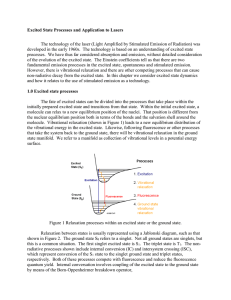
Lamb shift in radical-ion pairs produces a singlet
... the primary interest in them stems from their central role in photosynthesis [26, 27]. The photon energy absorbed by the chlorophyll antennae is transformed to an electronic excitation finally reaching the photosynthetic reaction center (RC), and resulting in the transmembrane charge separation essen ...
... the primary interest in them stems from their central role in photosynthesis [26, 27]. The photon energy absorbed by the chlorophyll antennae is transformed to an electronic excitation finally reaching the photosynthetic reaction center (RC), and resulting in the transmembrane charge separation essen ...
local pdf - Quantum Optics and Spectroscopy
... An ion in an electric trap provides an excellent system for carrying out precision spectroscopy. Laser cooling10, either directly or sympathetically via an auxiliary ion11, minimizes thermal line broadening. Long storage times allow for many repeated measurements on the same particle, and collisiona ...
... An ion in an electric trap provides an excellent system for carrying out precision spectroscopy. Laser cooling10, either directly or sympathetically via an auxiliary ion11, minimizes thermal line broadening. Long storage times allow for many repeated measurements on the same particle, and collisiona ...
chapter 8
... Blatt and Weisskopf (1952) have given some figures for the suppression factors in α-decay transition rates due to the angular momentum barrier. ...
... Blatt and Weisskopf (1952) have given some figures for the suppression factors in α-decay transition rates due to the angular momentum barrier. ...
Principles of remote sensing of atmospheric parameters
... ber (or wavelength) in the infrared or microwave regions where an atmospheric constituent absorbs radiation, it also emits thermal radiation according to Kirchhoff's Law. Since the radiance leaving the atmosphere is a function of the distribution of the emitting gases and of temperature throughout t ...
... ber (or wavelength) in the infrared or microwave regions where an atmospheric constituent absorbs radiation, it also emits thermal radiation according to Kirchhoff's Law. Since the radiance leaving the atmosphere is a function of the distribution of the emitting gases and of temperature throughout t ...
255
... of s-tetrazine, these are in good agreement with the available experimental data. All of the optimized transition states are first order saddle points. However, the imaginary frequency at the B3LYP level is significantly smaller than at HF or MP2. Table 4 summarizes the calculated barrier heights and ...
... of s-tetrazine, these are in good agreement with the available experimental data. All of the optimized transition states are first order saddle points. However, the imaginary frequency at the B3LYP level is significantly smaller than at HF or MP2. Table 4 summarizes the calculated barrier heights and ...
II sem P and SP
... DIATOMIC MOLECULES: Molecular quantum numbers. Bonding and anti-bonding orbitals from LCAO’s. Explanation of bond order for N2 and O2 and their ions. Rotational spectra and the effect of isotopic substitution. Effect of nuclear spin functions on Raman rotation spectra of H2 (Fermion) and D2 (Boson). ...
... DIATOMIC MOLECULES: Molecular quantum numbers. Bonding and anti-bonding orbitals from LCAO’s. Explanation of bond order for N2 and O2 and their ions. Rotational spectra and the effect of isotopic substitution. Effect of nuclear spin functions on Raman rotation spectra of H2 (Fermion) and D2 (Boson). ...
PDF ∗ , 88K - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... 10.1021/ja016605s CCC: $22.00 © 2002 American Chemical Society ...
... 10.1021/ja016605s CCC: $22.00 © 2002 American Chemical Society ...
Theoretical modeling of x-ray and vibrational spectroscopies applied to liquid
... [4, 5] and are very popular today. All commonly used MD force fields, e.g. SPC/E and TIP4P, give structures that correspond to the standard picture - this is also the case for ab initio simulations where the forces are calculated with Density Functional Theory (DFT). X-ray and neutron diffraction have ...
... [4, 5] and are very popular today. All commonly used MD force fields, e.g. SPC/E and TIP4P, give structures that correspond to the standard picture - this is also the case for ab initio simulations where the forces are calculated with Density Functional Theory (DFT). X-ray and neutron diffraction have ...
Electron Induced Fluorescence Spectra of Methane
... Electron induced fluorescence is a tool to study the electronic states of the molecules by observing emission from excited atoms, molecules, or their fragments after impact of monoenergetic electrons. Electrons with well defined energy collide with molecules and excite their electronic, vibrational ...
... Electron induced fluorescence is a tool to study the electronic states of the molecules by observing emission from excited atoms, molecules, or their fragments after impact of monoenergetic electrons. Electrons with well defined energy collide with molecules and excite their electronic, vibrational ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.