The Impact of Regional and Sectoral Productivity Changes on the U.S. Economy,
... The major part of research in macroeconomics has traditionally emphasized aggregate disturbances as sources of aggregate changes.1 Exceptions to this approach were Long and Plosser (1983), and Horvath (1998, 2000) who posited that because of input-output linkages, productivity disturbances at the le ...
... The major part of research in macroeconomics has traditionally emphasized aggregate disturbances as sources of aggregate changes.1 Exceptions to this approach were Long and Plosser (1983), and Horvath (1998, 2000) who posited that because of input-output linkages, productivity disturbances at the le ...
Technological Diversification Miklos Koren and Silvana Tenreyro
... Note: All variables are in logs. The equations for 0RBIS data countries use the 5-year standard deviation of annual (real) sales growth rates from 2002 to 2006 for developed countries. For Ghana, Kenya, and Nigeria, the unbalanced panel span 1992 to 2002 (see text). The two size measures (number of ...
... Note: All variables are in logs. The equations for 0RBIS data countries use the 5-year standard deviation of annual (real) sales growth rates from 2002 to 2006 for developed countries. For Ghana, Kenya, and Nigeria, the unbalanced panel span 1992 to 2002 (see text). The two size measures (number of ...
Wp 55 Storm The New Normal - Institute for New Economic Thinking
... (Chetty et al. 2016). America is no longer ‘great’, as its economic growth falters, nor ‘whole’, because, as part of the secular stagnation itself, it is becoming a dual economy—two countries, each with vastly different resources, expectations and potentials, as America’s middle class is vanishing ( ...
... (Chetty et al. 2016). America is no longer ‘great’, as its economic growth falters, nor ‘whole’, because, as part of the secular stagnation itself, it is becoming a dual economy—two countries, each with vastly different resources, expectations and potentials, as America’s middle class is vanishing ( ...
Why Do Inefficient Firms Survive? Management and Economic Development Michael Peters January 2012
... for managers is therefore at the level of the individual firm. I am focusing on a simpler problem what are the consequences of managerial scarcity at the aggregate level. The view that managerial inputs were the crucial factor determining the efficiency with which firms could expand features also pr ...
... for managers is therefore at the level of the individual firm. I am focusing on a simpler problem what are the consequences of managerial scarcity at the aggregate level. The view that managerial inputs were the crucial factor determining the efficiency with which firms could expand features also pr ...
Wage-led or Profit-led Supply: Wages, Productivity and
... golden rule and take a detour, treating our readers to a perhaps unusual account of a wellknown piece of recent economic history—the “Dutch employment miracle” of the 1980s and 1990s (Blanchard 2000; The Economist 2002; Becker and Schwartz 2005). What was so miraculous to many was the sharp and sust ...
... golden rule and take a detour, treating our readers to a perhaps unusual account of a wellknown piece of recent economic history—the “Dutch employment miracle” of the 1980s and 1990s (Blanchard 2000; The Economist 2002; Becker and Schwartz 2005). What was so miraculous to many was the sharp and sust ...
Who benefits from productivity growth? – The labour income share
... automation, suggesting that labour market dislocation will not end any time soon. In large part, the current wave of new technology is labour-saving in that it reduces the labour input needed in the production process across a wide range of output. While beneficial for labour productivity, this is a ...
... automation, suggesting that labour market dislocation will not end any time soon. In large part, the current wave of new technology is labour-saving in that it reduces the labour input needed in the production process across a wide range of output. While beneficial for labour productivity, this is a ...
Patience and the Wealth of Nations
... Role of proximate determinants • Can any single proximate determinant fully account for the relationship between patience and national income? – Patience and physical Capital (about a third of the ...
... Role of proximate determinants • Can any single proximate determinant fully account for the relationship between patience and national income? – Patience and physical Capital (about a third of the ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... National Bureau of Economic Research
... goal is to integrate GDP-by-industry accounts with the benchmark inputoutput accounts compiled every five years and the NIPAs, as well as the annual input-output accounts. Achievement of this objective will require several years of effort by the BEA, as well as the continuing participation and cooper ...
... goal is to integrate GDP-by-industry accounts with the benchmark inputoutput accounts compiled every five years and the NIPAs, as well as the annual input-output accounts. Achievement of this objective will require several years of effort by the BEA, as well as the continuing participation and cooper ...
The Impact of Regional and Sectoral Productivity Changes on the
... prising land and structures. As emphasized by Blanchard and Katz (1992), labor is allowed to move across both regions and sectors. Land and structures can be used by any sector but are …xed locally. Sectors are interconnected by way of input-output linkages but, in contrast to Long and Plosser (198 ...
... prising land and structures. As emphasized by Blanchard and Katz (1992), labor is allowed to move across both regions and sectors. Land and structures can be used by any sector but are …xed locally. Sectors are interconnected by way of input-output linkages but, in contrast to Long and Plosser (198 ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
... costs associated with trade but must instead incur …xed costs associated with managing a foreign a¢ liate. Second, …rms di¤er in their productivity. These assumptions imply that for each country there is a productivity cuto¤, which is determined by the country’s characteristics, such that only those ...
... costs associated with trade but must instead incur …xed costs associated with managing a foreign a¢ liate. Second, …rms di¤er in their productivity. These assumptions imply that for each country there is a productivity cuto¤, which is determined by the country’s characteristics, such that only those ...
The Global Productivity Distribution and Ricardian Comparative
... firms’ R&D choices in a many country, many industry Armington trade model. I keep the general equilibrium structure simple. There are no trade costs. Within each country-industry pair there is perfect competition between firms that produce an homogeneous output under decreasing returns to scale. Lab ...
... firms’ R&D choices in a many country, many industry Armington trade model. I keep the general equilibrium structure simple. There are no trade costs. Within each country-industry pair there is perfect competition between firms that produce an homogeneous output under decreasing returns to scale. Lab ...
Real Business Cycles
... short-term interest rates, and the latter are nearly always positively correlated with output, but the correlation of longerterm rates with output is often negative or close to zero. Prices appear to be countercyclical, but I argue below that this evidence is tenuous. Employment is approximately as ...
... short-term interest rates, and the latter are nearly always positively correlated with output, but the correlation of longerterm rates with output is often negative or close to zero. Prices appear to be countercyclical, but I argue below that this evidence is tenuous. Employment is approximately as ...
Canada–United States Labour Productivity Gap
... It has been argued that the disproportionate number of small firms in Canada relative to the United States, may have lowered Canadian aggregate productivity levels and that this, in turn, accounts for part of the gap in productivity levels between Canada and the United States. Generally, larger firm ...
... It has been argued that the disproportionate number of small firms in Canada relative to the United States, may have lowered Canadian aggregate productivity levels and that this, in turn, accounts for part of the gap in productivity levels between Canada and the United States. Generally, larger firm ...
Using Expenditure PPPs for Sectoral Output and Productivity
... comparisons are based on purchasers’ prices of final goods and services with a detailed product specification. Hence, to apply them to output and productivity comparisons by industry, the PPPs have to be mapped from expenditure categories to industry groups. The expenditure approach to sectoral PPPs ...
... comparisons are based on purchasers’ prices of final goods and services with a detailed product specification. Hence, to apply them to output and productivity comparisons by industry, the PPPs have to be mapped from expenditure categories to industry groups. The expenditure approach to sectoral PPPs ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES A THEORY OF DEMAND SHOCKS Guido Lorenzoni
... short-term volatility due to demand shocks. This is in line with existing evidence, based either on long-run restrictions or on sign restrictions on output and price responses. The crucial parameter that determines the relevance of demand shocks is the precision of the public signal. When the publi ...
... short-term volatility due to demand shocks. This is in line with existing evidence, based either on long-run restrictions or on sign restrictions on output and price responses. The crucial parameter that determines the relevance of demand shocks is the precision of the public signal. When the publi ...
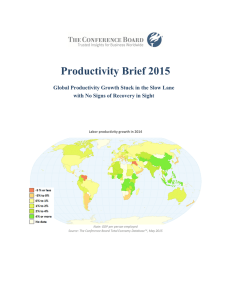
Productivity Brief 2015
... Because of the moderation in productivity growth in most global regions, the relative contribution of emerging and developing economies to world productivity growth increased marginally from 1.7 in 2013 to 1.8 percentage points in 2014, while the contribution of the mature economies declined from 0. ...
... Because of the moderation in productivity growth in most global regions, the relative contribution of emerging and developing economies to world productivity growth increased marginally from 1.7 in 2013 to 1.8 percentage points in 2014, while the contribution of the mature economies declined from 0. ...
Norwegian business cycles 1982–2003
... Business cycles are broadly-based movements of macroeconomic variables (Burns and Mitchell, 1946). During a boom, output rises, employment rises and unemployment falls. During a recession, output of goods and services decline, employment falls and unemployment rises. The sequence of booms and recess ...
... Business cycles are broadly-based movements of macroeconomic variables (Burns and Mitchell, 1946). During a boom, output rises, employment rises and unemployment falls. During a recession, output of goods and services decline, employment falls and unemployment rises. The sequence of booms and recess ...
Employment, productivity and output growth
... sustained productivity growth has lifted advanced industrialized nations to their present-day standards of living and, by any historical standards, has allowed them to eradicate mass poverty. The technological innovations and capital-intensive investments that were the mainsprings of this productivi ...
... sustained productivity growth has lifted advanced industrialized nations to their present-day standards of living and, by any historical standards, has allowed them to eradicate mass poverty. The technological innovations and capital-intensive investments that were the mainsprings of this productivi ...
Why Has the Cyclicality of Productivity Changed? What Does It Mean?
... In this paper, we seek to understand empirically the forces behind the changing cyclicality of productivity. Methodologically, we rely on growth accounting to derive and decompose productivity measures. We focus primarily on correlation with inputs and output to measure cyclicality, though we also i ...
... In this paper, we seek to understand empirically the forces behind the changing cyclicality of productivity. Methodologically, we rely on growth accounting to derive and decompose productivity measures. We focus primarily on correlation with inputs and output to measure cyclicality, though we also i ...
Why Has the Cyclicality of Productivity Changed? What Does It Mean? John G. Fernald and J. Christina Wang
... In this paper, we seek to understand empirically the forces behind the changing cyclicality of productivity. Methodologically, we rely on growth accounting to derive and decompose productivity measures. We focus primarily on correlation with inputs and output to measure cyc ...
... In this paper, we seek to understand empirically the forces behind the changing cyclicality of productivity. Methodologically, we rely on growth accounting to derive and decompose productivity measures. We focus primarily on correlation with inputs and output to measure cyc ...
Latin America in the Rear View Mirror - Carnegie
... Latin America is a long-run development failure. We say this because Latin America’s GDP per adult has been slipping further behind the U.S. over the last 50 years, while many other countries with broadly similar institutions and market structures have been gaining signiÞcant ground on the U.S. Figu ...
... Latin America is a long-run development failure. We say this because Latin America’s GDP per adult has been slipping further behind the U.S. over the last 50 years, while many other countries with broadly similar institutions and market structures have been gaining signiÞcant ground on the U.S. Figu ...
`UK Economic Performance Since 1997: Growth, Productivity and
... contribution of different sectors, such as finance, and different factor inputs such as capital and skills (sub-section 1.3). Overall, we find that British performance was impressive between 1997-2010 compared to other major countries both in terms of productivity and the labour market. The producti ...
... contribution of different sectors, such as finance, and different factor inputs such as capital and skills (sub-section 1.3). Overall, we find that British performance was impressive between 1997-2010 compared to other major countries both in terms of productivity and the labour market. The producti ...
Why are Americans More Productive than Canadians?
... States is equal to total hours, which is the product of average hours for persons at work times number of persons at work, divided by total employment. ...
... States is equal to total hours, which is the product of average hours for persons at work times number of persons at work, divided by total employment. ...
Natural Capital, Sustainability and Productivity
... smaller share of the value of total output over time. This is explained at least in part by the declining real prices of many resources. But one might also infer that there has been a reduction in the essentialness of natural capital in these sectors; put another way, the economy may be developing s ...
... smaller share of the value of total output over time. This is explained at least in part by the declining real prices of many resources. But one might also infer that there has been a reduction in the essentialness of natural capital in these sectors; put another way, the economy may be developing s ...
Technology, Employment, and the Business Cycle: DO Technology
... productivity in response to the same shock. In the following period, firms adjust their prices downward (since marginal cost is lower), aggregate demand and output will go up, and employment returns to its original level. The sign of the associated change in labor productivity depends again on wheth ...
... productivity in response to the same shock. In the following period, firms adjust their prices downward (since marginal cost is lower), aggregate demand and output will go up, and employment returns to its original level. The sign of the associated change in labor productivity depends again on wheth ...
Productivity

Productivity is an average measure of the efficiency of production. It can be expressed as the ratio of output to inputs used in the production process, i.e. output per unit of input. When all outputs and inputs are included in the productivity measure it is called total productivity. Outputs and inputs are defined in the total productivity measure as their economic values. The value of outputs minus the value of inputs is a measure of the income generated in a production process. It is a measure of total efficiency of a production process and as such the objective to be maximized in production process. Productivity measures that use one or more inputs or factors, but not all factors, are called partial productivities. A common example in economics is labor productivity, usually expressed as output per hour. At the company level, typical partial productivity measures are such things as worker hours, materials or energy per unit of production.In macroeconomics the approach is different. In macroeconomics one wants to examine an entity of many production processes and the output is obtained by summing up the value-added created in the single processes. This is done in order to avoid the double accounting of intermediate inputs. Value-added is obtained by subtracting the intermediate inputs from the outputs. The most well-known and used measure of value-added is the GDP (Gross Domestic Product). It is widely used as a measure of the economic growth of nations and industries. GDP is the income available for paying capital costs, labor compensation, taxes and profits.For a single input this means the ratio of output (value-added) to input. When multiple inputs are considered, such as labor and capital, it means the unaccounted for level of output compared to the level of inputs. This measure is called in macroeconomics Total Factor Productivity TFP or Multi Factor Productivity MFP.Productivity is a crucial factor in production performance of firms and nations. Increasing national productivity can raise living standards because more real income improves people's ability to purchase goods and services, enjoy leisure, improve housing and education and contribute to social and environmental programs. Productivity growth also helps businesses to be more profitable.