Marginal Revenue
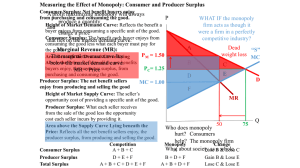
... Connecting the Pareto approach to efficiency with consumer and producer surplus Question: How did we argue that P monopoly was inefficient? We chose an individual, Joe, who Did not by a hamburger when the price was $1.50, the monopoly price. But would be a hamburger at a PM = 1.50 price of $1.40, a ...
... Connecting the Pareto approach to efficiency with consumer and producer surplus Question: How did we argue that P monopoly was inefficient? We chose an individual, Joe, who Did not by a hamburger when the price was $1.50, the monopoly price. But would be a hamburger at a PM = 1.50 price of $1.40, a ...
Contemporary Change in Russia:
... nobility (Misiunas & Taagepera 1993). In many respects, the Estonian and Latvian areas functioned as laboratories in which policies could be tested before being implemented in the rest of the vast Tsarist empire. Serfdom was abolished in 1819, 42 years earlier than in the rest of Russia. The agricul ...
... nobility (Misiunas & Taagepera 1993). In many respects, the Estonian and Latvian areas functioned as laboratories in which policies could be tested before being implemented in the rest of the vast Tsarist empire. Serfdom was abolished in 1819, 42 years earlier than in the rest of Russia. The agricul ...
Economics - Loudoun County Public Schools
... There are four units in the curriculum. Since the foundations of the units are conceptual, they take in and call for the study of more than just the Virginia SOLs. SOL connections are listed in red on the “Objectives” page, and appear also in the branches of each unit’s mind map. This means that whe ...
... There are four units in the curriculum. Since the foundations of the units are conceptual, they take in and call for the study of more than just the Virginia SOLs. SOL connections are listed in red on the “Objectives” page, and appear also in the branches of each unit’s mind map. This means that whe ...
Macroeconomic theories of investment and development of a New
... Jacobs (2015) says “The objective of New Economic Theory (NET) is to formulate the theoretical and practical knowledge required to maximize economic security, human welfare and individual well-being of all humanity in a manner consistent with universal human rights, cultural diversity and civilizati ...
... Jacobs (2015) says “The objective of New Economic Theory (NET) is to formulate the theoretical and practical knowledge required to maximize economic security, human welfare and individual well-being of all humanity in a manner consistent with universal human rights, cultural diversity and civilizati ...
Business fixed investment
... defines “profits” for the purpose of taxation Suppose first that the law defined profit as we did above – the rental price of capital minus the cost of the capital In this case, even though firms would be sharing a fraction of their profits with the government, it would still be rational for them to ...
... defines “profits” for the purpose of taxation Suppose first that the law defined profit as we did above – the rental price of capital minus the cost of the capital In this case, even though firms would be sharing a fraction of their profits with the government, it would still be rational for them to ...
OCR AS Economics Unit F582
... be answered. The examiner comments (blue text) have been added to give you some sense of what is rewarded in the exam and which areas can be developed. Again, these are not the only ways to answer such questions but they can be treated as one way of approaching questions of these types. ...
... be answered. The examiner comments (blue text) have been added to give you some sense of what is rewarded in the exam and which areas can be developed. Again, these are not the only ways to answer such questions but they can be treated as one way of approaching questions of these types. ...
An Empirical and Theoretical Analysis of the New Imperialism
... have brought about discussions of the economic and political strategies of capitalism and their limits. They therefore have an important public and political function. But in many cases the notions of imperialism employed in these discussions remain rather imprecise (Castree, 2006) or unexplained (B ...
... have brought about discussions of the economic and political strategies of capitalism and their limits. They therefore have an important public and political function. But in many cases the notions of imperialism employed in these discussions remain rather imprecise (Castree, 2006) or unexplained (B ...
Economic Growth Name School Affiliation
... extensive when more inputs from the four factors of production, namely land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial activities, trigger or explain the growth (Colombatto, 2006). By land, this means more than just land in the physical sense; it includes acreage water, trees, minerals, and other natural ...
... extensive when more inputs from the four factors of production, namely land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial activities, trigger or explain the growth (Colombatto, 2006). By land, this means more than just land in the physical sense; it includes acreage water, trees, minerals, and other natural ...
Chapter 9 High Road Capitalism
... compete over is price. There is therefore constant pressure to reduce costs so that prices can be lower. In high road capitalism competition is primarily over efficient production of value, productivity measured not by volume per unit of input, but revenue per unit of input. This means that firms do ...
... compete over is price. There is therefore constant pressure to reduce costs so that prices can be lower. In high road capitalism competition is primarily over efficient production of value, productivity measured not by volume per unit of input, but revenue per unit of input. This means that firms do ...
Answers to the Problems – Chapter 11
... infinite. More realistically, Lin would probably sell the quantity that maximizes his profit but that profit will be less than if he sells at the going market price of $10 a box. The elasticity of demand for Lin’s cookies is infinite. The elasticity of demand in the market for cookies is not infinit ...
... infinite. More realistically, Lin would probably sell the quantity that maximizes his profit but that profit will be less than if he sells at the going market price of $10 a box. The elasticity of demand for Lin’s cookies is infinite. The elasticity of demand in the market for cookies is not infinit ...
The Role of Seaports in the Process of Economic Growth
... seaport required enormous equipment and installations. These are called seaport infrastructures, which are necessary for treating merchant ships and freighting goods. Nowadays, the seaport is not a simple interface of treating ships and loading goods on board. It may be considered a service that is ...
... seaport required enormous equipment and installations. These are called seaport infrastructures, which are necessary for treating merchant ships and freighting goods. Nowadays, the seaport is not a simple interface of treating ships and loading goods on board. It may be considered a service that is ...
Central Statistical Office
... Build on the existing strengths of CSO, but necessary with a number of additional functions as well as changes: New functions in CSO for Support to the top management in: Liaison and support to other government agencies involved in the statistical system HR management External and intern ...
... Build on the existing strengths of CSO, but necessary with a number of additional functions as well as changes: New functions in CSO for Support to the top management in: Liaison and support to other government agencies involved in the statistical system HR management External and intern ...
Document
... List three policies that attempt to raise living standards by increasing one of the determinants of productivity. ...
... List three policies that attempt to raise living standards by increasing one of the determinants of productivity. ...
Lecture 14
... • E.g. China's GDP in 2004 was $1938 billion and Denmark's $220 billion, but Denmark's GDP per capita was $40,750 while China's was $1500. The living standards in Denmark are superior to those in China, since the average income for each person in Denmark is much higher. • An increase in GDP could ac ...
... • E.g. China's GDP in 2004 was $1938 billion and Denmark's $220 billion, but Denmark's GDP per capita was $40,750 while China's was $1500. The living standards in Denmark are superior to those in China, since the average income for each person in Denmark is much higher. • An increase in GDP could ac ...
ppt - 587 kb
... in what is purchased with that produce from other nations. “According therefore, as this produce, or what is purchased with it, bears a greater or smaller proportion to the number of those who are to consume it, the nation will be better or worse supplied with all the necessaries and conveniences fo ...
... in what is purchased with that produce from other nations. “According therefore, as this produce, or what is purchased with it, bears a greater or smaller proportion to the number of those who are to consume it, the nation will be better or worse supplied with all the necessaries and conveniences fo ...
Robert NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES PUBLIC FINANCE IN MODELS OF ECONOMIC GROWTH
... infinite in this model. If fixed costs were introduced, the number of firms could be determined from a zero-profit condition. However, this model—or one where n is set exogenously—has the same type of counter-intuitive scale effect that appeared in some of the learning-by-doing models: an increase i ...
... infinite in this model. If fixed costs were introduced, the number of firms could be determined from a zero-profit condition. However, this model—or one where n is set exogenously—has the same type of counter-intuitive scale effect that appeared in some of the learning-by-doing models: an increase i ...
PPT
... improvements to non-produced assets. Gross fixed capital formation is estimated using a ...
... improvements to non-produced assets. Gross fixed capital formation is estimated using a ...
Preview Sample 1
... new advertising campaign is described as opportunity cost. Answer: FALSE Explanation: Opportunity cost refers to the value of the most appealing alternative from all those that weren't chosen. In other words, opportunity cost is a way to measure the value of what you gave up when you pursued a diffe ...
... new advertising campaign is described as opportunity cost. Answer: FALSE Explanation: Opportunity cost refers to the value of the most appealing alternative from all those that weren't chosen. In other words, opportunity cost is a way to measure the value of what you gave up when you pursued a diffe ...
FAPP07_SG_04
... In determining a feasible region, you will need to graph a set of linear inequalities in the plane which involves the following: Graphing lines by the intercept method and determining which side to shade by using a test point (generally the origin); Graphing vertical and horizontal lines and det ...
... In determining a feasible region, you will need to graph a set of linear inequalities in the plane which involves the following: Graphing lines by the intercept method and determining which side to shade by using a test point (generally the origin); Graphing vertical and horizontal lines and det ...