Slide 1
... substance that contains one type of atom. All minerals are made of elements or compounds. • Compounds are groups of elements • Minerals made of compounds are made of the ...
... substance that contains one type of atom. All minerals are made of elements or compounds. • Compounds are groups of elements • Minerals made of compounds are made of the ...
O 95: Metal Substrates: Adsorption of Atoms and Inorganic Molecules
... In this study we combine quantitative LEED–IV, STM and DFT calculations to reinvestigate the adsorption behavior of oxygen on the Rh(100) surface in the coverage regime up to 0.67 ML. In this range three distinct phases exist: A (2 × 2)–O [1], a (2 × 2)–2O [2] and a (3×1)–2O structure [3]. The propo ...
... In this study we combine quantitative LEED–IV, STM and DFT calculations to reinvestigate the adsorption behavior of oxygen on the Rh(100) surface in the coverage regime up to 0.67 ML. In this range three distinct phases exist: A (2 × 2)–O [1], a (2 × 2)–2O [2] and a (3×1)–2O structure [3]. The propo ...
Igneous Rocks: Crystallization and Cooling Rate
... Students view the prepared slides underneath the microscope and determine if it is the same substance as Salol based on the crystallization pattern that forms. Students should be able to justify their reasoning, and relate it back to the atoms and molecules in the substances. ...
... Students view the prepared slides underneath the microscope and determine if it is the same substance as Salol based on the crystallization pattern that forms. Students should be able to justify their reasoning, and relate it back to the atoms and molecules in the substances. ...
Hints for Names and Formulas (Ch. 4 in Zumdahl Chemistry)
... (9) most covalent inorganic molecules are gases (sometimes liquids) at room temperature (R.T.) IONIC COMPOUNDS (1) ionic compounds are never called molecules and have covalent bonds only in their polyatomic ions (2) ionic compounds are generally classified as salts, acids, or bases (3) ionic compoun ...
... (9) most covalent inorganic molecules are gases (sometimes liquids) at room temperature (R.T.) IONIC COMPOUNDS (1) ionic compounds are never called molecules and have covalent bonds only in their polyatomic ions (2) ionic compounds are generally classified as salts, acids, or bases (3) ionic compoun ...
Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement and Problem Solving
... (evaporate easily) can be evaporated from a mixture. Example Salt Water Distillation: Separate mixtures based on difference in boiling points Filtration: A solid is filtered from a liquid. Example: spaghetti noodles from water. Decantation: pouring out liquid to separate from solid. (separate ...
... (evaporate easily) can be evaporated from a mixture. Example Salt Water Distillation: Separate mixtures based on difference in boiling points Filtration: A solid is filtered from a liquid. Example: spaghetti noodles from water. Decantation: pouring out liquid to separate from solid. (separate ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... b. Describe the bonding. What's bonded to what, and what kinds of bonds are involved (ionic, covalent, intermolecular forces, etc.)? The Si-O framework is an anion that can be a small or an extended structure. The Si-O framework forms an ionic compound with metal ions (except in the case of SiO2, wh ...
... b. Describe the bonding. What's bonded to what, and what kinds of bonds are involved (ionic, covalent, intermolecular forces, etc.)? The Si-O framework is an anion that can be a small or an extended structure. The Si-O framework forms an ionic compound with metal ions (except in the case of SiO2, wh ...
Chapter 2 - OrgSites.com
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 1. Most organic compounds contain ___ and ___. 2. Summarize what Stanley Miller was able to demonstrate in 1953. ...
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds 1. Most organic compounds contain ___ and ___. 2. Summarize what Stanley Miller was able to demonstrate in 1953. ...
What Is A Mineral?
... Name 2 things that all minerals have in common? Inorganic, Crystalline Structure, Formed Naturally, ...
... Name 2 things that all minerals have in common? Inorganic, Crystalline Structure, Formed Naturally, ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life It would be difficult to appreciate fully the characteristics of living matter and its functions without looking at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of ...
... Thibodeau: Anatomy and Physiology, 5/e Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life It would be difficult to appreciate fully the characteristics of living matter and its functions without looking at the basic principles of chemistry as they apply to life processes. In fact, it is almost impossible to speak of ...
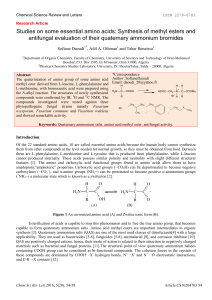
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... Figure 1 An un-ionized amino acid (A) and Zwitter ionic form (B). Esterification of acids is capable to stop this phenomenon and to free the true amino group, that becomes capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quater ...
... Figure 1 An un-ionized amino acid (A) and Zwitter ionic form (B). Esterification of acids is capable to stop this phenomenon and to free the true amino group, that becomes capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quater ...
Chemical Reaction and Matter Review
... Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because this will change the formulas. Classify Chemical Reactions Chemists have identified millions of d ...
... Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because this will change the formulas. Classify Chemical Reactions Chemists have identified millions of d ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
Chapter 5: Atoms to Minerals
... Many minerals form from molten rock in which the atoms can move freely. Once it begins to cool the ions move closer together to form chemical bonds Many different minerals will form. The composition of the magma will control what type form. The slower the magma cools the larger the grains. Can also ...
... Many minerals form from molten rock in which the atoms can move freely. Once it begins to cool the ions move closer together to form chemical bonds Many different minerals will form. The composition of the magma will control what type form. The slower the magma cools the larger the grains. Can also ...
Chapter 1
... Chemical bonding Formation of a compound by combining two or more elements Atoms gain or lose outermost electrons to form ions Oppositely charged ions attract one another to produce a neutral chemical compound ...
... Chemical bonding Formation of a compound by combining two or more elements Atoms gain or lose outermost electrons to form ions Oppositely charged ions attract one another to produce a neutral chemical compound ...
03 nanoparticles part 7 File - e-learning
... At higher temperatures, high crystallinity is achieved. Different growth rates in different directions will determine the habit (rods, cylinders, cubes). Only in case of equal growth rate in all directions, the habit may be spherical. ...
... At higher temperatures, high crystallinity is achieved. Different growth rates in different directions will determine the habit (rods, cylinders, cubes). Only in case of equal growth rate in all directions, the habit may be spherical. ...
rocks and minerals quiz
... All objects in the universe are composed of matter. Matter provides weight and takes up space. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. STATES OF MATTER Matter usually exists in three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquids have an indefin ...
... All objects in the universe are composed of matter. Matter provides weight and takes up space. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. STATES OF MATTER Matter usually exists in three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquids have an indefin ...
Chemistry I Syllabus 2011-2012
... inorganic, kinetic energy, law of conservation of mass, light energy, luster, malleability, melting point, metal, metalloid, molecule, nonmetal, organic, phase change, physical properties, potential energy, pure substance, reactivity with air (oxidation), solute, solution, solvent, strength, sub-let ...
... inorganic, kinetic energy, law of conservation of mass, light energy, luster, malleability, melting point, metal, metalloid, molecule, nonmetal, organic, phase change, physical properties, potential energy, pure substance, reactivity with air (oxidation), solute, solution, solvent, strength, sub-let ...
Minerals Vocab File
... Chapter 3—Minerals of the Earth’s Crust Mineral—a naturally formed, inorganic solid with a crystalline structure Element—a pure substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means Atom—the smallest part of an element that has all of the properties of ...
... Chapter 3—Minerals of the Earth’s Crust Mineral—a naturally formed, inorganic solid with a crystalline structure Element—a pure substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means Atom—the smallest part of an element that has all of the properties of ...
rocks and minerals quiz
... All objects in the universe are composed of matter. Matter provides weight and takes up space. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. STATES OF MATTER Matter usually exists in three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquids have an indefin ...
... All objects in the universe are composed of matter. Matter provides weight and takes up space. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. STATES OF MATTER Matter usually exists in three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. Liquids have an indefin ...
File
... Extensive - Properties that do depend on the amount of matter present. Mass - A measurement of the amount of matter in an object (grams). Weight - A measurement of the gravitational force of attraction of the earth acting on an object. Volume - A measurement of the amount of space a substance occup ...
... Extensive - Properties that do depend on the amount of matter present. Mass - A measurement of the amount of matter in an object (grams). Weight - A measurement of the gravitational force of attraction of the earth acting on an object. Volume - A measurement of the amount of space a substance occup ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
... Compounds of 3A elements have more covalent character than similar 2A compounds. Aluminum has the physical properties of a metal, but its halides exist as covalent dimers. ...
4He Solubility in Apatite is Low But Possibly Significant
... closure to diffusive loss). In U-Th/He dating, this component is assumed to be negligible because of the mobility of helium and its generally low concentration in the atmosphere. However there are geological environments in which 4He is present in significant quantities, so an assessment of whether ...
... closure to diffusive loss). In U-Th/He dating, this component is assumed to be negligible because of the mobility of helium and its generally low concentration in the atmosphere. However there are geological environments in which 4He is present in significant quantities, so an assessment of whether ...
Crystal Structure of Mixed-metal Phosphite, Pb2Ga(HPIIIO3)3(PVO3)
... c=12.544(3) Å and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure of Pb2Ga(HPO3)3(PO3) exhibits a complicated 3D framework based on PbO6 and GaO6 octahedral connected by HPO3 and H2PO3 anions via corner- or edge-sharing. Keywords: Crystal structure; Hydrothermal reactions; Mixed-metal phosphites; 3D framework; Sin ...
... c=12.544(3) Å and α=β=γ=90°. The crystal structure of Pb2Ga(HPO3)3(PO3) exhibits a complicated 3D framework based on PbO6 and GaO6 octahedral connected by HPO3 and H2PO3 anions via corner- or edge-sharing. Keywords: Crystal structure; Hydrothermal reactions; Mixed-metal phosphites; 3D framework; Sin ...