business cycle composition and reasons
... • (E.g.) inventions, technological innovations, natural causes etc. • These fluctuations can also occur because of ineffective government policy. • This results in fluctuations in the rate of increase in the money supply, which causes changes in the rate of increase in prices, production and e ...
... • (E.g.) inventions, technological innovations, natural causes etc. • These fluctuations can also occur because of ineffective government policy. • This results in fluctuations in the rate of increase in the money supply, which causes changes in the rate of increase in prices, production and e ...
1.2 The Business Environment as a Complex Adaptive System
... economic, social (or sociological), and technological. Individual factors are identified under each of these headings and their impact on the organization is explored. Inevitably, some writers have argued that other aspects of the environment should be ...
... economic, social (or sociological), and technological. Individual factors are identified under each of these headings and their impact on the organization is explored. Inevitably, some writers have argued that other aspects of the environment should be ...
True/False Questions
... a. the maximum combinations of two goods or services that can be produced when resources are fully used and the best technology is employed. b. the minimum combinations of two goods or services that can be produced when resources are fully used and the best technology is employed. c. the maximum com ...
... a. the maximum combinations of two goods or services that can be produced when resources are fully used and the best technology is employed. b. the minimum combinations of two goods or services that can be produced when resources are fully used and the best technology is employed. c. the maximum com ...
Keeping America`s Edge
... the Free World. It also established a set of political and economic institutions and programs — the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the Marshall Plan, the Bretton Woods system, the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and so forth — that encouraged rapid economic development within this ...
... the Free World. It also established a set of political and economic institutions and programs — the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the Marshall Plan, the Bretton Woods system, the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, and so forth — that encouraged rapid economic development within this ...
Inflation, Recession, and Stagflation
... being described by the long-run Walrasian equations, such a view is only ...
... being described by the long-run Walrasian equations, such a view is only ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES A DYNAMIC SPATIAL MODEL Paul Krugman Paper No. 4219
... thing would be to assume that labor and possibly capital are the mobile factors, while land is the immobile factor; and that both mobile and immobile factors are used in both sectors. To do this, however, we would ...
... thing would be to assume that labor and possibly capital are the mobile factors, while land is the immobile factor; and that both mobile and immobile factors are used in both sectors. To do this, however, we would ...
Basic Real Estate Appraisal - PowerPoint
... the market. But in order to enter the market, the rights must have the four elements of utility, scarcity, demand, and transferability. We know that real estate is affected by changing business conditions, such as employment, income and price levels, production volumes, and building construction cos ...
... the market. But in order to enter the market, the rights must have the four elements of utility, scarcity, demand, and transferability. We know that real estate is affected by changing business conditions, such as employment, income and price levels, production volumes, and building construction cos ...
Business cycles recessions and economic booms
... just felt that cycles were an aberration which time would solve cycles automatically – i.e., the system was self-correcting. The Classical School felt that in a slump, prices and wages would fall and would continue to do so until they wiped out the lack of demand and the economy would start up again ...
... just felt that cycles were an aberration which time would solve cycles automatically – i.e., the system was self-correcting. The Classical School felt that in a slump, prices and wages would fall and would continue to do so until they wiped out the lack of demand and the economy would start up again ...
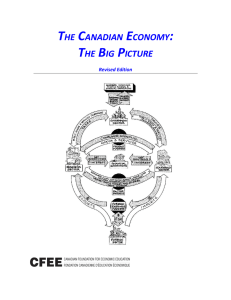
the canadian economy - Canadian Foundation for Economic
... Production: It's a Job – For Some A second key role of an economy is to create jobs through production activity so that people can find employment. Third, through its efforts to produce goods and services and its employment of people’s skills, the economy provides people with an opportunity to earn ...
... Production: It's a Job – For Some A second key role of an economy is to create jobs through production activity so that people can find employment. Third, through its efforts to produce goods and services and its employment of people’s skills, the economy provides people with an opportunity to earn ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... Measuring the Economy’s Output 3. Changes in business inventory is an entry that represents the difference between what has been produced and what is sold. Although this entry is very small compared to total GDP, it is one of the most important indicators of future business activity. It has an impo ...
... Measuring the Economy’s Output 3. Changes in business inventory is an entry that represents the difference between what has been produced and what is sold. Although this entry is very small compared to total GDP, it is one of the most important indicators of future business activity. It has an impo ...
gross domestic product
... 2006-2007, India's GDP grew at an impressive 9.2 per cent. The share of different sectors of the economy in India's GDP is as follows: Agriculture - 18.5 %, Industry - 26.4 % and Services - 55.1 % ...
... 2006-2007, India's GDP grew at an impressive 9.2 per cent. The share of different sectors of the economy in India's GDP is as follows: Agriculture - 18.5 %, Industry - 26.4 % and Services - 55.1 % ...
Management & Engineering Developing Circular Economy in the Ecological Economic Region
... scale of the industrial parks in the EERPYL is too small. Its features are not obvious and industrial structures are identical. There are some other problems, and these problems will restrict seriously development of regional recycling economy. Digital research showed that many county industrial clu ...
... scale of the industrial parks in the EERPYL is too small. Its features are not obvious and industrial structures are identical. There are some other problems, and these problems will restrict seriously development of regional recycling economy. Digital research showed that many county industrial clu ...
goods and services produced by nationals within the
... they themselves were produced. If potato produced and then stored in a cold storage during the previous year is used to produce potato chips in the current year, we shall not consider these potatoes as intermediate goods. How shall we classify capital goods? Capital goods are used to produce other g ...
... they themselves were produced. If potato produced and then stored in a cold storage during the previous year is used to produce potato chips in the current year, we shall not consider these potatoes as intermediate goods. How shall we classify capital goods? Capital goods are used to produce other g ...
Review Packet
... If the rate of inflation is less than 3 percent (and greater than 0 percent, of course), it is considered “acceptable”. Types of Inflation Demand-pull inflation: more spending than the economy’s capacity to produce. The excess demand increases the prices of the limited real output, causing prices to ...
... If the rate of inflation is less than 3 percent (and greater than 0 percent, of course), it is considered “acceptable”. Types of Inflation Demand-pull inflation: more spending than the economy’s capacity to produce. The excess demand increases the prices of the limited real output, causing prices to ...
The Role of Technologies in World
... voyaging, as opposed to the human powered ships used by most world-empires, would not have been successful without the software technologies of reliable systems of navigation and increasingly reliable maps (Hugill 1993). As Wallerstein notes, the emphasis of the worldeconomy was, from it’s beginning ...
... voyaging, as opposed to the human powered ships used by most world-empires, would not have been successful without the software technologies of reliable systems of navigation and increasingly reliable maps (Hugill 1993). As Wallerstein notes, the emphasis of the worldeconomy was, from it’s beginning ...