is social capital really capital?
... Narayan and Pritchett (1997:3) define “capital” as something accumulated which contributes to higher income or better outcomes. The “something” is only described as horizontal connections and linkages without further definition. Then, they describe five processes in which social capital changes outc ...
... Narayan and Pritchett (1997:3) define “capital” as something accumulated which contributes to higher income or better outcomes. The “something” is only described as horizontal connections and linkages without further definition. Then, they describe five processes in which social capital changes outc ...
Social solidarities: the search for solidarity in
... order is at all possible given the scarcity of material resources. The answer of classical sociologists to this question revolved around the concept of solidarity. Their understanding of so ...
... order is at all possible given the scarcity of material resources. The answer of classical sociologists to this question revolved around the concept of solidarity. Their understanding of so ...
SOCIOLOGICAL THEORY AND THE PROBLEM OF COLLECTIVE
... Since the nineteenth century beginnings of sociological theory, there has been much attention paid to individuals as actors and to societies, systems and structures. This stems from a commitment to some underlying tenets of the Enlightenment, even though it is not necessarily acknowledged, and from ...
... Since the nineteenth century beginnings of sociological theory, there has been much attention paid to individuals as actors and to societies, systems and structures. This stems from a commitment to some underlying tenets of the Enlightenment, even though it is not necessarily acknowledged, and from ...
Test Bank for Sociology in Our Times, 9th
... A note left at the scene of a suicide expressed the victim’s concern that he felt little sense of moral guidance. He indicated that he was uncertain about what was right or wrong in today’s world. Using Emile Durkheim’s theory, sociologists might conclude that the suicide victim was feeling: a. b. c ...
... A note left at the scene of a suicide expressed the victim’s concern that he felt little sense of moral guidance. He indicated that he was uncertain about what was right or wrong in today’s world. Using Emile Durkheim’s theory, sociologists might conclude that the suicide victim was feeling: a. b. c ...
1 Educating the Nation: III. Social Mobility* In my first two addresses
... demands or even by political calculation, but rather by the spread of a democratic political discourse which held that all citizens deserved ‘the best’ education much as they deserved the best health care in a welfare state based on universal (or the maximum possible) provision; and that the power o ...
... demands or even by political calculation, but rather by the spread of a democratic political discourse which held that all citizens deserved ‘the best’ education much as they deserved the best health care in a welfare state based on universal (or the maximum possible) provision; and that the power o ...
Social economy and social entrepreneurship
... economy and social entrepreneurship, one could debate to no end on what the term ‘social’ means in each of these cases, what exactly is included or left out. This uncertainty not only poses conceptual problems in describing these phenomena, but also risks undermining the very important role that the ...
... economy and social entrepreneurship, one could debate to no end on what the term ‘social’ means in each of these cases, what exactly is included or left out. This uncertainty not only poses conceptual problems in describing these phenomena, but also risks undermining the very important role that the ...
Regional Differences in the Treatment of Karl Marx
... a people at a given time, it is necessary to trace its history to show how the particular form developed and then to relate it to other aspects of the sociocultural system within which it occurs. The emphasis tends to be upon the uniqueness of each historical period, rather than upon recurrent patte ...
... a people at a given time, it is necessary to trace its history to show how the particular form developed and then to relate it to other aspects of the sociocultural system within which it occurs. The emphasis tends to be upon the uniqueness of each historical period, rather than upon recurrent patte ...
Social Structure
... – The family, the most universal social institution, takes responsibility for raising the young and teaching them accepted norms and values. – The economic institution organizes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. – The political institution is the system of norms th ...
... – The family, the most universal social institution, takes responsibility for raising the young and teaching them accepted norms and values. – The economic institution organizes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. – The political institution is the system of norms th ...
The Second Road to Phenomenological Sociology
... of “Truth in the Religions: A Sociological and Psychological Approach” by W. Montgomery Watt, Berger used the phrase “the social construction of reality” (1964:292). Today, more than 40 years after this term was coined, it is in fashion to call a paper, dissertation or a book “The Social Constructio ...
... of “Truth in the Religions: A Sociological and Psychological Approach” by W. Montgomery Watt, Berger used the phrase “the social construction of reality” (1964:292). Today, more than 40 years after this term was coined, it is in fashion to call a paper, dissertation or a book “The Social Constructio ...
man and society
... explanation of the origin of society. According to it, society is not made but a spontaneous growth. It is the result of a gradual evolution. It is continuous development from unorganized to organize from less perfect to more perfect and various factors helped in its development from time to time. K ...
... explanation of the origin of society. According to it, society is not made but a spontaneous growth. It is the result of a gradual evolution. It is continuous development from unorganized to organize from less perfect to more perfect and various factors helped in its development from time to time. K ...
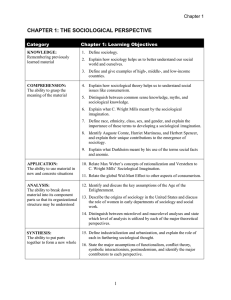
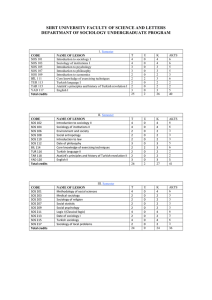
departmant of sociology undergraduate program
... environment and economic development, industry and environmental problems, the role of environment in settlement human health and environment, urbanization-environment relationship, environmental values in the formation of human society, environmental factor in the crowds, compliance with human-envi ...
... environment and economic development, industry and environmental problems, the role of environment in settlement human health and environment, urbanization-environment relationship, environmental values in the formation of human society, environmental factor in the crowds, compliance with human-envi ...
McNeill, F., and Dawson, M. (2014) Social solidarity, penal evolution
... work, the theorizing has tended to be Foucauldian (see Cohen, 1985; Simon, 1993; Robinson, 2002) or, more rarely, Marxist (see Young, 1976). We might crudely summarise the analyses as converging in a depiction of probation primarily as a disciplinary technology directed at the urban poor, at least w ...
... work, the theorizing has tended to be Foucauldian (see Cohen, 1985; Simon, 1993; Robinson, 2002) or, more rarely, Marxist (see Young, 1976). We might crudely summarise the analyses as converging in a depiction of probation primarily as a disciplinary technology directed at the urban poor, at least w ...
In The Construction of Social Reality and subsequent writings that
... within humanly created institutions. But these facts, that actions are done for reasons, and thus subject to constraints of rationality, and that sometimes the actions are done within human institutions, together imply that the behavior in question is performed under the presupposition of free will, ...
... within humanly created institutions. But these facts, that actions are done for reasons, and thus subject to constraints of rationality, and that sometimes the actions are done within human institutions, together imply that the behavior in question is performed under the presupposition of free will, ...