Fundamental processes: Atomic Physics
... the highest occupied sub‐shell (outermost electron) of gaseous atom Second ionizaIon energy: minimum energy needed to remove the second electron from the highest occupied sub‐shell of gaseous atom Third, fourth, … ionizaIon energy – analogous “Total” ionizaIon energy: minimum energy ...
... the highest occupied sub‐shell (outermost electron) of gaseous atom Second ionizaIon energy: minimum energy needed to remove the second electron from the highest occupied sub‐shell of gaseous atom Third, fourth, … ionizaIon energy – analogous “Total” ionizaIon energy: minimum energy ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... 33. The 3p subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains __________ electrons. (a). 2 (b).6 (c). 36 (d). 10 Explanation: Since Xe is a noble gas, its subshells will be completely filled regardless of their principal quantum number. Thus the 3p subshell will contain 6 electrons. 34. [Ar]4s23d ...
... 33. The 3p subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains __________ electrons. (a). 2 (b).6 (c). 36 (d). 10 Explanation: Since Xe is a noble gas, its subshells will be completely filled regardless of their principal quantum number. Thus the 3p subshell will contain 6 electrons. 34. [Ar]4s23d ...
Statistical Mechanics That Takes into Account Angular
... system. The kinetic energy of majority of systems is a positive definite quadric form of all momenta. It determines a closed hypersurface in the subspace of momenta of the phase space. If motions of all particles are finite, the hypersurface of the fixed energy is closed and the layer that envelops ...
... system. The kinetic energy of majority of systems is a positive definite quadric form of all momenta. It determines a closed hypersurface in the subspace of momenta of the phase space. If motions of all particles are finite, the hypersurface of the fixed energy is closed and the layer that envelops ...
Quantum Computing Using Electrons Floating on
... The dephasing rate is essentially determined by in-plane scattering, in which the electron does not make an interband transition. For transitions 1 ! 2, the corresponding coupling Hd h1j Her j1i h2j Her j2i is determined by the difference of the diagonal matrix elements of the operator Her on the ...
... The dephasing rate is essentially determined by in-plane scattering, in which the electron does not make an interband transition. For transitions 1 ! 2, the corresponding coupling Hd h1j Her j1i h2j Her j2i is determined by the difference of the diagonal matrix elements of the operator Her on the ...
Pattern Formation in the Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
... Kelvin has been identified for these quantum phases. Besides, there exists a macroscopic description of quantum phases in terms of some local order parameter φ which is a spatially varying function minimizing a free-energy functional. Such a Ginzburg-Landau approach has been developed for the FQHE a ...
... Kelvin has been identified for these quantum phases. Besides, there exists a macroscopic description of quantum phases in terms of some local order parameter φ which is a spatially varying function minimizing a free-energy functional. Such a Ginzburg-Landau approach has been developed for the FQHE a ...
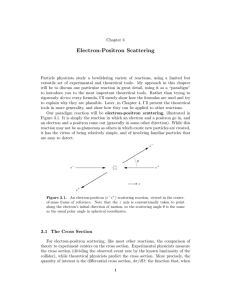
Electron-Positron Scattering
... electron (if the arrow points up) or positron (if the arrow points down), with the initial-state particles at the bottom of the diagram and the final-state particles at the top. The wavy lines represent photons, which in this case are called “virtual” particles, since they appear as intermediate quan ...
... electron (if the arrow points up) or positron (if the arrow points down), with the initial-state particles at the bottom of the diagram and the final-state particles at the top. The wavy lines represent photons, which in this case are called “virtual” particles, since they appear as intermediate quan ...
7. Atoms
... from first principles. We will answer questions like: what determines the number of elements in each row? Why are there gaps at the top, and two rows at the bottom that we can’t fit in elsewhere? What’s special about the sequence of atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 26, 54, 86, . . . that label the inert ga ...
... from first principles. We will answer questions like: what determines the number of elements in each row? Why are there gaps at the top, and two rows at the bottom that we can’t fit in elsewhere? What’s special about the sequence of atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 26, 54, 86, . . . that label the inert ga ...
Electronic structure, plane waves and pseudopotentials
... In the special case that the electrons are evenly spread throughout space, we can actually compute Exc [ρ]. We can use this as an approximation to the true Exc in our calculations. ...
... In the special case that the electrons are evenly spread throughout space, we can actually compute Exc [ρ]. We can use this as an approximation to the true Exc in our calculations. ...
PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
... in a doped T-shaped quantum wire ( studied by photoluminescence-excitation spectra ) ...
... in a doped T-shaped quantum wire ( studied by photoluminescence-excitation spectra ) ...
Comparison of density functionals for energy and structural
... to give qualitatively incorrect results for systems, such as transition metal complexes, where there are a number of lowlying virtual orbitals. Highly parametrized density functionals ?HPDFs? provide an alternative to hybrid functionals at the cost of a large number of parameters to optimize. In one ...
... to give qualitatively incorrect results for systems, such as transition metal complexes, where there are a number of lowlying virtual orbitals. Highly parametrized density functionals ?HPDFs? provide an alternative to hybrid functionals at the cost of a large number of parameters to optimize. In one ...
Gauge-Gravity Duality and the Black Hole Interior
... (i) Typical states have no interior. (ii) Typical interior states are highly excited. In this case there could be large corrections to the commutators (2), but again there is a firewall [24]. (iii) Strong complementarity. The strong complementarity proposal [26,27] states that the theory describing ...
... (i) Typical states have no interior. (ii) Typical interior states are highly excited. In this case there could be large corrections to the commutators (2), but again there is a firewall [24]. (iii) Strong complementarity. The strong complementarity proposal [26,27] states that the theory describing ...
Polarization, reactivity and quantum molecular capacitance: From
... 0 by the atomic frontiers orbitals in the Eq. (13), one recovers an earlier result derived by Chattaraj et al.26 Surprisingly, the electrostatic potential generated by the Fukui function27 (Eqs (1) and (2)) evaluated at the nucleus of an atom is also a measure of its chemical hardness28. It is in ...
... 0 by the atomic frontiers orbitals in the Eq. (13), one recovers an earlier result derived by Chattaraj et al.26 Surprisingly, the electrostatic potential generated by the Fukui function27 (Eqs (1) and (2)) evaluated at the nucleus of an atom is also a measure of its chemical hardness28. It is in ...
Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules
... • The lower the value of the variational integral, the closer the trial variational function to the real eigenfunction of ground state. • To arrive at a good approximation to the ground-state energy E1, we try many trial variational functions and look for the one that gives the lowest value of the v ...
... • The lower the value of the variational integral, the closer the trial variational function to the real eigenfunction of ground state. • To arrive at a good approximation to the ground-state energy E1, we try many trial variational functions and look for the one that gives the lowest value of the v ...
electron orbits atomic spectra the Bohr atom
... of the atom again. In the model, electrons and nucleus are tiny and the electrons are separated by large distances from the positively charged nuclei. Let’s build such an atom. Any problems here? ...
... of the atom again. In the model, electrons and nucleus are tiny and the electrons are separated by large distances from the positively charged nuclei. Let’s build such an atom. Any problems here? ...
introductory concepts - New Age International
... The quantity ml, referred to as the magnetic quantum number, specifies the splitting of energies with a given n and l in a magnetic field. The number ms is called the spin quantum number; it shows that the spin of the electron about its own axis is quantised. The values of the four quantum numbers a ...
... The quantity ml, referred to as the magnetic quantum number, specifies the splitting of energies with a given n and l in a magnetic field. The number ms is called the spin quantum number; it shows that the spin of the electron about its own axis is quantised. The values of the four quantum numbers a ...
Plasmons in a superlattice in a parabolic quantum well M. Sundaram
... polarized parallel to the growth direction. Hence, the unpolarized FIR light from a spectrometer was focused on the edge of the sample and sent edgewise through it to a bolometer. The path length was ;4 mm. Front gates were used to tune the number of electrons in the wells from 0 to ;531011 cm22 as ...
... polarized parallel to the growth direction. Hence, the unpolarized FIR light from a spectrometer was focused on the edge of the sample and sent edgewise through it to a bolometer. The path length was ;4 mm. Front gates were used to tune the number of electrons in the wells from 0 to ;531011 cm22 as ...
Lecture 8 Gaussian basis sets CHEM6085: Density Functional Theory
... • CGs which extend further from the nucleus than the atomic orbitals. Such “diffuse functions” improve the predicted properties of species with extended electronic densities such as anions or molecules forming hydrogen bonds. Examples: 4-31+G, 6-31+G • Basis sets are considered “balanced” when they ...
... • CGs which extend further from the nucleus than the atomic orbitals. Such “diffuse functions” improve the predicted properties of species with extended electronic densities such as anions or molecules forming hydrogen bonds. Examples: 4-31+G, 6-31+G • Basis sets are considered “balanced” when they ...
PowerPoint Version
... As the program can only deal with one pseudized state per angular momentum channel, this implies the elimination of the “genuinely valence” 6s state from the calculation In other words, the pseudopotential has been generated for an ion ...
... As the program can only deal with one pseudized state per angular momentum channel, this implies the elimination of the “genuinely valence” 6s state from the calculation In other words, the pseudopotential has been generated for an ion ...
Computational Quantum Chemistry of Chemical Kinetic Modeling
... the atomic orbitals with appropiate linear weighting coefficients, Figure 1 below for carbon Monoxide as example), in contrast to the approach of valence bond theory in which the orbitals are associated with the constituent atoms. The full analytical calculation of the molecular orbitals for most sy ...
... the atomic orbitals with appropiate linear weighting coefficients, Figure 1 below for carbon Monoxide as example), in contrast to the approach of valence bond theory in which the orbitals are associated with the constituent atoms. The full analytical calculation of the molecular orbitals for most sy ...
ON THE SHAPES OF ATOMS
... As for closed-shell atoms, there is no controversy about the shape of atoms having half-filled valence orbitals, s 1 , p 3 , d 5 , f 7 . Expression 1 is taken as still applying if the population factor 2 is replaced by 1 for the singly occupied (K. orbitals. Thus, the total electron distribution is ...
... As for closed-shell atoms, there is no controversy about the shape of atoms having half-filled valence orbitals, s 1 , p 3 , d 5 , f 7 . Expression 1 is taken as still applying if the population factor 2 is replaced by 1 for the singly occupied (K. orbitals. Thus, the total electron distribution is ...
Interatomic Methods for the Dispersion Energy Derived from the
... the onset of the damping in terms of the distance. Typically, only one of these parameters is adjusted for a given DFT functional by minimizing the error with respect to high-level quantum-chemical binding energies. Another disadvantage of the damping function, as used in DFT-D and DFT+vdW methods, ...
... the onset of the damping in terms of the distance. Typically, only one of these parameters is adjusted for a given DFT functional by minimizing the error with respect to high-level quantum-chemical binding energies. Another disadvantage of the damping function, as used in DFT-D and DFT+vdW methods, ...
The Spectrum of Helium and Calcium
... Ca is somewhat similar to that of He in that singlet and triplet excited systems exist. In addition, in calcium we have bound states where both of the s electrons are excited. In Figure 2 we show an energy level diagram of Ca. 4b. Singlet states. Look at the first four columns of Fig. 2. They are la ...
... Ca is somewhat similar to that of He in that singlet and triplet excited systems exist. In addition, in calcium we have bound states where both of the s electrons are excited. In Figure 2 we show an energy level diagram of Ca. 4b. Singlet states. Look at the first four columns of Fig. 2. They are la ...