Molecular diagnostics of mitochondrial disorders
... The mitochondrial respiratory chain (RC) results from the expression of both mitochondrial and nuclear genes. The number of diseasecausing mutations in nuclear genes is steadily growing and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) deletions and mutations account for no more than 15–20% of pediatric patients. Unfor ...
... The mitochondrial respiratory chain (RC) results from the expression of both mitochondrial and nuclear genes. The number of diseasecausing mutations in nuclear genes is steadily growing and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) deletions and mutations account for no more than 15–20% of pediatric patients. Unfor ...
Page 1 Name KEY_______________________ Genetics C3032
... b. In C. elegans mating a true breed hermaphrodite homozygous for a recessive, X-linked mutation with a wild type male always results in mutant males . ...
... b. In C. elegans mating a true breed hermaphrodite homozygous for a recessive, X-linked mutation with a wild type male always results in mutant males . ...
DNA methylation
... The molecular basis of epigenetics is complex. It involves modifications of the activation of certain genes, but not the basic structure of DNA. Additionally, the chromatin proteins associated with DNA may be activated or silenced. This accounts for why the differentiated cells in a multi-cellular ...
... The molecular basis of epigenetics is complex. It involves modifications of the activation of certain genes, but not the basic structure of DNA. Additionally, the chromatin proteins associated with DNA may be activated or silenced. This accounts for why the differentiated cells in a multi-cellular ...
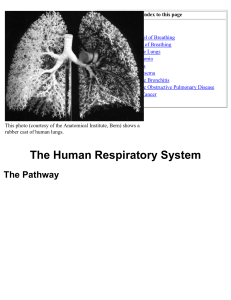
The Human Respiratory System
... Any irritant reaching the bronchi and bronchioles will stimulate an increased secretion of mucus. In ...
... Any irritant reaching the bronchi and bronchioles will stimulate an increased secretion of mucus. In ...
08MicrobialGenetExamIIAnswers
... Incompatible because the plasmids both utilize the same proteins to regulate when its origins of replication fire, one plasmid is likely to be replicated more frequently than the other. This may be because its origin has slightly higher affinity for the initiation proteins, it is smaller and therefo ...
... Incompatible because the plasmids both utilize the same proteins to regulate when its origins of replication fire, one plasmid is likely to be replicated more frequently than the other. This may be because its origin has slightly higher affinity for the initiation proteins, it is smaller and therefo ...
Inheritance Principles and Human Genetics
... Alleles – different forms of a gene Locus – location on a chromosome where specific genes are found Linkage – when genes on a chromosome “stay together” even during crossing-over Genetic recombination – the “recombining” of genes as a result of crossing-over ...
... Alleles – different forms of a gene Locus – location on a chromosome where specific genes are found Linkage – when genes on a chromosome “stay together” even during crossing-over Genetic recombination – the “recombining” of genes as a result of crossing-over ...
ppt - The Marko Lab
... HbS: heterozygotes resistant HbC: hets: 29% less likely, homoz: 93% less likely ...
... HbS: heterozygotes resistant HbC: hets: 29% less likely, homoz: 93% less likely ...
Eukaryotic Genes
... • Many primary gene transcripts can be spliced in different ways to produce distinct RNA molecules that each encode a different protein. • Alternative splicing often produces two forms of the same protein that are necessary at different stage of development or in different cell types. • Immunoglobul ...
... • Many primary gene transcripts can be spliced in different ways to produce distinct RNA molecules that each encode a different protein. • Alternative splicing often produces two forms of the same protein that are necessary at different stage of development or in different cell types. • Immunoglobul ...
Service information: Hereditary Non
... Diagnostic mutation screening of the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 genes by a combination of next generation sequencing (NGS) and MLPA is therefore predicted to detect pathogenic mutations with high sensitivity in HNPCC/Lynch syndrome. However, if a mutation is not detected by the testing procedure, a d ...
... Diagnostic mutation screening of the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 genes by a combination of next generation sequencing (NGS) and MLPA is therefore predicted to detect pathogenic mutations with high sensitivity in HNPCC/Lynch syndrome. However, if a mutation is not detected by the testing procedure, a d ...
Regulation of Gene Transcription
... Uses a lot of the same mechanisms as prokaryotes, but their greater complexity makes it necessary to have more complex controls as well. Eukaryotic genomes are also larger and typically have many more genes Greater regulation is also necessary to achieve finer control, this therefore increases the n ...
... Uses a lot of the same mechanisms as prokaryotes, but their greater complexity makes it necessary to have more complex controls as well. Eukaryotic genomes are also larger and typically have many more genes Greater regulation is also necessary to achieve finer control, this therefore increases the n ...
Ch 20 Lecture
... consortium separately announced sequencing over 90% of the human genome D. By mid-2001, the genomes of about 50 species had been completely (or almost completely) sequenced E. There are still gaps in the human sequence ...
... consortium separately announced sequencing over 90% of the human genome D. By mid-2001, the genomes of about 50 species had been completely (or almost completely) sequenced E. There are still gaps in the human sequence ...
Transcriptional Deregulation of Mutated BCL6 Alleles by Loss of
... diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL) and 5–14% of follicular lymphomas (FL), the BCL6 locus is altered by chromosomal translocations that deregulate its expression by a mechanism known as promoter substitution. In addition, the BCL6 5′ noncoding sequences are targeted by multiple somatic mutations ...
... diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL) and 5–14% of follicular lymphomas (FL), the BCL6 locus is altered by chromosomal translocations that deregulate its expression by a mechanism known as promoter substitution. In addition, the BCL6 5′ noncoding sequences are targeted by multiple somatic mutations ...
mutations
... Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought of as negative because they disrupt the normal function of genes. However, without mutations, organisms cannot evolve, because mutations are the source of gen ...
... Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought of as negative because they disrupt the normal function of genes. However, without mutations, organisms cannot evolve, because mutations are the source of gen ...
Test Information Sheet ASPA Gene Analysis in Canavan Disease
... At this time, more than 70 mutations have been identified in the ASPA gene including missense, nonsense, splicing, small deletions/insertions and large deletions. In one study of 23 non-Ashkenazi Jewish patients from diverse ethnic backgrounds, large deletions that would not be detected by sequence ...
... At this time, more than 70 mutations have been identified in the ASPA gene including missense, nonsense, splicing, small deletions/insertions and large deletions. In one study of 23 non-Ashkenazi Jewish patients from diverse ethnic backgrounds, large deletions that would not be detected by sequence ...
Sample Test Report
... Certain common genetic point mutations have been characterized that reduce the function of the MTHFR enzyme. These are the C677T mutation (which is a change from cytosine to thymine at position 677 within the gene) and the A1298C mutation (which is a change from adenine to cytosine at position 1298 ...
... Certain common genetic point mutations have been characterized that reduce the function of the MTHFR enzyme. These are the C677T mutation (which is a change from cytosine to thymine at position 677 within the gene) and the A1298C mutation (which is a change from adenine to cytosine at position 1298 ...
Hematology and Hematological Malignancies
... From a normal individual, there should be fragments of many different lengths – which will look like a smear of DNA from the many different VDJ rearrangements (a normal polyclonal population of cells) If an individual has an abnormal expanded monoclonal population of cells, a distinct band will be s ...
... From a normal individual, there should be fragments of many different lengths – which will look like a smear of DNA from the many different VDJ rearrangements (a normal polyclonal population of cells) If an individual has an abnormal expanded monoclonal population of cells, a distinct band will be s ...
Supplementary Figure and Table Legends (doc 22K)
... A table of pair-wise Pearson correlation values between samples based on the log2 expression ratio shows sample correlation. High correlation coefficients between biological replicates are highlighted in green, and those correlation coefficients outside of biological replicates are highlighted in b ...
... A table of pair-wise Pearson correlation values between samples based on the log2 expression ratio shows sample correlation. High correlation coefficients between biological replicates are highlighted in green, and those correlation coefficients outside of biological replicates are highlighted in b ...
Understanding Your Pathology Report: Colon Cancer
... number of repeat sequences; this is called microsatellite instability (MSI). MSI is a way to measure a deficiency of mismatch repair (MMR) in tumor DNA. A deficiency of MMR results in an increase in mutations within the colon cells, which partly contributes to the development of colon cancer. There ...
... number of repeat sequences; this is called microsatellite instability (MSI). MSI is a way to measure a deficiency of mismatch repair (MMR) in tumor DNA. A deficiency of MMR results in an increase in mutations within the colon cells, which partly contributes to the development of colon cancer. There ...
Complementation Help - Biological Sciences
... mutations in strains of haploid yeast that have similar mutant phenotypes. In this example we will call the two strains "m1" and "m2", for mutation#1 and mutation#2. The mutant phenotype could be colony colour, auxotrophy of the same compound, or any other character that distiguishes it from wild ty ...
... mutations in strains of haploid yeast that have similar mutant phenotypes. In this example we will call the two strains "m1" and "m2", for mutation#1 and mutation#2. The mutant phenotype could be colony colour, auxotrophy of the same compound, or any other character that distiguishes it from wild ty ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.