CLARK LAP Wednesday March 26 2014 STRAWBERRY DNA
... through the cheesecloth and into the tall glass until there is very little liquid left in the funnel (only wet pulp remains). How does the filtered strawberry liquid look? • Pour the filtered strawberry liquid from the tall glass into the small glass jar so that the jar is one quarter full. • Measur ...
... through the cheesecloth and into the tall glass until there is very little liquid left in the funnel (only wet pulp remains). How does the filtered strawberry liquid look? • Pour the filtered strawberry liquid from the tall glass into the small glass jar so that the jar is one quarter full. • Measur ...
BIOL 105 S 2013 Practice Quiz Supp DNA
... Messenger RNA carries genetic information from the chromosomes to the ______. A) ribosomes B) endoplasmic reticulum C) nucleolus D) plasmids Answer A A ________ codes for a specific sequence of amino acids in a protein. A) gene B) nucleotide C) polyribosome D) nucleic acid Answer A The study of the ...
... Messenger RNA carries genetic information from the chromosomes to the ______. A) ribosomes B) endoplasmic reticulum C) nucleolus D) plasmids Answer A A ________ codes for a specific sequence of amino acids in a protein. A) gene B) nucleotide C) polyribosome D) nucleic acid Answer A The study of the ...
Lecture 11 Gene1cs BIOL 335
... Conjuga>on of Hfr strains is similar to F+ strains, via a pilus F-containing chromosome is nicked at the F locus, and a single strand is passed through the pilus to the recipient cell DNA is transferred un>l complete, or un>l the pilus falls apart. Strands are replicated in both cells ...
... Conjuga>on of Hfr strains is similar to F+ strains, via a pilus F-containing chromosome is nicked at the F locus, and a single strand is passed through the pilus to the recipient cell DNA is transferred un>l complete, or un>l the pilus falls apart. Strands are replicated in both cells ...
Genetics Assessment
... in the jellyfish genome. Can scientists, and indeed science students, insert this gene into other organisms? Today you will perform a transformation using a paper model. What is a transformation? Bacteria have an extra piece of DNA that is much smaller than the rest of their genome, called a plasmid ...
... in the jellyfish genome. Can scientists, and indeed science students, insert this gene into other organisms? Today you will perform a transformation using a paper model. What is a transformation? Bacteria have an extra piece of DNA that is much smaller than the rest of their genome, called a plasmid ...
Chapter 11 – What is DNA and how does it work?
... •Bases – AGCU (U = Uracil) •Goes from nucleus to cytoplasm and ribosome •Produced in Transcription ...
... •Bases – AGCU (U = Uracil) •Goes from nucleus to cytoplasm and ribosome •Produced in Transcription ...
16. Biotechnology
... that can renew itself. These cells can differentiate to yield some or all of the major cell types of that tissue or organ. These are more limited than embryonic stem cells. ...
... that can renew itself. These cells can differentiate to yield some or all of the major cell types of that tissue or organ. These are more limited than embryonic stem cells. ...
Evolution of genomes
... than what could be achieved by recombination alone. Most modifications in the course of evolution are due to copying errors in the process of DNA replication called mutations. These copying errors provide the raw material that natural selection acts on. Deleterious mutations tend to be eliminated by ...
... than what could be achieved by recombination alone. Most modifications in the course of evolution are due to copying errors in the process of DNA replication called mutations. These copying errors provide the raw material that natural selection acts on. Deleterious mutations tend to be eliminated by ...
Chapter 12
... – Only 1.5% of the DNA codes for proteins, tRNAs, or rRNAs – The remaining 88.5% of the DNA contains – Control regions such as promoters and enhancers – Unique noncoding DNA – Repetitive DNA – Found in centromeres and telomeres – Found dispersed throughout the genome, related to transposable element ...
... – Only 1.5% of the DNA codes for proteins, tRNAs, or rRNAs – The remaining 88.5% of the DNA contains – Control regions such as promoters and enhancers – Unique noncoding DNA – Repetitive DNA – Found in centromeres and telomeres – Found dispersed throughout the genome, related to transposable element ...
Secondary structures
... UTRs: un-translated regions (important for translational control) Exons will be spliced together by removal of the Introns Poly-adenylation site important for transcription termination (but also: mRNA stability, export mRNA from nucleus etc.) ...
... UTRs: un-translated regions (important for translational control) Exons will be spliced together by removal of the Introns Poly-adenylation site important for transcription termination (but also: mRNA stability, export mRNA from nucleus etc.) ...
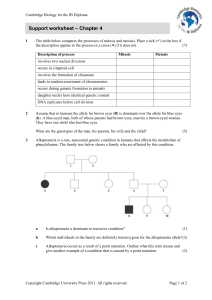
Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The table below compares the processes of mitosis and meiosis. Place a tick () in the box if the description applies to the process or a cross () if it does not. ...
... The table below compares the processes of mitosis and meiosis. Place a tick () in the box if the description applies to the process or a cross () if it does not. ...
Application/registration document for work with biohazards and
... 7. Is a vector (specific phage, plasmid or virus) required? Yes: Identify specific vector No 8. Target recipient of recombinant DNA (please indicate species or cell lines used): ...
... 7. Is a vector (specific phage, plasmid or virus) required? Yes: Identify specific vector No 8. Target recipient of recombinant DNA (please indicate species or cell lines used): ...
DNA, The Genetic Material
... DNA strands “unzip” down the middle between the hydrogen bonds. Each half reconstructs its complimentary half from free floating nucleotides. The two new DNA strands each contain ½ of the original “double helix” – semiconservative. DNA unzips – origins of replication – multiple sites on DNA strand w ...
... DNA strands “unzip” down the middle between the hydrogen bonds. Each half reconstructs its complimentary half from free floating nucleotides. The two new DNA strands each contain ½ of the original “double helix” – semiconservative. DNA unzips – origins of replication – multiple sites on DNA strand w ...
Quiz Questions - The University of Sheffield
... mRNA processing in human cells (or select F)? A. Introns usually represent the greater part of a primary transcript. B. Exons are removed from pre-mRNA in the nucleus by splicing during and after transcription. C. The 5’ nucleotide cap structure is added to all transcripts. D. The poly-A tail is ...
... mRNA processing in human cells (or select F)? A. Introns usually represent the greater part of a primary transcript. B. Exons are removed from pre-mRNA in the nucleus by splicing during and after transcription. C. The 5’ nucleotide cap structure is added to all transcripts. D. The poly-A tail is ...
Mutations - Miss Garry`s Biology Class Website!
... c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adapted to it environment ...
... c. Harmful effect phenotype is different. The organism is less adapted to it environment ...
Preparation of SCRATCHY Hybrid Protein Libraries
... of hybrid enzymes (ITCHY) technology (1) and DNA shuffling (2). It generates combinatorial libraries of hybrid proteins consisting of multiple fragments from two or more parental DNA sequences with no restriction to DNA sequence identity between the original sequences (3). Such multi-crossover hybri ...
... of hybrid enzymes (ITCHY) technology (1) and DNA shuffling (2). It generates combinatorial libraries of hybrid proteins consisting of multiple fragments from two or more parental DNA sequences with no restriction to DNA sequence identity between the original sequences (3). Such multi-crossover hybri ...