Exam 2 Study Guide Outline
... o Giffen Good (theoretical) Individual to market demand Gains from exchange o Consumer and Producer Surplus o Excise taxes and Deadweight Loss (Excess Burden of Tax) o Tax Revenue & elasticity o Tax Incidence (distribution of economic burden of tax) ...
... o Giffen Good (theoretical) Individual to market demand Gains from exchange o Consumer and Producer Surplus o Excise taxes and Deadweight Loss (Excess Burden of Tax) o Tax Revenue & elasticity o Tax Incidence (distribution of economic burden of tax) ...
International Trade
... • Modern Macro is “new.” • Before 1930s, the economy was thought to be primarily self-regulating (thought that markets would ‘clear’ by themselves). • Production and Unemployment in the Great Depression changed that view. • Production was extremely low. Employment was extremely low. • John Maynard ...
... • Modern Macro is “new.” • Before 1930s, the economy was thought to be primarily self-regulating (thought that markets would ‘clear’ by themselves). • Production and Unemployment in the Great Depression changed that view. • Production was extremely low. Employment was extremely low. • John Maynard ...
UZBEKISTAN UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 07.00 GMT, WEDNESDAY, 6 AUGUST 2014
... Slower money supply growth contributed to smaller price increases in 2013, but the inflation rate remained high at 12.1%, compared to 13.2% in 2012. Inflationary pressure was due to a weaker currency, import restrictions, an upward adjustment in administered prices, and higher public spending. ...
... Slower money supply growth contributed to smaller price increases in 2013, but the inflation rate remained high at 12.1%, compared to 13.2% in 2012. Inflationary pressure was due to a weaker currency, import restrictions, an upward adjustment in administered prices, and higher public spending. ...
Steady-State Growth Equilibrium
... forest of uplifted arms demanding work becomes ever thicker, while the arms themselves become ever thinner…" Hence the necessity of socialist revolution to overthrow the market economy and establish a truly human world with a fair-rather than an appallingly skewed--distribution of income. And Marx w ...
... forest of uplifted arms demanding work becomes ever thicker, while the arms themselves become ever thinner…" Hence the necessity of socialist revolution to overthrow the market economy and establish a truly human world with a fair-rather than an appallingly skewed--distribution of income. And Marx w ...
Economic Growth
... • What is capital deepening and how does it affect economic growth? • How does the savings rate help the economy to grow? • Why is technological progress important? ...
... • What is capital deepening and how does it affect economic growth? • How does the savings rate help the economy to grow? • Why is technological progress important? ...
Growth and Development
... Net investment adds to the capital stock, increasing potential GDP. Investment spending also adds to aggregate demand, but investment spending must increase from period to period if the potential income arising from increased capital is to be realized. “Balanced growth” is a rate of income growth wh ...
... Net investment adds to the capital stock, increasing potential GDP. Investment spending also adds to aggregate demand, but investment spending must increase from period to period if the potential income arising from increased capital is to be realized. “Balanced growth” is a rate of income growth wh ...
Economic Systems and Development
... Developing Countries • Type: minimal economic growth; high number of people living in poverty • Characteristics: low income & GDP per capita; low productivity; weak industry; many obstacles • Country Examples: most countries in the world; (Examples: Afghanistan, Cuba, Nicaragua, Guatemala, most Afr ...
... Developing Countries • Type: minimal economic growth; high number of people living in poverty • Characteristics: low income & GDP per capita; low productivity; weak industry; many obstacles • Country Examples: most countries in the world; (Examples: Afghanistan, Cuba, Nicaragua, Guatemala, most Afr ...
PDF Download
... smallest government deficits (less than 1 % of GDP on average during the period 1994 to 1999) were registered by Croatia, Slovenia, and Estonia. Estonia also did best in increasing its exports, export growth averaging 20%. Exports of the other CEE countries are also rising sharply. It is obvious tha ...
... smallest government deficits (less than 1 % of GDP on average during the period 1994 to 1999) were registered by Croatia, Slovenia, and Estonia. Estonia also did best in increasing its exports, export growth averaging 20%. Exports of the other CEE countries are also rising sharply. It is obvious tha ...
Why do Economies Grow?
... Determinants of Productivity • Factors of production determine productivity: ...
... Determinants of Productivity • Factors of production determine productivity: ...
CHINA UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 07.00 GMT, WEDNESDAY, 6 AUGUST 2014
... Economic growth could slightly moderate this year ...
... Economic growth could slightly moderate this year ...
Homework Quiz 7
... list 3 richest and 3 poorest economies in the world (per capita GDP), include numbers ...
... list 3 richest and 3 poorest economies in the world (per capita GDP), include numbers ...
Y1 Real GDP - Personal homepages
... How fast can the economy grow? • Mainstream view: 2.5% growth per year • Some even say 5% may be sustainable • Several nations have been able to double their GDP in less than 28 years • What are the implications for use of natural resources? • What would ecological economists say? ...
... How fast can the economy grow? • Mainstream view: 2.5% growth per year • Some even say 5% may be sustainable • Several nations have been able to double their GDP in less than 28 years • What are the implications for use of natural resources? • What would ecological economists say? ...
Chapter 25 Key Question Solutions
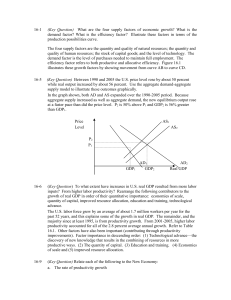
... 25-8 (Key Question) To what extent have increases in U.S. real GDP resulted from more labor inputs? From higher labor productivity? Rearrange the following contributors to the growth of real GDP in order of their quantitative importance: economies of scale, quantity of capital, improved resource all ...
... 25-8 (Key Question) To what extent have increases in U.S. real GDP resulted from more labor inputs? From higher labor productivity? Rearrange the following contributors to the growth of real GDP in order of their quantitative importance: economies of scale, quantity of capital, improved resource all ...
CAD - Bond
... are in conflict with the comparative advantages determined by their endowments They need subsidies, but these can’t be afforded, so governments use administrative measures (e.g. Monopolies, suppressed interest rates, overvalued currencies, price controls on inputs These controls then lead to sho ...
... are in conflict with the comparative advantages determined by their endowments They need subsidies, but these can’t be afforded, so governments use administrative measures (e.g. Monopolies, suppressed interest rates, overvalued currencies, price controls on inputs These controls then lead to sho ...
United States: class 1
... temporal comparisons: 50s and 60s vs. 70s and 80s cross-national comparisons: U.S. vs. other industrialized countries ...
... temporal comparisons: 50s and 60s vs. 70s and 80s cross-national comparisons: U.S. vs. other industrialized countries ...
Growth - Jubilee Debt Campaign
... afford to go on growing, particularly if we want to give people in poorer countries a chance of being able to at least meet their basic needs…Growth is a side issue. The end goal is about prosperity in terms of greater wellbeing, in terms of greater equality, in terms of having a cleaner environment ...
... afford to go on growing, particularly if we want to give people in poorer countries a chance of being able to at least meet their basic needs…Growth is a side issue. The end goal is about prosperity in terms of greater wellbeing, in terms of greater equality, in terms of having a cleaner environment ...
GROWTH, PRODUCTIVITY, AND THE WEALTH OF NATIONS
... • Predictions of long-term catastrophe were wrong – Increases in technology and capital overwhelmed diminishing marginal productivity of labor. ...
... • Predictions of long-term catastrophe were wrong – Increases in technology and capital overwhelmed diminishing marginal productivity of labor. ...
ch 9 sp 2017
... C. decreasing returns to scale. The five important sources of growth are (1) institutions with incentives compatible with growth; (2) technological development; (3) available resources; (4) capital accumulation; and (5) entrepreneurship. 6. (p. 184) A resource the United States lacked in the 20th Ce ...
... C. decreasing returns to scale. The five important sources of growth are (1) institutions with incentives compatible with growth; (2) technological development; (3) available resources; (4) capital accumulation; and (5) entrepreneurship. 6. (p. 184) A resource the United States lacked in the 20th Ce ...
16-1 (Key Question) What are the four supply factors of economic
... growth has grown substantially due to innovations using microchips, computers, new telecommunications devices and the Internet. All of these innovations describe features of what we call information technology, which connects information in all parts of the world with information seekers. New inform ...
... growth has grown substantially due to innovations using microchips, computers, new telecommunications devices and the Internet. All of these innovations describe features of what we call information technology, which connects information in all parts of the world with information seekers. New inform ...
Economic growth

Economic growth is the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy over time. It is conventionally measured as the percent rate of increase in real gross domestic product, or real GDP. Of more importance is the growth of the ratio of GDP to population (GDP per capita, which is also called per capita income). An increase in growth caused by more efficient use of inputs (such as physical capital, population, or territory) is referred to as intensive growth. GDP growth caused only by increases in the amount of inputs available for use is called extensive growth.In economics, ""economic growth"" or ""economic growth theory"" typically refers to growth of potential output, i.e., production at ""full employment"". As an area of study, economic growth is generally distinguished from development economics. The former is primarily the study of how countries can advance their economies. The latter is the study of the economic development process particularly in low-income countries.Growth is usually calculated in real terms – i.e., inflation-adjusted terms – to eliminate the distorting effect of inflation on the price of goods produced. Measurement of economic growth uses national income accounting. Since economic growth is measured as the annual percent change of gross domestic product (GDP), it has all the advantages and drawbacks of that measure.