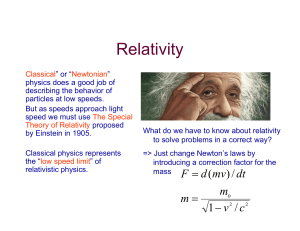
In-Class Examples: Elastic Potential Energy and Non
... against 2 rubber bands. It takes a force of 30 N to stretch the bands 1.0 cm.
a. What is the potential energy stored in the bands when a 50.0 g stone is
placed in the cup and pulled back 0.20 m from the equilibrium position?
...
Variable speed of light
Variable speed of light (VSL) is a hypothesis that states that the speed of light, usually denoted by c, may be a function of space and time. Variable speed of light occurs in some situations of classical physics as equivalent formulations of accepted theories, but also in various alternative theories of gravitation and cosmology, many of them non-mainstream. In classical physics, the refractive index describes how light slows down when traveling through a medium. The speed of light in vacuum instead is considered a constant, and defined by the SI as 299792458 m/s. Alternative theories therefore usually modify the definitions of meter and seconds. VSL should not be confused with faster than light theories. Notable VSL attempts have been done by Einstein in 1911, by Robert Dicke in 1957, and by several researchers starting from the late 1980s. Since some of them contradict established concepts, VSL theories are a matter of debate.