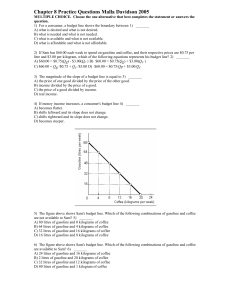
Ch 24
... The Demand Curve a Monopolist Faces (cont'd) • Perfect competition versus monopoly – The perfect competitor doesn’t have to worry about lowering price to sell more – In a purely competitive situation, the firm accounts for a small part of the market • It can sell its entire output, whatever that ma ...
... The Demand Curve a Monopolist Faces (cont'd) • Perfect competition versus monopoly – The perfect competitor doesn’t have to worry about lowering price to sell more – In a purely competitive situation, the firm accounts for a small part of the market • It can sell its entire output, whatever that ma ...
Managerial Economics
... Answer: To begin, fill out the normal form for this game of simultaneous moves. For example, at Nintendo price $350 and Sega price $40, Nintendo’s demand is .7 and Sega’s is 1.4, so Nintendo profits $(350-50)x.7 = $210 and Sega profits $(4010)x1.4 = $42. Goods gross complements because a higher pric ...
... Answer: To begin, fill out the normal form for this game of simultaneous moves. For example, at Nintendo price $350 and Sega price $40, Nintendo’s demand is .7 and Sega’s is 1.4, so Nintendo profits $(350-50)x.7 = $210 and Sega profits $(4010)x1.4 = $42. Goods gross complements because a higher pric ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... curves of profit-making existing firms begin to shift to the left, pushing marginal revenue with them as consumers switch to the new close substitutes. This process continues until profits are eliminated, which occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average total cost curve. ...
... curves of profit-making existing firms begin to shift to the left, pushing marginal revenue with them as consumers switch to the new close substitutes. This process continues until profits are eliminated, which occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average total cost curve. ...
document
... relative to another good, we substitute consumption towards the good that has become relatively less expensive. Income Effect - When the price of a good decreases the consumers real income has risen, thus creating the potential for consumption of both goods to increase. ...
... relative to another good, we substitute consumption towards the good that has become relatively less expensive. Income Effect - When the price of a good decreases the consumers real income has risen, thus creating the potential for consumption of both goods to increase. ...
Chapter 11: Standard Costs and Variance Analysis
... dollar amount or a percentage dollar amount. ...
... dollar amount or a percentage dollar amount. ...
Widget Case
... D. Notice also that Size 2, if utilized sufficiently, will allow us to produce at a lower possible cost than Size 1. That is, with Size 2, if we produce and sell 4 widgets per day, we can produce each widget at a cost $1,080 each. There is no way we can produce a widget at a cost this low with the S ...
... D. Notice also that Size 2, if utilized sufficiently, will allow us to produce at a lower possible cost than Size 1. That is, with Size 2, if we produce and sell 4 widgets per day, we can produce each widget at a cost $1,080 each. There is no way we can produce a widget at a cost this low with the S ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
PDF
... burley tobacco production by employing duality theory and flexible functional forms, and is one of very few attempts to apply duality theory to the production of specific agricultural commodities at the farm level. This study follows the framework suggested by Diewert and employed by Kohli and by Wo ...
... burley tobacco production by employing duality theory and flexible functional forms, and is one of very few attempts to apply duality theory to the production of specific agricultural commodities at the farm level. This study follows the framework suggested by Diewert and employed by Kohli and by Wo ...
Oligopoly
... The Equilibrium for an Oligopoly A Nash equilibrium is a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the others have chosen. When firms in an oligopoly individually choose production to maximize profit, they produce qu ...
... The Equilibrium for an Oligopoly A Nash equilibrium is a situation in which economic actors interacting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the others have chosen. When firms in an oligopoly individually choose production to maximize profit, they produce qu ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.