum wage is people who have a job will get paid more money. The bad points of raising the minimum wage are: some people will lose their jobs (with a price ceiling ...
Principles of Economics, Case/Fair/Oster, 11e
... ◦ Each buyer/seller has a negligible impact on market price ◦ Why? (Key assumptions) Goods offered for sale - exactly the same Buyers and sellers – numerous ...
... ◦ Each buyer/seller has a negligible impact on market price ◦ Why? (Key assumptions) Goods offered for sale - exactly the same Buyers and sellers – numerous ...
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
... Product (MRP) • Output must be sold, so the real value of a worker to the firm is the worker’s marginal revenue product (MRP). – Marginal revenue product – the change in total revenue associated with one additional unit of input: ...
... Product (MRP) • Output must be sold, so the real value of a worker to the firm is the worker’s marginal revenue product (MRP). – Marginal revenue product – the change in total revenue associated with one additional unit of input: ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.