Adding or Subtracting Fractions
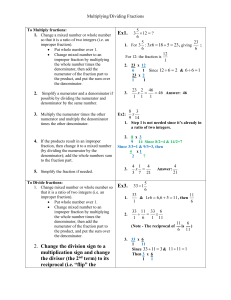
... Notice that the factor that we multiple by has the value of one so the value of the original fraction remains unchanged. We can also divide numerator and denominator by like factors to reduce the fraction to lower terms. If we divide by all the common factors the fraction will be in lowest terms. Ex ...
... Notice that the factor that we multiple by has the value of one so the value of the original fraction remains unchanged. We can also divide numerator and denominator by like factors to reduce the fraction to lower terms. If we divide by all the common factors the fraction will be in lowest terms. Ex ...
Text (PDF format)
... 47. Show that by removing two white squares and two black squares from an 8 × 8 checkerboard (colored as in the text) you can make it impossible to tile the remaining squares using dominoes. ∗ 48. Find all squares, if they exist, on an 8 × 8 checkerboard such that the board obtained by removing one ...
... 47. Show that by removing two white squares and two black squares from an 8 × 8 checkerboard (colored as in the text) you can make it impossible to tile the remaining squares using dominoes. ∗ 48. Find all squares, if they exist, on an 8 × 8 checkerboard such that the board obtained by removing one ...
2-1 - Net Start Class
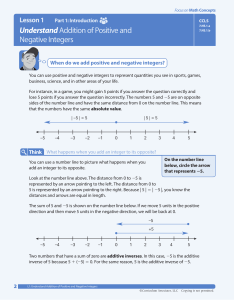
... numbers and their opposites. By using integers, you can express elevations above, below, and at sea level. Sea level has an elevation of 0 feet. ...
... numbers and their opposites. By using integers, you can express elevations above, below, and at sea level. Sea level has an elevation of 0 feet. ...
Division by zero
In mathematics, division by zero is division where the divisor (denominator) is zero. Such a division can be formally expressed as a/0 where a is the dividend (numerator). In ordinary arithmetic, the expression has no meaning, as there is no number which, multiplied by 0, gives a (assuming a≠0), and so division by zero is undefined. Since any number multiplied by zero is zero, the expression 0/0 also has no defined value and is called an indeterminate form. Historically, one of the earliest recorded references to the mathematical impossibility of assigning a value to a/0 is contained in George Berkeley's criticism of infinitesimal calculus in The Analyst (""ghosts of departed quantities"").There are mathematical structures in which a/0 is defined for some a such as in Riemann spheres and real projective lines; however, such structures cannot satisfy every ordinary rule of arithmetic (the field axioms).In computing, a program error may result from an attempt to divide by zero. Depending on the programming environment and the type of number (e.g. floating point, integer) being divided by zero, it may generate positive or negative infinity by the IEEE 754 floating point standard, generate an exception, generate an error message, cause the program to terminate, or result in a special not-a-number value.