A
... to out-of-region buyers. As long as New England residents spend a substantial portion of their income on food, automobiles, appliances, fuels, and clothing produced outside the region, they cannot expect to increase regional income and employment unless they are successful in national and world mark ...
... to out-of-region buyers. As long as New England residents spend a substantial portion of their income on food, automobiles, appliances, fuels, and clothing produced outside the region, they cannot expect to increase regional income and employment unless they are successful in national and world mark ...
NBF Economic Research, IMF - Portfolio Management Association
... • March 11, upgrade its Term Securities Lending Facility, up to $200 billion of Treasury securities for 28 days against agency debt (Fannie Mae and • Freddie Mac) or AAA MBS. Increases currency swap with ECB and SNB. • March 16, cuts the discount rate by 25 bps after a Sunday meeting. Create a lendi ...
... • March 11, upgrade its Term Securities Lending Facility, up to $200 billion of Treasury securities for 28 days against agency debt (Fannie Mae and • Freddie Mac) or AAA MBS. Increases currency swap with ECB and SNB. • March 16, cuts the discount rate by 25 bps after a Sunday meeting. Create a lendi ...
Chapter 24 Measuring Domestic Output and National
... A. We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased by $100. B. We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased, but we cannot determine the amount. C. We can say with certainty that the nominal GDP has increased, but we can't say whether real GDP has increased or decreased. D. We need more ...
... A. We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased by $100. B. We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased, but we cannot determine the amount. C. We can say with certainty that the nominal GDP has increased, but we can't say whether real GDP has increased or decreased. D. We need more ...
Chapter 01 Powerpoint slides sample Chapter 1 Powerpoint
... Credited to James Buchanan (Nobel Laureate 1986) • Believed individuals self-interested in both private and public economic affairs • Gov’t just another venue through which to pursue economic self-interest • Buchanan’s Public Choice Theory adds political content to concept of individual decision-mak ...
... Credited to James Buchanan (Nobel Laureate 1986) • Believed individuals self-interested in both private and public economic affairs • Gov’t just another venue through which to pursue economic self-interest • Buchanan’s Public Choice Theory adds political content to concept of individual decision-mak ...
Chapter_25_26
... New growth theories also emphasize the possibility that each new increment of investment is more productive than the last. • contrasts with the Neoclassical assumption of diminishing marginal returns. The sources of increasing returns usually fall into one of two categories: ...
... New growth theories also emphasize the possibility that each new increment of investment is more productive than the last. • contrasts with the Neoclassical assumption of diminishing marginal returns. The sources of increasing returns usually fall into one of two categories: ...
Understanding China`s Economic Transformation
... about organizing production. As Lord Keynes once observed (so we are told), “When the facts change, I change my mind. What do you do, sir?” Deng’s lack of interest in the color of mice-catching cats is emblematic here. We see that the core of pragmatism is concerned with purpose. The pragmatist will ...
... about organizing production. As Lord Keynes once observed (so we are told), “When the facts change, I change my mind. What do you do, sir?” Deng’s lack of interest in the color of mice-catching cats is emblematic here. We see that the core of pragmatism is concerned with purpose. The pragmatist will ...
View/Open
... Results at the macro and micro levels reveal that although the impact of the crisis was not as large as initially expected, it has affected some specific sectors in the economy and in varying degrees. For instance, workers in the manufacturing sector are most likely to be displaced or could experien ...
... Results at the macro and micro levels reveal that although the impact of the crisis was not as large as initially expected, it has affected some specific sectors in the economy and in varying degrees. For instance, workers in the manufacturing sector are most likely to be displaced or could experien ...
Economic Reforms and Agriculture in Bangladesh: Assessment of Impacts using Economy‐wide Simulation Models
... • A rise in subsidies to agricultural sectors would provide extra incentives for investing in agriculture. • However, it should also be kept in mind that such subsidies put heavy burden on government’s exchequer. Therefore, phased reduction of such subsidies would be warranted. • To be effectiv ...
... • A rise in subsidies to agricultural sectors would provide extra incentives for investing in agriculture. • However, it should also be kept in mind that such subsidies put heavy burden on government’s exchequer. Therefore, phased reduction of such subsidies would be warranted. • To be effectiv ...
Environmental Kuznets Curve
... characteristics correlated with both income and pollution levels, the most important being environmental regulatory stringency. The EKC pattern does not provide evidence of market failures or efficient policies in rich or poor countries. Rather, there are multiple underlying mechanisms, some of whic ...
... characteristics correlated with both income and pollution levels, the most important being environmental regulatory stringency. The EKC pattern does not provide evidence of market failures or efficient policies in rich or poor countries. Rather, there are multiple underlying mechanisms, some of whic ...
Essay - Globalisation Effects on China
... winners, such as China and Australia, others have been pushed to the margins, such as Zimbabwe. An international convergence of economic performance is shown through China’s ‘catch up’ against the GDP of the developing world. That is, China’s economy, measured on a Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) basi ...
... winners, such as China and Australia, others have been pushed to the margins, such as Zimbabwe. An international convergence of economic performance is shown through China’s ‘catch up’ against the GDP of the developing world. That is, China’s economy, measured on a Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) basi ...
The Solow Model of Economic Growth
... Growth vs. Income • Poor (developing) countries (low capital/income ratio) are below their eventual steady state. Therefore, these countries should be growing rapidly • Wealthy (developed) countries (high capital/labor ratio) are at or above their eventual steady state. Therefore, these countries w ...
... Growth vs. Income • Poor (developing) countries (low capital/income ratio) are below their eventual steady state. Therefore, these countries should be growing rapidly • Wealthy (developed) countries (high capital/labor ratio) are at or above their eventual steady state. Therefore, these countries w ...
Slide 1
... Historical patterns show protracted period of sluggishness following booms Sources: IMF, International Financial Statistics; and staff calculations. Note: Unweighted average of real credit growth around boom years identified between 1983 and 2008. Credit was deflated by the CPI index. Boom year in s ...
... Historical patterns show protracted period of sluggishness following booms Sources: IMF, International Financial Statistics; and staff calculations. Note: Unweighted average of real credit growth around boom years identified between 1983 and 2008. Credit was deflated by the CPI index. Boom year in s ...
economic reforms and human capital development
... additional input in the production of goods, while retaining the other features of the neoclassical growth model. In the model, the labour force can accumulate human capital, which is then used together with physical capital to generate the output of the economy. In one version of the model, human c ...
... additional input in the production of goods, while retaining the other features of the neoclassical growth model. In the model, the labour force can accumulate human capital, which is then used together with physical capital to generate the output of the economy. In one version of the model, human c ...
Unit 4: Macroeconomic Statistics and Analysis
... accepted jobs with lower wages out of necessity are not figured into the percentage and therefore undercount the actual rate of unemployed workers. Others argue that the numbers are too high. These people argue that many people work in what is known as the underground economy. Workers who work “unde ...
... accepted jobs with lower wages out of necessity are not figured into the percentage and therefore undercount the actual rate of unemployed workers. Others argue that the numbers are too high. These people argue that many people work in what is known as the underground economy. Workers who work “unde ...
Economics “Ask the Instructor” Clip 76 Transcript
... A given government expenditure might cause private-sector spending to decrease if what is provided by government is exactly what households or businesses had planned to purchase for themselves. For example, suppose that you were intending to buy a pair of brown shoes, and government buys the shoes a ...
... A given government expenditure might cause private-sector spending to decrease if what is provided by government is exactly what households or businesses had planned to purchase for themselves. For example, suppose that you were intending to buy a pair of brown shoes, and government buys the shoes a ...
III. Growth and inflation: drivers and prospects
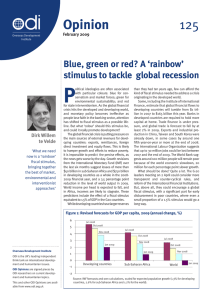
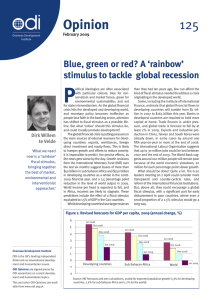
... Restoring sustainable global growth poses significant challenges. In crisis-hit countries, it is unrealistic to expect the level of output to return to its pre-crisis trend. This would require the growth rate to exceed the pre-crisis average for several years. Historical evidence shows that this rar ...
... Restoring sustainable global growth poses significant challenges. In crisis-hit countries, it is unrealistic to expect the level of output to return to its pre-crisis trend. This would require the growth rate to exceed the pre-crisis average for several years. Historical evidence shows that this rar ...
Juraj Dobrila University of Pula
... link between labour productivity and tourism could happen because stronger tourism activity causes attraction of employment. As we know tourism is a traditional service & labour intensive sector, and in nature it is much less productive than a various manufacturing production. In generally, overall ...
... link between labour productivity and tourism could happen because stronger tourism activity causes attraction of employment. As we know tourism is a traditional service & labour intensive sector, and in nature it is much less productive than a various manufacturing production. In generally, overall ...
Productivity in the National Health Service
... outputs are always being introduced, while others are phased out. Obviously, no index of total productivity could be compiled using the ratio of price weighted outputs on the LHS of (1) to the cost-weighted inputs on the RHS of (1) because the index would always be unity, or 100 in index terminology ...
... outputs are always being introduced, while others are phased out. Obviously, no index of total productivity could be compiled using the ratio of price weighted outputs on the LHS of (1) to the cost-weighted inputs on the RHS of (1) because the index would always be unity, or 100 in index terminology ...
Transformation in economics
Transformation in economics refers to a long-term change in dominant economic activity in terms of prevailing relative engagement or employment of able individuals.Human economic systems undergo a number of deviations and departures from the ""normal"" state, trend or development. Among them are Disturbance (short-term disruption, temporary disorder), Perturbation (persistent or repeated divergence, predicament, decline or crisis), Deformation (damage, regime change, loss of self-sustainability, distortion), Transformation (long-term change, restructuring, conversion, new “normal”) and Renewal (rebirth, transmutation, corso-ricorso, renaissance, new beginning).Transformation is a unidirectional and irreversible change in dominant human economic activity (economic sector). Such change is driven by slower or faster continuous improvement in sector productivity growth rate. Productivity growth itself is fueled by advances in technology, inflow of useful innovations, accumulated practical knowledge and experience, levels of education, viability of institutions, quality of decision making and organized human effort. Individual sector transformations are the outcomes of human socio-economic evolution.Human economic activity has so far undergone at least four fundamental transformations:From nomadic hunting and gathering (H/G) to localized agricultureFrom localized agriculture (A) to internationalized industryFrom international industry (I) to global servicesFrom global services (S) to public sector (including government, welfare and unemployment, GWU)This evolution naturally proceeds from securing necessary food, through producing useful things, to providing helpful services, both private and public (See H/G→A→I→S→GWU sequence in Fig. 1). Accelerating productivity growth rates speed up the transformations, from millennia, through centuries, to decades of the recent era. It is this acceleration which makes transformation relevant economic category of today, more fundamental in its impact than any recession, crisis or depression. The evolution of four forms of capital (Indicated in Fig. 1) accompanies all economic transformations.Transformation is quite different from accompanying cyclical recessions and crises, despite the similarity of manifested phenomena (unemployment, technology shifts, socio-political discontent, bankruptcies, etc.). However, the tools and interventions used to combat crisis are clearly ineffective for coping with non-cyclical transformations. The problem is whether we face a mere crisis or a fundamental transformation (globalization→relocalization).