040102IV&fluids 116KB Jan 14 2015 08:21:45 AM
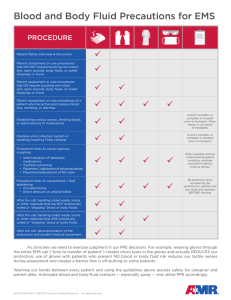
... many drops per ml does the typical microdrip tubing set have? ...
... many drops per ml does the typical microdrip tubing set have? ...
Central_Venous_Access
... rule out with a CXR. Requires a chest tube. More likely on left because of higher dome of left pleura. 2. Hemothorax from vascular injury 3. Hydrothorax from IV fluid administration into the pleural space ...
... rule out with a CXR. Requires a chest tube. More likely on left because of higher dome of left pleura. 2. Hemothorax from vascular injury 3. Hydrothorax from IV fluid administration into the pleural space ...
Section: 2-1
... 8. Lovenox is to be given subcutaneously only. DO NOT administer via IV or IM injection. EQUIPMENT: Alcohol prep pad Lovenox prefilled syringe (30 mg per 0.3 mL) Protamine Sulfate (antidote-give same dose as Lovenox), if ordered by physician PROCEDURE: 1. Adhere to Standard Precautions. 2. Identify ...
... 8. Lovenox is to be given subcutaneously only. DO NOT administer via IV or IM injection. EQUIPMENT: Alcohol prep pad Lovenox prefilled syringe (30 mg per 0.3 mL) Protamine Sulfate (antidote-give same dose as Lovenox), if ordered by physician PROCEDURE: 1. Adhere to Standard Precautions. 2. Identify ...
Parenteral Administration of Medication in Small
... A 22 to 25 gauge needle attached to a syringe is embedded in the muscle at a ______ angle. As with a SQ injection, the needle hub is checked for blood before administration of medication to make certain a vessel is not inadvertently penetrated. › How did we do this? ...
... A 22 to 25 gauge needle attached to a syringe is embedded in the muscle at a ______ angle. As with a SQ injection, the needle hub is checked for blood before administration of medication to make certain a vessel is not inadvertently penetrated. › How did we do this? ...
Surgical Checklist – Declaw with Alter
... Keeps blood pressure constant, making sure oxygen is delivered to all cells Provides access port in case emergency medications are needed ...
... Keeps blood pressure constant, making sure oxygen is delivered to all cells Provides access port in case emergency medications are needed ...
Blood and Body Fluid Precautions for EMS
... or other materials that are NOT extensively soiled or “dripping” blood or body fluids. ...
... or other materials that are NOT extensively soiled or “dripping” blood or body fluids. ...
IV THERAPY
... IVs are not a big problem usually unless the medication being administered is very irritant, such as certain chemotherapy and circulatory medicines. The intravenous infusion must be stopped, obviously, to avoid putting any more fluid or medication into the tissues. Another IV may need to be started ...
... IVs are not a big problem usually unless the medication being administered is very irritant, such as certain chemotherapy and circulatory medicines. The intravenous infusion must be stopped, obviously, to avoid putting any more fluid or medication into the tissues. Another IV may need to be started ...
1-3 - IV Therapy
... – Allows for IVP, a direct single dose – For the use of long-term continuous infusion (short-term during hospital stay) – PPN (peripheral parenteral nutrition) when limited nutritional therapy rather than total pareteral nutrition is needed. • Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) – given through a centr ...
... – Allows for IVP, a direct single dose – For the use of long-term continuous infusion (short-term during hospital stay) – PPN (peripheral parenteral nutrition) when limited nutritional therapy rather than total pareteral nutrition is needed. • Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) – given through a centr ...
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) - Catherine Heykoop
... DVT occurs when a thrombus forms in in one of the deep vein of the body, usually the leg. ...
... DVT occurs when a thrombus forms in in one of the deep vein of the body, usually the leg. ...
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion A branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO)
... degree of the macular edema leakage. Fundus photographs are often used to document findings and to allow interval management. When the blocked veins cover a large area, new abnormal vessels may grow on the retinal surface, which can bleed into the eye and cause floaters and further blurred vision. T ...
... degree of the macular edema leakage. Fundus photographs are often used to document findings and to allow interval management. When the blocked veins cover a large area, new abnormal vessels may grow on the retinal surface, which can bleed into the eye and cause floaters and further blurred vision. T ...
right patient | right time | right line
... of antibiotics. However, PIVs typically need to be replaced every couple days, usually due to performance failure, while midline catheters can provide access for several weeks (<30 days). Midline catheters are also ideal for patients that may require more than five days of intravenous therapy. A mid ...
... of antibiotics. However, PIVs typically need to be replaced every couple days, usually due to performance failure, while midline catheters can provide access for several weeks (<30 days). Midline catheters are also ideal for patients that may require more than five days of intravenous therapy. A mid ...
Peripheral vein cannulation
... hematoma formation. Larger veins are generally more easily cannulated and are preferable to smaller veins in the same region. Veins of the upper extremity are preferred due to the increased risk of thrombosis and thrombophlebitis with venous cannulation of the lower extremities. Whenever possible, a ...
... hematoma formation. Larger veins are generally more easily cannulated and are preferable to smaller veins in the same region. Veins of the upper extremity are preferred due to the increased risk of thrombosis and thrombophlebitis with venous cannulation of the lower extremities. Whenever possible, a ...
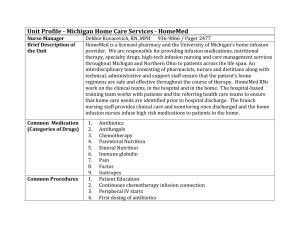
Unit Profile - Michigan Home Care Services - HomeMed
... technical, administrative and support staff ensure that the patient‘s home regimens are safe and effective throughout the course of therapy. HomeMed RNs work on the clinical teams, in the hospital and in the home. The hospital-based training team works with patients and the referring health care tea ...
... technical, administrative and support staff ensure that the patient‘s home regimens are safe and effective throughout the course of therapy. HomeMed RNs work on the clinical teams, in the hospital and in the home. The hospital-based training team works with patients and the referring health care tea ...
Central Venous Access Devices Central venous access device, or
... which is a long tube that threads up through a vein in your arm and into one of the large veins above your heart. After the PICC line is placed, you will have an x-ray so that the position of the PICC line can be checked. The PICC line will then be sutured into position, in order to keep it in place ...
... which is a long tube that threads up through a vein in your arm and into one of the large veins above your heart. After the PICC line is placed, you will have an x-ray so that the position of the PICC line can be checked. The PICC line will then be sutured into position, in order to keep it in place ...
IV Course for Marines
... – Allow the IV fluid to fill the line completely, eliminating any air within the line – Once the tubing is completely filled, clamp the line again by rotating the thumb clamp to the closed position – You are now ready to select an IV site ...
... – Allow the IV fluid to fill the line completely, eliminating any air within the line – Once the tubing is completely filled, clamp the line again by rotating the thumb clamp to the closed position – You are now ready to select an IV site ...
IV Course for Marines - Operational Medicine Medical
... – Allow the IV fluid to fill the line completely, eliminating any air within the line – Once the tubing is completely filled, clamp the line again by rotating the thumb clamp to the closed position – You are now ready to select an IV site ...
... – Allow the IV fluid to fill the line completely, eliminating any air within the line – Once the tubing is completely filled, clamp the line again by rotating the thumb clamp to the closed position – You are now ready to select an IV site ...
Pre-Cardioversion-Orders-Oct
... Insert intravenous catheter on either upper extremity and start 0.9% Normal Saline IV at 100ml/hour unless otherwise indicated, all intravenous fluids require extension tubing c aIV fluids _____________________________________ at______________ mL/hour Insert Saline Lock intravenous catheter on ei ...
... Insert intravenous catheter on either upper extremity and start 0.9% Normal Saline IV at 100ml/hour unless otherwise indicated, all intravenous fluids require extension tubing c aIV fluids _____________________________________ at______________ mL/hour Insert Saline Lock intravenous catheter on ei ...
Chapter 8
... naloxone, aspirin, and possibly others based on local protocol. AEMTs may administer intravenous (IV) fluids, including 5% dextrose in water (D5W), normal saline, and lactated Ringer’s solution. AEMTs may only administer medications and fluids when either directly ordered by medical control or a ...
... naloxone, aspirin, and possibly others based on local protocol. AEMTs may administer intravenous (IV) fluids, including 5% dextrose in water (D5W), normal saline, and lactated Ringer’s solution. AEMTs may only administer medications and fluids when either directly ordered by medical control or a ...
Intravenous infusions, Parenteral admixtures, and rate of flow
... Example: A medication order for a patient weighing 154 lb calls for 0.25 mg of amphotericin B (Antifungal) per kg of body weight to be added to 500 ml of 5% dextrose injection. If the amphotericin B is to be obtained from a constituted injection that contains 50mg/10ml, how many milliliters should b ...
... Example: A medication order for a patient weighing 154 lb calls for 0.25 mg of amphotericin B (Antifungal) per kg of body weight to be added to 500 ml of 5% dextrose injection. If the amphotericin B is to be obtained from a constituted injection that contains 50mg/10ml, how many milliliters should b ...
Pediatric Medication Calculation
... 1. Why a specific product is being given 2. A safe volume over a safe time has been ordered 3. The common side effects of giving the product • No solutions other than normal saline and 5% albumin should be in IV tubing used to administer blood products ...
... 1. Why a specific product is being given 2. A safe volume over a safe time has been ordered 3. The common side effects of giving the product • No solutions other than normal saline and 5% albumin should be in IV tubing used to administer blood products ...
Central Line Reference Guide - IV
... dressing age Confirmation of on going assessment Leads to faster treatment of complications Prevents bacteria from entering catheter ...
... dressing age Confirmation of on going assessment Leads to faster treatment of complications Prevents bacteria from entering catheter ...
outline3294
... A. The procedure for entering a vein with a needle or catheter B. Purpose 1. To draw blood from a donor or for laboratory testing 2. To administer fluids such as nutrients, drug and contrast mediums (such as sodium fluorescein) 3. To maintain an open vein in case of emergency C. Considerations for v ...
... A. The procedure for entering a vein with a needle or catheter B. Purpose 1. To draw blood from a donor or for laboratory testing 2. To administer fluids such as nutrients, drug and contrast mediums (such as sodium fluorescein) 3. To maintain an open vein in case of emergency C. Considerations for v ...
Intravenous therapy

Intravenous therapy (IV therapy or iv therapy in short) is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. Intravenous simply means ""within vein"". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals. It is commonly referred to as a drip because many systems of administration employ a drip chamber, which prevents air from entering the blood stream (air embolism), and allows an estimation of flow rate.Intravenous therapy may be used to correct electrolyte imbalances, to deliver medications, for blood transfusion or as fluid replacement to correct, for example, dehydration. Intravenous therapy can also be used for chemotherapy.Compared with other routes of administration, the intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver fluids and medications throughout the body. The bioavailability of the medication is 100% in IV therapy.