Amphibians and Mammals
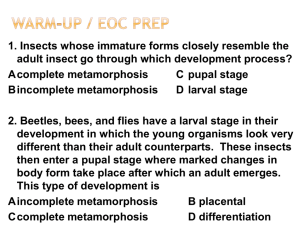
... 2. Beetles, bees, and flies have a larval stage in their development in which the young organisms look very different than their adult counterparts. These insects then enter a pupal stage where marked changes in body form take place after which an adult emerges. This type of development is ...
... 2. Beetles, bees, and flies have a larval stage in their development in which the young organisms look very different than their adult counterparts. These insects then enter a pupal stage where marked changes in body form take place after which an adult emerges. This type of development is ...
CHAPTER 16 EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS
... - a random change in allele frequency that occurs in small populations - it occurs when: individuals that carry a particular allele may have more descendants than other individuals; may cause an allele to become more common in a population - may occur when groups of individuals colonize a new habita ...
... - a random change in allele frequency that occurs in small populations - it occurs when: individuals that carry a particular allele may have more descendants than other individuals; may cause an allele to become more common in a population - may occur when groups of individuals colonize a new habita ...
Evolution, drift and selection
... biologist and geneticist) wrote in his book ‘The Theory of Evolution’ “any population of entities which has the properties of multiplication, heredity and variation” It is impossible to try to define Evolution without reference to Charles Darwin (1809 -1882). Darwin was a British naturalist whose gr ...
... biologist and geneticist) wrote in his book ‘The Theory of Evolution’ “any population of entities which has the properties of multiplication, heredity and variation” It is impossible to try to define Evolution without reference to Charles Darwin (1809 -1882). Darwin was a British naturalist whose gr ...
Population Genetics
... are differences in genotype frequency from generation to generation evident? Are we sure that these differences have not happened due chance alone? Significance of the difference in frequency chi-square analysis ( X2 ) P.200 X2 = (O # – E# )2 E# X2 = 0 it is hardy-weinberg equilibrium ( H0 or ...
... are differences in genotype frequency from generation to generation evident? Are we sure that these differences have not happened due chance alone? Significance of the difference in frequency chi-square analysis ( X2 ) P.200 X2 = (O # – E# )2 E# X2 = 0 it is hardy-weinberg equilibrium ( H0 or ...
Histology
... tissue usually are attached to bones and controlled by conscious effort Cells, or muscle fibers, are long and threadlike Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by nerve action and then relax immediately. ...
... tissue usually are attached to bones and controlled by conscious effort Cells, or muscle fibers, are long and threadlike Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by nerve action and then relax immediately. ...
Cells Working Together Transcript
... WHICH PROVIDES THE BODY WITH OXYGEN AND HELPS IT GET RID OF THE WASTE PRODUCT CARBON DIOXIDE. THE LUNGS ARE THE MAIN RESPIRATORY ORGANS. THE NINTH AND LAST ORGAN SYSTEM IS THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, WHICH ALLOWS US TO HAVE CHILDREN. THE FEMALE OVARIES AND THE MALE TESTIS ARE THE MAIN ORGANS OF THE REP ...
... WHICH PROVIDES THE BODY WITH OXYGEN AND HELPS IT GET RID OF THE WASTE PRODUCT CARBON DIOXIDE. THE LUNGS ARE THE MAIN RESPIRATORY ORGANS. THE NINTH AND LAST ORGAN SYSTEM IS THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, WHICH ALLOWS US TO HAVE CHILDREN. THE FEMALE OVARIES AND THE MALE TESTIS ARE THE MAIN ORGANS OF THE REP ...
BESC 201, Introduction to Bioenvironmental Science
... Physiology, science of: study of a group of internal traits of organisms, largely encompassed by organ system functions and their interactions with each other, and their response to the external environment (DeWitt, just now) ...
... Physiology, science of: study of a group of internal traits of organisms, largely encompassed by organ system functions and their interactions with each other, and their response to the external environment (DeWitt, just now) ...
3.3 The Process of Evolution: How Does Natural Selection Work?
... genetically (height) 3. In each generation, many more offspring are produced than can possible survive. Thus only some individuals in a population live long enough to produce offspring and some will produce more than others 4. The subset of individuals that survive best and produce the most offsprin ...
... genetically (height) 3. In each generation, many more offspring are produced than can possible survive. Thus only some individuals in a population live long enough to produce offspring and some will produce more than others 4. The subset of individuals that survive best and produce the most offsprin ...
Tissues- A group of similar cells that perform a common function.
... • Stratified- cells layered one on another • Transitional- differing cell shapes in a stratified or layered sheet (Figure 5-2) ...
... • Stratified- cells layered one on another • Transitional- differing cell shapes in a stratified or layered sheet (Figure 5-2) ...
Evolution Review 1. What are the four types of evidence for
... 5. An insecticide is a chemical that kills insects. Most insects are killed the first time they’re exposed to an insecticide. However, some insects have a trait that enables them to survive their firs ...
... 5. An insecticide is a chemical that kills insects. Most insects are killed the first time they’re exposed to an insecticide. However, some insects have a trait that enables them to survive their firs ...
6 - smw15.org
... A dominant gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is more evident in the phenotype A recessive gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is less evident in the phenotype X-linked genes are genes located on the X chromosome ...
... A dominant gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is more evident in the phenotype A recessive gene is the member of an interacting pair of alleles whose influence is less evident in the phenotype X-linked genes are genes located on the X chromosome ...
The Human Immune System
... The First Line of Defense ~Stomach Acid~ - Swallowed bacteria are broken down by incredibly strong acids in the stomach that break down your food - The stomach must produce a coating of special mucus or this acid would eat through the stomach! ...
... The First Line of Defense ~Stomach Acid~ - Swallowed bacteria are broken down by incredibly strong acids in the stomach that break down your food - The stomach must produce a coating of special mucus or this acid would eat through the stomach! ...
Genetics and Evolution
... Gene pool: The combined genetic information of all members of a particular population Relative frequency: Number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of time other alleles for the same gene occur Evolution involves a change in relative frequencies of alleles in a g ...
... Gene pool: The combined genetic information of all members of a particular population Relative frequency: Number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of time other alleles for the same gene occur Evolution involves a change in relative frequencies of alleles in a g ...
Evolution - whitburnscience
... biologist and geneticist) wrote in his book ‘The Theory of Evolution’ “any population of entities which has the properties of multiplication, heredity and variation” It is impossible to try to define Evolution without reference to Charles Darwin (1809 -1882). Darwin was a British naturalist whose gr ...
... biologist and geneticist) wrote in his book ‘The Theory of Evolution’ “any population of entities which has the properties of multiplication, heredity and variation” It is impossible to try to define Evolution without reference to Charles Darwin (1809 -1882). Darwin was a British naturalist whose gr ...
Honors Biology II
... chemistry, or behavior. These characteristics strongly influence what capabilities an organism will have and how it will react, and therefore influence how likely it is to survive and reproduce. ...
... chemistry, or behavior. These characteristics strongly influence what capabilities an organism will have and how it will react, and therefore influence how likely it is to survive and reproduce. ...
PPEvolution_notes_01_April
... -Fish in caves don’t use their eyes so they ________________________________r -Elephants use their trunks a lot so they get longer Although false, his theory ____________________________________________ to explain how organisms adapted to their environment over time ...
... -Fish in caves don’t use their eyes so they ________________________________r -Elephants use their trunks a lot so they get longer Although false, his theory ____________________________________________ to explain how organisms adapted to their environment over time ...
or Print Your Own Glossary Only 5 Pages Long!!
... Archaebacteria - classification kingdom made up of bacteria that live in extreme environments; differentiated from other prokaryotes by various important chemical differences Arteries - a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body's organs Asymmetry - irregular in shape; without ...
... Archaebacteria - classification kingdom made up of bacteria that live in extreme environments; differentiated from other prokaryotes by various important chemical differences Arteries - a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body's organs Asymmetry - irregular in shape; without ...
Bell Work: 4/8/13
... What is the function of this organ system? transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells breaking food down into nutrients that cells can use producing offspring ...
... What is the function of this organ system? transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells breaking food down into nutrients that cells can use producing offspring ...
Specialized Cells - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... All cells in the human body have the same complement of DNA, but yet each type of cell is different, e.g. a muscle cell is different to a brain cell. Why? All cells in the human body have the same complement of DNA, but in different cells, different parts of the DNA are turned on and off. One DNA is ...
... All cells in the human body have the same complement of DNA, but yet each type of cell is different, e.g. a muscle cell is different to a brain cell. Why? All cells in the human body have the same complement of DNA, but in different cells, different parts of the DNA are turned on and off. One DNA is ...
Ch 16.Evolution of Populations.Biology.Landis
... 24. What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle state? ...
... 24. What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle state? ...
Document
... 61. What is this process called? A. fertilization B. gamete formation C. inheritance D. reproduction ...
... 61. What is this process called? A. fertilization B. gamete formation C. inheritance D. reproduction ...
Evolution Tutorial
... 5. The American cougar and the African lion both share a common _________________ from the past. 6. Are all cat species related? ________ Why? _______________________ 7. Evolution works because is takes an existing structure and ____________ that structure. Click the GENES tab. 8. New individuals bo ...
... 5. The American cougar and the African lion both share a common _________________ from the past. 6. Are all cat species related? ________ Why? _______________________ 7. Evolution works because is takes an existing structure and ____________ that structure. Click the GENES tab. 8. New individuals bo ...
Name Date ______ Midterm.Review.Fill
... The best way to carry a microscope is to hold the arm and the base. ...
... The best way to carry a microscope is to hold the arm and the base. ...























