biod10
... have done rather well for itself over the last billion years. The answer is simple; we want to use the ecosystem’s resources and still have them available to us in the future. Indeed, we have vastly increased the land’s natural carrying capacity through our management, but at what cost? The basic pr ...
... have done rather well for itself over the last billion years. The answer is simple; we want to use the ecosystem’s resources and still have them available to us in the future. Indeed, we have vastly increased the land’s natural carrying capacity through our management, but at what cost? The basic pr ...
Biodiversity and Sustainability
... How many species of plants and animals do you think there are in the world? Do you agree or disagree with the statement below and why? “If humans don’t have any use for a plant or an animal, then it might as well not exist in the first place.” ...
... How many species of plants and animals do you think there are in the world? Do you agree or disagree with the statement below and why? “If humans don’t have any use for a plant or an animal, then it might as well not exist in the first place.” ...
MS Word doc
... The South African Network for Coastal and Oceanic Research (SANCOR) has been intensely involved in marine research and management for over thirty years and has a proud record of addressing the country’s needs including the development of two phases of the national Sea and Coast Programme, which has ...
... The South African Network for Coastal and Oceanic Research (SANCOR) has been intensely involved in marine research and management for over thirty years and has a proud record of addressing the country’s needs including the development of two phases of the national Sea and Coast Programme, which has ...
Relationships Within Ecosystems
... competition demand for resources, such as food, water, and shelter, in short supply in a community ...
... competition demand for resources, such as food, water, and shelter, in short supply in a community ...
16-6 what is convection? r"
... Differences in density within a gas or liquid can cause convection currents within the gas or liquid. Under Earth's crust is a thick layer of rock called the mantle. The part of the mantle closest to Earth's core acts like a thick, hot liquid. The part of the mantle that is farthest from the core ,r ...
... Differences in density within a gas or liquid can cause convection currents within the gas or liquid. Under Earth's crust is a thick layer of rock called the mantle. The part of the mantle closest to Earth's core acts like a thick, hot liquid. The part of the mantle that is farthest from the core ,r ...
The effects of interaction of biotic and abiotic factors
... strongly influenced by snow melting, permafrost thawing, leaf development (Uchida et al. 2010), leaf senescence and soil freezing (Christiansen et al. 2012). The transition between late spring/early summer, at the onset of the growing season, is important because ecosystems shift from low CO2 releas ...
... strongly influenced by snow melting, permafrost thawing, leaf development (Uchida et al. 2010), leaf senescence and soil freezing (Christiansen et al. 2012). The transition between late spring/early summer, at the onset of the growing season, is important because ecosystems shift from low CO2 releas ...
Section 1: Developing a Theory Key Ideas • Why is evolutionary
... Is evolution the survival of the fittest? Natural selection can act only on the heritable variation that exists in a population. Chance variations do not always provide the best adaptation for a given time and place. So, evolution does not always produce the “fittest” forms, just those that “fit” we ...
... Is evolution the survival of the fittest? Natural selection can act only on the heritable variation that exists in a population. Chance variations do not always provide the best adaptation for a given time and place. So, evolution does not always produce the “fittest” forms, just those that “fit” we ...
Environment Module 1_Ecological concepts
... These mineral nutrients are always in circulation moving from non-living to living and then back to non-living components of ecosystem in more or less circular fashion. ...
... These mineral nutrients are always in circulation moving from non-living to living and then back to non-living components of ecosystem in more or less circular fashion. ...
Ecotope - Laboratory for Anthropogenic Landscape Ecology
... Like ecosystems, ecotopes are identified using relatively flexible criteria. In the case of ecotopes, by criteria defined within a specific ecological mapping and classification system. However, just as ecosystems are defined by the interaction of biotic and abiotic components, ecotope classificatio ...
... Like ecosystems, ecotopes are identified using relatively flexible criteria. In the case of ecotopes, by criteria defined within a specific ecological mapping and classification system. However, just as ecosystems are defined by the interaction of biotic and abiotic components, ecotope classificatio ...
SURFACE WATER
... b. may have white water rapids and waterfalls c. high level of energy d. erodes bed more than banks e. few tributaries and usually carries a small volume of water 2. mature rivers = curving stream that flows down a gradual slope and erodes its sides a. well established tributaries and carries more w ...
... b. may have white water rapids and waterfalls c. high level of energy d. erodes bed more than banks e. few tributaries and usually carries a small volume of water 2. mature rivers = curving stream that flows down a gradual slope and erodes its sides a. well established tributaries and carries more w ...
EOG Review Booklet
... of a gas. A precipitate is a solid that forms from mixing two liquids. The production of a gas can be seen as bubbles. Freezing or boiling a substance, however, are physical changes. In every case, a chemical change has occurred if the identity (molecular structure) of a substance has changed. If th ...
... of a gas. A precipitate is a solid that forms from mixing two liquids. The production of a gas can be seen as bubbles. Freezing or boiling a substance, however, are physical changes. In every case, a chemical change has occurred if the identity (molecular structure) of a substance has changed. If th ...
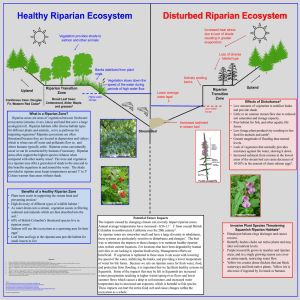
What is a Riparian Zone?
... Annual average temperatures have increased ~0.56-1.1°C from coastal British Columbia to northwestern California over the 20th century5. As riparian zones are somewhat small and have a large diversity in inhabitants, these systems are particularly sensitive to disturbance and changes7. The best way t ...
... Annual average temperatures have increased ~0.56-1.1°C from coastal British Columbia to northwestern California over the 20th century5. As riparian zones are somewhat small and have a large diversity in inhabitants, these systems are particularly sensitive to disturbance and changes7. The best way t ...
4. alpine and meadow ecosystems
... Decreased snowpacks and the expected expansion of forests into higher altitudes threaten species that rely on the cold, rocky, and open terrain of the alpine region for survival. However, climate is not the only limiting factor of tree growth into alpine areas, the rocky terrain of the alpine provid ...
... Decreased snowpacks and the expected expansion of forests into higher altitudes threaten species that rely on the cold, rocky, and open terrain of the alpine region for survival. However, climate is not the only limiting factor of tree growth into alpine areas, the rocky terrain of the alpine provid ...
3 - Greene ESC
... how organisms are related with species being the most fundamental unit of the classification system. Related how biologists arrange organisms into a hierarch of groups and subgroups based on similarities and differences that reflect their evolutionary relationships. 13. Explain that the variation of ...
... how organisms are related with species being the most fundamental unit of the classification system. Related how biologists arrange organisms into a hierarch of groups and subgroups based on similarities and differences that reflect their evolutionary relationships. 13. Explain that the variation of ...
uncorrected page proofs - Oxford University Press
... live in nests. You may have seen the massive termite mounds in Kakadu National Park in the Northern Territory. Termites also have microorganisms that live in their gut, which break down the cellulose of plant material such as grasses, plants and wood. Scientists have estimated that termites recycle ...
... live in nests. You may have seen the massive termite mounds in Kakadu National Park in the Northern Territory. Termites also have microorganisms that live in their gut, which break down the cellulose of plant material such as grasses, plants and wood. Scientists have estimated that termites recycle ...
6 Cell Respiration and Gas Exchange
... binding of O2 to 1 subunit induces remaining subunits to change shape slightly increasing affinity for O2 ...
... binding of O2 to 1 subunit induces remaining subunits to change shape slightly increasing affinity for O2 ...
Theoretical Predictions of Body Tissue and Blood Temperature
... Understanding the thermal response of the human body under various environmental and thermal stress conditions is of growing importance. Calculation of the core body temperature and the survivability of the body during immersion in cold water require detailed modeling of both the body tissue and the ...
... Understanding the thermal response of the human body under various environmental and thermal stress conditions is of growing importance. Calculation of the core body temperature and the survivability of the body during immersion in cold water require detailed modeling of both the body tissue and the ...
Purple packet-Changes over Time/Evolution (PDF
... to determine the age of the fossil. The absolute age of the fossil can be determined though radiometric dating and determining the layer of rock in which the fossil was found. Older layers are found deeper within the earth than newer layers. The age and morphologies (appearances) of fossils can be u ...
... to determine the age of the fossil. The absolute age of the fossil can be determined though radiometric dating and determining the layer of rock in which the fossil was found. Older layers are found deeper within the earth than newer layers. The age and morphologies (appearances) of fossils can be u ...
Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecology - The University of Tennessee
... Derived from the Greek work oikos, meaning house or home, ecology is concerned with plants and animals in their homes or habitats, their interrelationships and the environmental factors that affect them. By understanding ecological principles, we gain a better understanding of the earth and how plan ...
... Derived from the Greek work oikos, meaning house or home, ecology is concerned with plants and animals in their homes or habitats, their interrelationships and the environmental factors that affect them. By understanding ecological principles, we gain a better understanding of the earth and how plan ...
General Biology II Course Outcome Summary Course Information
... Learning Objectives a. Apply scientific nomenclature to name organisms b. Utilize taxonomy to classify organisms c. Read and interpret a phylogenetic tree d. Describe the three domain system and characteristics of each Describe organisms from the domains Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives a. D ...
... Learning Objectives a. Apply scientific nomenclature to name organisms b. Utilize taxonomy to classify organisms c. Read and interpret a phylogenetic tree d. Describe the three domain system and characteristics of each Describe organisms from the domains Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives a. D ...
Nervous tissue
... 3. What is a tissue & what are the 4 types? 4. What is metabolism? 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 types of thermoregulation? 7. How do organisms exchange heat with their environment? 8. How can organisms exchange heat within their bodies? 9. How do we achieve homeosta ...
... 3. What is a tissue & what are the 4 types? 4. What is metabolism? 5. What is homeostasis & how is it achieved? 6. What are the 2 types of thermoregulation? 7. How do organisms exchange heat with their environment? 8. How can organisms exchange heat within their bodies? 9. How do we achieve homeosta ...
Strand 4 Concept 2: HEREDITY (Life Science)
... PO #: 4: Compare the symbiotic and competitive relationships in organisms within an ecosystem. 4. Which is an example of symbiosis? A. two animals compete for food D. two animals help each other find food B. a lion preys on an antelope C. a plant loses its leaves 5. Honeybees move from one flower to ...
... PO #: 4: Compare the symbiotic and competitive relationships in organisms within an ecosystem. 4. Which is an example of symbiosis? A. two animals compete for food D. two animals help each other find food B. a lion preys on an antelope C. a plant loses its leaves 5. Honeybees move from one flower to ...
Land Use Element
... LU225 Regulate development in and near designated fish and wildlife habitat conservation areas in order to protect the remaining native wildlife species and significant fish populations, especially salmonids. LU226 Whenever possible((, maintain in their natural or native state those areas that conta ...
... LU225 Regulate development in and near designated fish and wildlife habitat conservation areas in order to protect the remaining native wildlife species and significant fish populations, especially salmonids. LU226 Whenever possible((, maintain in their natural or native state those areas that conta ...
Intro to Wildlife Management
... Establishing open, grassy areas around wetlands Planting millet, wild rice and other aquatic plants in wetlands Providing artificial nesting sites (wood duck boxes, old tires and islands surrounded by open water) • Preventing pollution of water from agriculture, industry and domestic waste. ...
... Establishing open, grassy areas around wetlands Planting millet, wild rice and other aquatic plants in wetlands Providing artificial nesting sites (wood duck boxes, old tires and islands surrounded by open water) • Preventing pollution of water from agriculture, industry and domestic waste. ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.