Ecology
... deer, mice, raccoons, bacteria, mushrooms, & ferns or Humans that form a community with deer that live here in the ecosystem Batesville. ...
... deer, mice, raccoons, bacteria, mushrooms, & ferns or Humans that form a community with deer that live here in the ecosystem Batesville. ...
Name Test Date___________ Ecology Notes – Chapters 3,4,5,6
... E. Ecological Pyramids – diagrams that show the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Ecologists recognize three types of ecological pyramids…. 1. Energy Pyramid – there is no limit to the # of trophic levels that a food chain can su ...
... E. Ecological Pyramids – diagrams that show the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food chain or food web. Ecologists recognize three types of ecological pyramids…. 1. Energy Pyramid – there is no limit to the # of trophic levels that a food chain can su ...
ecosystems
... What organisms are decomposers in most ecosystems? Fungi and Bacteria What do the decomposers do? ...
... What organisms are decomposers in most ecosystems? Fungi and Bacteria What do the decomposers do? ...
Time to model all life on Earth - Department of Mathematics and
... millions) of birds, mammals, plants and bacteria. Ecologists have also mathematically determined numerous ‘rules of existence’ for some organisms, such as that an animal’s metabolic rate is proportional to its mass raised to a power of around 0.70 (ref. 5). ...
... millions) of birds, mammals, plants and bacteria. Ecologists have also mathematically determined numerous ‘rules of existence’ for some organisms, such as that an animal’s metabolic rate is proportional to its mass raised to a power of around 0.70 (ref. 5). ...
ecology - benanbiology
... reduction with movement up the trophic levels • The units for pyramids of biomass are: dry weight of organic matter (per square metre) • This shows the amount of energy (in kiloJoules [kJ]) present at each trophic level • The full units for a pyramid of energy are: kJ m2 year-1 (sometimes kcal m-2 y ...
... reduction with movement up the trophic levels • The units for pyramids of biomass are: dry weight of organic matter (per square metre) • This shows the amount of energy (in kiloJoules [kJ]) present at each trophic level • The full units for a pyramid of energy are: kJ m2 year-1 (sometimes kcal m-2 y ...
learn the importance of recording data in a field - Build-A
... the effort to compare and contrast their findings with those of other students SC.5.N.1.1 Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring t ...
... the effort to compare and contrast their findings with those of other students SC.5.N.1.1 Define a problem, use appropriate reference materials to support scientific understanding, plan and carry out scientific investigations of various types such as: systematic observations, experiments requiring t ...
1.8_Evolution
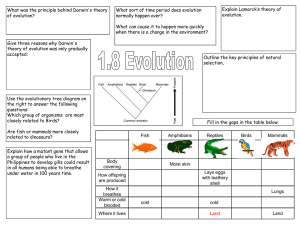
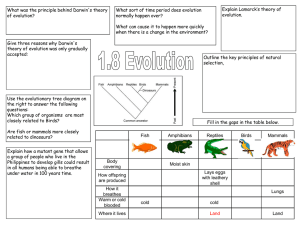
... What was the principle behind Darwin's theory of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms ...
... What was the principle behind Darwin's theory of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms ...
File
... What was the principle behind Darwin's theory of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms ...
... What was the principle behind Darwin's theory of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms ...
Animals as Environmental Sentinels of Human Pollution
... “...organisms whose known characteristics can be measured to assess the extent of environmental…implications…and to provide early warning of those implications.” ...
... “...organisms whose known characteristics can be measured to assess the extent of environmental…implications…and to provide early warning of those implications.” ...
Spring Final Review PP
... glacial retreat, ocean acidification, and an increase in extreme weather events are all consequences of global warming. ...
... glacial retreat, ocean acidification, and an increase in extreme weather events are all consequences of global warming. ...
Historical Range of Variability Revisited
... conditions without any explicit prescription for how that body of knowledge should be applied to land management decisions. HRV concepts are applicable to most management goals and outcomes because of three premises that are well supported by theory and practice: ...
... conditions without any explicit prescription for how that body of knowledge should be applied to land management decisions. HRV concepts are applicable to most management goals and outcomes because of three premises that are well supported by theory and practice: ...
CHAPTER 15
... b. Competition happens whenever two or more organisms need the same thing, which is in short supply. […] Plants compete for light, root space, and sometimes for water and minerals from the soil. Animals compete for food, and a place to live and reproduce. Competition between living organisms only ha ...
... b. Competition happens whenever two or more organisms need the same thing, which is in short supply. […] Plants compete for light, root space, and sometimes for water and minerals from the soil. Animals compete for food, and a place to live and reproduce. Competition between living organisms only ha ...
Miller Review Chapter 10 Chapter 10: Sustainability Terrestrial
... 1. Downside – with only one or two tree species they are much less biologically diverse and less sustainable than old-growth and second-growth forest because they violate nature’s biodiversity principal of sustainability a. Do NOT provide the wildlife habitats and ecosystem services such as water st ...
... 1. Downside – with only one or two tree species they are much less biologically diverse and less sustainable than old-growth and second-growth forest because they violate nature’s biodiversity principal of sustainability a. Do NOT provide the wildlife habitats and ecosystem services such as water st ...
and non-living things (abiotic factors)
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
Ecology Notes
... in water as dissolved CO2 and as HCO3- ions • CO2 is used by algae and aquatic plants for photosynthesis ...
... in water as dissolved CO2 and as HCO3- ions • CO2 is used by algae and aquatic plants for photosynthesis ...
Chapter 9 Surface Water
... Chapter 9 – Surface Water Chapter 10 – Groundwater Chapter 15 – Earth’s Oceans Tentative Test Date : ...
... Chapter 9 – Surface Water Chapter 10 – Groundwater Chapter 15 – Earth’s Oceans Tentative Test Date : ...
A woodland ecosystem - Forest of Avon Trust
... compete for food: the squirrels feed on acorns, while the tits feed on moth larvae. The two species occupy different niches within the oak ecosystem. ...
... compete for food: the squirrels feed on acorns, while the tits feed on moth larvae. The two species occupy different niches within the oak ecosystem. ...
Ecosystems - Selwyn 5th Grade Page
... rises, saltwater is brought into the estuary. Freshwater comes down the rivers and creeks and mixes with this saltwater. Plants found in estuaries need to be adapted to salty conditions Some plants, like pickle weed, can absorb the salt water and store the salt in special compartments, called vacuol ...
... rises, saltwater is brought into the estuary. Freshwater comes down the rivers and creeks and mixes with this saltwater. Plants found in estuaries need to be adapted to salty conditions Some plants, like pickle weed, can absorb the salt water and store the salt in special compartments, called vacuol ...
File
... – Released and/or escaped pets Problems with invasive species: – Prey on native species – Outcompete native species for resources • Food and space • Can lead to extinction of native species – Introduce new pathogens/diseases to native species that have never been exposed to them – Toxic to native sp ...
... – Released and/or escaped pets Problems with invasive species: – Prey on native species – Outcompete native species for resources • Food and space • Can lead to extinction of native species – Introduce new pathogens/diseases to native species that have never been exposed to them – Toxic to native sp ...
Available
... 2) Biotic Substances (Living Components): This is indeed the trophic structure of any ecosystem, where living organisms are distinguished on the basis of their nutritional relationships. From this trophic (nutritional) standpoint, an ecosystem has two components: (a) Autotrophic Component of Produce ...
... 2) Biotic Substances (Living Components): This is indeed the trophic structure of any ecosystem, where living organisms are distinguished on the basis of their nutritional relationships. From this trophic (nutritional) standpoint, an ecosystem has two components: (a) Autotrophic Component of Produce ...
Principles of Ecology
... Productivity is usually measured as biomass (dry weight of organic matter) per unit area per a specified time interval, e.g. kg/m2/yr The trophic structure of an ecosystem is often represented by an ecological pyramid, with the primary producers at the base and the other levels above Most of the foo ...
... Productivity is usually measured as biomass (dry weight of organic matter) per unit area per a specified time interval, e.g. kg/m2/yr The trophic structure of an ecosystem is often represented by an ecological pyramid, with the primary producers at the base and the other levels above Most of the foo ...
Jeffrey Park, Yale Institute for Biospheric Studies
... Evolution produced more than one chemical pathway to photosynthesis, and each has a different preference for light over heavy carbon atoms. One can trace the encroachment of grasses, which use a geologically recent pathway to photosynthesis, into regions of forest and shrubland, whose plants use an ...
... Evolution produced more than one chemical pathway to photosynthesis, and each has a different preference for light over heavy carbon atoms. One can trace the encroachment of grasses, which use a geologically recent pathway to photosynthesis, into regions of forest and shrubland, whose plants use an ...
Ecology
... cows and eat the insects disturbed by the walking cows. Cowbirds have an unusual method for reproducing. The brown-headed cowbird goes to the nest of a different bird species, such as a red-wing blackbird. The cowbird rolls one of the blackbird’s eggs out of the nest and lays its own egg in place. T ...
... cows and eat the insects disturbed by the walking cows. Cowbirds have an unusual method for reproducing. The brown-headed cowbird goes to the nest of a different bird species, such as a red-wing blackbird. The cowbird rolls one of the blackbird’s eggs out of the nest and lays its own egg in place. T ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.