Solid-state physics
... form covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are shared amongst the whole crystal in metallic bonding. Finally, the noble gases do not undergo any of these types of bonding. In solid form, the noble gases are held together with van der Waals forces resulting from the polarisation of the electronic char ...
... form covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are shared amongst the whole crystal in metallic bonding. Finally, the noble gases do not undergo any of these types of bonding. In solid form, the noble gases are held together with van der Waals forces resulting from the polarisation of the electronic char ...
Mineral definition and classification
... systems, and all crystal structures currently recognized fit in one Bravais lattice and one crystal system. This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement that is often expressed in the geometric form that the crystal takes. Even when the mineral grains are too small ...
... systems, and all crystal structures currently recognized fit in one Bravais lattice and one crystal system. This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement that is often expressed in the geometric form that the crystal takes. Even when the mineral grains are too small ...
SAXS on lipid structures
... which is grained to powder, is poured into a sample holder, usually a tiny glass tube. This tube is mounted into the direct beam, and in a distance D an x-ray detector is recording the diffraction pattern. It is assumed that the grains are small enough and available in such an amount, that the beam ...
... which is grained to powder, is poured into a sample holder, usually a tiny glass tube. This tube is mounted into the direct beam, and in a distance D an x-ray detector is recording the diffraction pattern. It is assumed that the grains are small enough and available in such an amount, that the beam ...
Crystal pressure in nanoscale pores Many pharmaceutical
... Breaking up isn’t hard to do: Crystal pressure in nanoscale pores Many pharmaceutical compounds are poorly soluble in water. This is problematic because most pharmaceuticals are delivered orally and must dissolve in the gastrointestinal fluid to be absorbed by the body. Drug dissolution rate is prop ...
... Breaking up isn’t hard to do: Crystal pressure in nanoscale pores Many pharmaceutical compounds are poorly soluble in water. This is problematic because most pharmaceuticals are delivered orally and must dissolve in the gastrointestinal fluid to be absorbed by the body. Drug dissolution rate is prop ...
CCP4 - Software for Protein Structure Solution
... facilities by Pharma industry – 100s of crystals – Speed critical ...
... facilities by Pharma industry – 100s of crystals – Speed critical ...
Supplementary Materials
... mM ‘stock solution’ was then generated from this by dilution in a buffer containing 100 mM HEPES-NaOH pH 7.5 and DMSO (at varying concentrations between 0 and 25 % (v/v), sufficient to keep the compound in solution). Crystals of CHK2 bound to inhibitor were produced using 25 µl of purified CHK2 kina ...
... mM ‘stock solution’ was then generated from this by dilution in a buffer containing 100 mM HEPES-NaOH pH 7.5 and DMSO (at varying concentrations between 0 and 25 % (v/v), sufficient to keep the compound in solution). Crystals of CHK2 bound to inhibitor were produced using 25 µl of purified CHK2 kina ...
Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination
... Effective field acting on nuclei is influenced by magnetic field due to spin of neighbouring nuclei. This effect is called spin-spin coupling. Spin-spin coupling give rise to the peak splitting in NMR spectra This effect is observable only between protons on covalently bonded atoms and only if the d ...
... Effective field acting on nuclei is influenced by magnetic field due to spin of neighbouring nuclei. This effect is called spin-spin coupling. Spin-spin coupling give rise to the peak splitting in NMR spectra This effect is observable only between protons on covalently bonded atoms and only if the d ...
Crystal Modelling
... Look at models A to J. Some are pictures or ideas. Others are things you can hold or try out. Work out which stage of X-ray crystallography each model helps to explain. Some stages have more than one model. Some models help explain more than one stage. Choose five or fewer models. Plan how to use th ...
... Look at models A to J. Some are pictures or ideas. Others are things you can hold or try out. Work out which stage of X-ray crystallography each model helps to explain. Some stages have more than one model. Some models help explain more than one stage. Choose five or fewer models. Plan how to use th ...
Key Stage 3 – Crystal Modelling
... Look at models A to J. Some are pictures or ideas. Others are things you can hold or try out. Work out which stage of X-ray crystallography each model helps to explain. Some stages have more than one model. Some models help explain more than one stage. Choose five or fewer models. Plan how to use th ...
... Look at models A to J. Some are pictures or ideas. Others are things you can hold or try out. Work out which stage of X-ray crystallography each model helps to explain. Some stages have more than one model. Some models help explain more than one stage. Choose five or fewer models. Plan how to use th ...
The structure of RNase E at the core of the RNA
... of the sheet corroborated the choice of enantiomer for the hexagonal spacegroup (subsequently confirmed by molecular replacement against all possible hexagonal space groups). The positions of the Se atoms were identified in anomalous Fourier maps using phases from partial models, and these were recy ...
... of the sheet corroborated the choice of enantiomer for the hexagonal spacegroup (subsequently confirmed by molecular replacement against all possible hexagonal space groups). The positions of the Se atoms were identified in anomalous Fourier maps using phases from partial models, and these were recy ...
X-ray diffraction techniques X
... X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystallographic structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam ...
... X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystallographic structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam ...
Downing
... New instrumentation, along with continuing methods development -The keys to better and faster structure solutions Role for EM is mainly structures not amenable to x-ray ...
... New instrumentation, along with continuing methods development -The keys to better and faster structure solutions Role for EM is mainly structures not amenable to x-ray ...
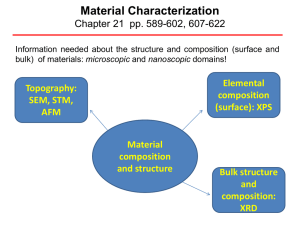
Material Characterization
... as forming different sets of planes in the crystal (colored lines in graph on left). For a given set of lattice planes with an inter-plane distance of d, the condition for a diffraction (peak) to occur can be simply written as ...
... as forming different sets of planes in the crystal (colored lines in graph on left). For a given set of lattice planes with an inter-plane distance of d, the condition for a diffraction (peak) to occur can be simply written as ...
Chapter 3 Crystallography and Diffraction Techniques
... since sinφ < 1. If a < λ, only the zero order direct beam is observed. On the other hand, if a » λ, sinφ and φ must be very small and 1st order diffraction beam is not distinguishable from the primary beam; likewise for beams with n = 1,2,…, etc.). ...
... since sinφ < 1. If a < λ, only the zero order direct beam is observed. On the other hand, if a » λ, sinφ and φ must be very small and 1st order diffraction beam is not distinguishable from the primary beam; likewise for beams with n = 1,2,…, etc.). ...
Protein Structure Determination and Design
... Part I: Protein Structure Determination Methods. 1. What are the four steps of X-ray crystallography as identified by the video found at the following link: http://pdb101.rcsb.org/teach/biomolecular-structures-and-models/learning-materials 1. _________________________________________________________ ...
... Part I: Protein Structure Determination Methods. 1. What are the four steps of X-ray crystallography as identified by the video found at the following link: http://pdb101.rcsb.org/teach/biomolecular-structures-and-models/learning-materials 1. _________________________________________________________ ...
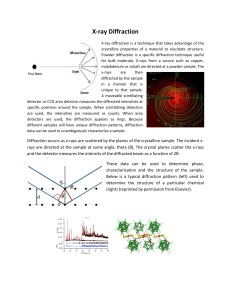
X-ray Diffraction
... x-ray can be calculated based on the sample. Any deviation from this calculation in the data can be used to obtain density profiles of the thin film (source http://www.ptb.de/). ...
... x-ray can be calculated based on the sample. Any deviation from this calculation in the data can be used to obtain density profiles of the thin film (source http://www.ptb.de/). ...
Structure of Minerals
... Quartz (SiO2) may form long, regular six sided crystals. The angles at which crystal faces meet is always the same for each kind of mineral. To describe these shapes crystallographic axes are used. They are drawn perpendicular to crystal faces. ...
... Quartz (SiO2) may form long, regular six sided crystals. The angles at which crystal faces meet is always the same for each kind of mineral. To describe these shapes crystallographic axes are used. They are drawn perpendicular to crystal faces. ...
Knight_ch24
... transitions. 2. Designed the first atomic spectrometer. 3. Fit the visible lines in the spectrum of hydrogen to a simple formula. 4. Discovered that x rays are diffracted by crystals. 5. Proposed a relation between the frequency of an electromagnetic wave and the energy of photons. ...
... transitions. 2. Designed the first atomic spectrometer. 3. Fit the visible lines in the spectrum of hydrogen to a simple formula. 4. Discovered that x rays are diffracted by crystals. 5. Proposed a relation between the frequency of an electromagnetic wave and the energy of photons. ...
Improved ferroelectric materials - structural
... Various doping studies have been carried out in BaTiO3 with an objective to improve its properties. For example, rare earth elements such as cerium (Ce) and lanthanum (La) have been partially doped in the Barium site to shift the dielectric maximum towards room temperature. ...
... Various doping studies have been carried out in BaTiO3 with an objective to improve its properties. For example, rare earth elements such as cerium (Ce) and lanthanum (La) have been partially doped in the Barium site to shift the dielectric maximum towards room temperature. ...
STUDY OF MOLECULAR CRYSTAL OF HYDROXY
... Acetanilides are mainly used as a pro-drugs and drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects. The most used drugs are paracetamol and phenacetin. Paracetamol, as metabolite of phenacetin, has similar medicamental property but does not share phenacetin’s carcirogenic side effects. Therefore it is one ...
... Acetanilides are mainly used as a pro-drugs and drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects. The most used drugs are paracetamol and phenacetin. Paracetamol, as metabolite of phenacetin, has similar medicamental property but does not share phenacetin’s carcirogenic side effects. Therefore it is one ...
Crystallization Worksheet Answer Key
... Toxicity: radical side effects on the body from the drug ...
... Toxicity: radical side effects on the body from the drug ...
X-ray crystallography

X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystallography is still the chief method for characterizing the atomic structure of new materials and in discerning materials that appear similar by other experiments. X-ray crystal structures can also account for unusual electronic or elastic properties of a material, shed light on chemical interactions and processes, or serve as the basis for designing pharmaceuticals against diseases.In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement, a crystal is mounted on a goniometer. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected orientations. The crystal is bombarded with a finely focused monochromatic beam of X-rays, producing a diffraction pattern of regularly spaced spots known as reflections. The two-dimensional images taken at different rotations are converted into a three-dimensional model of the density of electrons within the crystal using the mathematical method of Fourier transforms, combined with chemical data known for the sample. Poor resolution (fuzziness) or even errors may result if the crystals are too small, or not uniform enough in their internal makeup.X-ray crystallography is related to several other methods for determining atomic structures. Similar diffraction patterns can be produced by scattering electrons or neutrons, which are likewise interpreted by Fourier transformation. If single crystals of sufficient size cannot be obtained, various other X-ray methods can be applied to obtain less detailed information; such methods include fiber diffraction, powder diffraction and (if the sample is not crystallized) small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).If the material under investigation is only available in the form of nanocrystalline powders or suffers from poor crystallinity, the methods of electron crystallography can be applied for determining the atomic structure.For all above mentioned X-ray diffraction methods, the scattering is elastic; the scattered X-rays have the same wavelength as the incoming X-ray. By contrast, inelastic X-ray scattering methods are useful in studying excitations of the sample, rather than the distribution of its atoms.