Understanding-Business-9th-Edition-Nickels-Test-Bank
... True/false questions are in plain text. Multiple choice questions are in bold text. Questions on boxed material are in bold text with a tilde~. Essay questions are in bold underlined text. Minicase questions are in bold with an asterisk*. ...
... True/false questions are in plain text. Multiple choice questions are in bold text. Questions on boxed material are in bold text with a tilde~. Essay questions are in bold underlined text. Minicase questions are in bold with an asterisk*. ...
Why Do Inefficient Firms Survive? Management and Economic Development Michael Peters January 2012
... rial resources and traditional producers survive in those sectors of the economy where bigger firms are limited in the amount of managerial resources they want to buy at at the current market price. However, the precise mechanism how managerial inputs are allocated across producer differs from Penr ...
... rial resources and traditional producers survive in those sectors of the economy where bigger firms are limited in the amount of managerial resources they want to buy at at the current market price. However, the precise mechanism how managerial inputs are allocated across producer differs from Penr ...
- Rainer Maurer
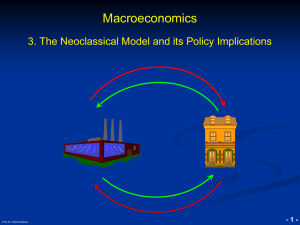
... immediately if demand and/or supply changes. As a result, disturbances of the general market equilibrium do not persist. After a shock, the economy finds immediately back to a general market equilibrium. This is the fundamental difference between the neoclassical and the Keynesian model, where price ...
... immediately if demand and/or supply changes. As a result, disturbances of the general market equilibrium do not persist. After a shock, the economy finds immediately back to a general market equilibrium. This is the fundamental difference between the neoclassical and the Keynesian model, where price ...
Chapter 1 “The Wretched Spirit of Monopoly”
... All of these points, understandably, lead to a need for a revamping of modern antitrust thinking that is heavily guided (and misguided) by the conventional microeconomic theory of monopoly under which so many legal scholars and judges have mistakenly equated market dominance with monopoly— monopoly ...
... All of these points, understandably, lead to a need for a revamping of modern antitrust thinking that is heavily guided (and misguided) by the conventional microeconomic theory of monopoly under which so many legal scholars and judges have mistakenly equated market dominance with monopoly— monopoly ...
Chapter 3 (Revised Jan
... interest on loans than they pay on deposits. These services are referred to as “FISIM” in the 1993 SNA and are measured by the difference between interest received on loans and the interest paid on deposits. The SNA recommends that FISIM should be shown as an imputed expenditure by the sector that b ...
... interest on loans than they pay on deposits. These services are referred to as “FISIM” in the 1993 SNA and are measured by the difference between interest received on loans and the interest paid on deposits. The SNA recommends that FISIM should be shown as an imputed expenditure by the sector that b ...
chapter 05
... C) How does demand for a good change when there is an increase in a consumer's income? D) How does a consumer choose which goods to consume given his/her income? Answer: B Difficulty: Easy AACSB: Analytical Thinking Topic: Macroeconomic Questions 6) Which of the following questions can be answered u ...
... C) How does demand for a good change when there is an increase in a consumer's income? D) How does a consumer choose which goods to consume given his/her income? Answer: B Difficulty: Easy AACSB: Analytical Thinking Topic: Macroeconomic Questions 6) Which of the following questions can be answered u ...
chapter 3: gdp and the main expenditure
... and the associated price and volume indices will be calculated for the aggregates shown in the third column of Table 2. This is done because there are differences between countries in the relative importance of individual consumption expenditures by NPISHs and, especially, by government. For example ...
... and the associated price and volume indices will be calculated for the aggregates shown in the third column of Table 2. This is done because there are differences between countries in the relative importance of individual consumption expenditures by NPISHs and, especially, by government. For example ...
The equilibrium approach to money and the business cycle
... In any case, this distinction between statics and dynamics is not equivalent to the one ascribed above to the “Anglo-Saxon-French” tradition, namely of statics as an analysis that abstracts from time, and dynamics as that of (any) movements in time. Thus, following Löwe, the static (or equilibrium) ...
... In any case, this distinction between statics and dynamics is not equivalent to the one ascribed above to the “Anglo-Saxon-French” tradition, namely of statics as an analysis that abstracts from time, and dynamics as that of (any) movements in time. Thus, following Löwe, the static (or equilibrium) ...
Changes in Inventory Managment and the Business Cycle
... and inventory investment are empirical regularities of postwar business cycles. Blinder and Maccini (1991) show that the average movement in inventory investment during recessionary periods in the postwar era account for 87 percent of Gross National Product (GNP) movement from peak to trough. Comput ...
... and inventory investment are empirical regularities of postwar business cycles. Blinder and Maccini (1991) show that the average movement in inventory investment during recessionary periods in the postwar era account for 87 percent of Gross National Product (GNP) movement from peak to trough. Comput ...
the aggregate market
... A definition: Aggregate Demand is the aggregate or total expenditure on final goods and services produced in the domestic economy, at a range of price levels, during a given time period (usually a year). Three points: ...
... A definition: Aggregate Demand is the aggregate or total expenditure on final goods and services produced in the domestic economy, at a range of price levels, during a given time period (usually a year). Three points: ...
HAyEK`S CRITIQUE OF The General Theory
... the form of final goods and services and the income generated by such investments in the form of final demand. Thus, for Hayek, the biggest economic problem is that consumers should be willing to “wait” long enough to allow the consumer goods to emerge in final markets. Otherwise the phenomenon of i ...
... the form of final goods and services and the income generated by such investments in the form of final demand. Thus, for Hayek, the biggest economic problem is that consumers should be willing to “wait” long enough to allow the consumer goods to emerge in final markets. Otherwise the phenomenon of i ...
Financial Collateral and Macroeconomic Amplification∗
... …xed in total supply to one. Capital is held by bankers as well as borrowers. All agents have linear preferences de…ned over non-durable consumption. The remainder of this section provides further details on the key characteristics of the actors populating the model economy and their decision rules. ...
... …xed in total supply to one. Capital is held by bankers as well as borrowers. All agents have linear preferences de…ned over non-durable consumption. The remainder of this section provides further details on the key characteristics of the actors populating the model economy and their decision rules. ...
Production and Growth
... Natural Resources Natural resources can be important but are not necessary for an economy to be highly productive in producing goods and services. ...
... Natural Resources Natural resources can be important but are not necessary for an economy to be highly productive in producing goods and services. ...
the eleventh national economic and social development plan
... tradition. Of primary importance, it must serve to benefit all Thai citizens, who must be included in the decision-making process. This aspect of development aims at “self-reliance.” It proceeds with caution, self-evaluation, and prudence, by taking a step-by-step approach, and is tested before bein ...
... tradition. Of primary importance, it must serve to benefit all Thai citizens, who must be included in the decision-making process. This aspect of development aims at “self-reliance.” It proceeds with caution, self-evaluation, and prudence, by taking a step-by-step approach, and is tested before bein ...
the eleventh national economic and social development plan
... serve to benefit all Thai citizens, who must be included in the decision-making process. This aspect of development aims at “self-reliance.” It proceeds with caution, self-evaluation, and prudence, by taking a step-by-step approach, and is tested before being distributed to the public. Since the Eig ...
... serve to benefit all Thai citizens, who must be included in the decision-making process. This aspect of development aims at “self-reliance.” It proceeds with caution, self-evaluation, and prudence, by taking a step-by-step approach, and is tested before being distributed to the public. Since the Eig ...
Unpaid Work and the Economy: Linkages and Their Implications
... What is excluded from the production boundary is the production of services for own final consumption within households (excluding the services of paid domestic staff) and voluntary unpaid services. This is non-SNA work, and it is excluded from the national income accounts. Unpaid (Non-SNA) Work as ...
... What is excluded from the production boundary is the production of services for own final consumption within households (excluding the services of paid domestic staff) and voluntary unpaid services. This is non-SNA work, and it is excluded from the national income accounts. Unpaid (Non-SNA) Work as ...