Nickel complexes of a diphosphine-ketone ligand: oxidation
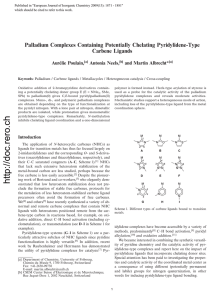
... important to note that the oxidation state of the metal does not change during the reaction. This type of reaction generally happens under the cooperative functions of an electron-deficient transitionmetal and an electron-rich Lewis base[29]. The hydride is accepted by the metal centre whilst the pr ...
... important to note that the oxidation state of the metal does not change during the reaction. This type of reaction generally happens under the cooperative functions of an electron-deficient transitionmetal and an electron-rich Lewis base[29]. The hydride is accepted by the metal centre whilst the pr ...
expansion and electrical conductivity of montmorillonite in ammonia
... of carbon black was spread on the flat surfaces of the clay plugs before putting them in the conductance cell, in order to ensure good electrical contact with the platinum electrodes. Clay films, prepared by evaporating the dilute clay suspension in aluminum dishes, were used for X-ray diffraction a ...
... of carbon black was spread on the flat surfaces of the clay plugs before putting them in the conductance cell, in order to ensure good electrical contact with the platinum electrodes. Clay films, prepared by evaporating the dilute clay suspension in aluminum dishes, were used for X-ray diffraction a ...
investigation of the mechanism of phosphotriesterase
... this investigation of the binuclear active site of Mn(II)-substituted PTE. The theory and use of EPR in the study of binuclear enzymes will be discussed in Chapter II. Organophosphates contribute to half of all pesticides, mostly insecticides, used in the United States (1). The majority of organopho ...
... this investigation of the binuclear active site of Mn(II)-substituted PTE. The theory and use of EPR in the study of binuclear enzymes will be discussed in Chapter II. Organophosphates contribute to half of all pesticides, mostly insecticides, used in the United States (1). The majority of organopho ...
Chapter 12: EDTA Titrations
... (c) Tetradentate = 4 binding sites; Example is ATP (Figure 11-2) ...
... (c) Tetradentate = 4 binding sites; Example is ATP (Figure 11-2) ...
this PDF file - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... metal 0-donor bond and a metal to ligand n-acceptor bond. Back donation of the electron density ro the ?(*orbitals of the C-C multiple bond systems can thus take place. The M=C=C group is almost linear. The angle at C, is between 1.25 and 1.41 %1 which corresponds to a b n d order between two and th ...
... metal 0-donor bond and a metal to ligand n-acceptor bond. Back donation of the electron density ro the ?(*orbitals of the C-C multiple bond systems can thus take place. The M=C=C group is almost linear. The angle at C, is between 1.25 and 1.41 %1 which corresponds to a b n d order between two and th ...
Disproportionation of Gold(II)
... IP3, which are more pertinent to disproportionation reactions, are much smaller than these effects on IP1. For both the B3PW91 and CCSD(T) methods, relativity decreases IP2 (22 kcal/mol for the former; 9 kcal/mol for the latter) and also IP3 (30 kcal/ mol for DFT, 10 kcal/mol for CCSD(T)). The same ...
... IP3, which are more pertinent to disproportionation reactions, are much smaller than these effects on IP1. For both the B3PW91 and CCSD(T) methods, relativity decreases IP2 (22 kcal/mol for the former; 9 kcal/mol for the latter) and also IP3 (30 kcal/ mol for DFT, 10 kcal/mol for CCSD(T)). The same ...
CHEMICAL EFFECTS IN X-RAY EMISSION SPECTRA OF
... just by some compounds of an element and not by all of them. He thus proved the existence of ...
... just by some compounds of an element and not by all of them. He thus proved the existence of ...
Quantitative Chemical Analysis 7e
... 12-1 Metal-Chelate complexes • Metal ions are Lewis acids, accepting electrons pairs from electron-donating ligands that are Lewis bases. • Monodentate ligand: binds to a metal ion through only one atom. • Multidentate ligand: attaches to a metal ion through more than one ligand atom, also known as ...
... 12-1 Metal-Chelate complexes • Metal ions are Lewis acids, accepting electrons pairs from electron-donating ligands that are Lewis bases. • Monodentate ligand: binds to a metal ion through only one atom. • Multidentate ligand: attaches to a metal ion through more than one ligand atom, also known as ...
WOR3135 GB 38 No2
... methathesis of the bis(ylide) dimer [Au2Cl2{µ-(CH2)2PPh2}2] with the silver(I) salts [Ag(OTf)P] (P = TPPMS, TPPDS, TPPTS, TPA, DAPTA) as shown in Scheme 3 [30]. The TPA derivative has been characterized crystallographically and the Au-Au bond length was determined to be 2.6275(4) Å [30]. Remarkably, ...
... methathesis of the bis(ylide) dimer [Au2Cl2{µ-(CH2)2PPh2}2] with the silver(I) salts [Ag(OTf)P] (P = TPPMS, TPPDS, TPPTS, TPA, DAPTA) as shown in Scheme 3 [30]. The TPA derivative has been characterized crystallographically and the Au-Au bond length was determined to be 2.6275(4) Å [30]. Remarkably, ...
Crystallization of sulfides from alkali polysulfide fluxes
... exhibits antiferromagnetic ordering at 18 K, and the antiferromagnetic phase diagram and an anomalously large band gap shift near the Neel temperature have been measured by Blazey and Rohrer 14). NaCrS2 slowly decomposes at room temperature in air. The decomposition at high temperatures starts after ...
... exhibits antiferromagnetic ordering at 18 K, and the antiferromagnetic phase diagram and an anomalously large band gap shift near the Neel temperature have been measured by Blazey and Rohrer 14). NaCrS2 slowly decomposes at room temperature in air. The decomposition at high temperatures starts after ...
Brief Guide to the Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry
... The boundaries between ‘organic’ and ‘inorganic’ compounds are blurred. The nomenclature types described in this document are applicable to compounds, molecules and ions that do not contain carbon, but also to many structures that do contain carbon (Section 2), notably those containing elements of G ...
... The boundaries between ‘organic’ and ‘inorganic’ compounds are blurred. The nomenclature types described in this document are applicable to compounds, molecules and ions that do not contain carbon, but also to many structures that do contain carbon (Section 2), notably those containing elements of G ...
Brief Guide to the Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry
... The boundaries between ‘organic’ and ‘inorganic’ compounds are blurred. The nomenclature types described in this document are applicable to compounds, molecules and ions that do not contain carbon, but also to many structures that do contain carbon (Section 2), notably those containing elements of G ...
... The boundaries between ‘organic’ and ‘inorganic’ compounds are blurred. The nomenclature types described in this document are applicable to compounds, molecules and ions that do not contain carbon, but also to many structures that do contain carbon (Section 2), notably those containing elements of G ...
Structure and binding of Mg(II) ions and di-metal bridge
... increases linearly with increasing water coordination from a minimal value of 1.938 Å for coordination with one water to 2.111 Å when fully coordinated with six water molecules (an increase of 0.173 Å). The gas-phase optimized coordination distances are slightly larger than those of other theoret ...
... increases linearly with increasing water coordination from a minimal value of 1.938 Å for coordination with one water to 2.111 Å when fully coordinated with six water molecules (an increase of 0.173 Å). The gas-phase optimized coordination distances are slightly larger than those of other theoret ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
... order rate law, such that: Rate = k[N2O5]. When the reaction was carried out at a certain temperature using an initial concentration [N2O5]0 = 0.100 M, the concentration of N2O5 after 5.00 minutes (300 seconds) was found to be 0.0125 M. (a) Determine the rate constant k (s–1) for the above reaction. ...
paper
... (Figure 1) for fabricating FETs with GO as a hole injection layer between MoS2 and metal contacts. One architecture is proposed in Figure 1a, where MoS2 is used as the active channel material, and hafnia, a highk oxide, is employed as the top-gate dielectric.8,11 In Figure 1b, we show another possib ...
... (Figure 1) for fabricating FETs with GO as a hole injection layer between MoS2 and metal contacts. One architecture is proposed in Figure 1a, where MoS2 is used as the active channel material, and hafnia, a highk oxide, is employed as the top-gate dielectric.8,11 In Figure 1b, we show another possib ...
A E M , Apr. 2004, p. 2551–2555
... reduced Cu toxicity at a high Cu concentration (1,000 M) where solid precipitates were observed (Fig. 1c). CuS precipitates were not observed below 10 M Cu, while significant CuS precipitates occurred at 100 M Cu and above. Pyrococcus strain GB-D showed the effectiveness of soluble ZnS(aq) comple ...
... reduced Cu toxicity at a high Cu concentration (1,000 M) where solid precipitates were observed (Fig. 1c). CuS precipitates were not observed below 10 M Cu, while significant CuS precipitates occurred at 100 M Cu and above. Pyrococcus strain GB-D showed the effectiveness of soluble ZnS(aq) comple ...
Integrated Chemical Systems
... width of 16 G at room temperature (Figure 1A). Since the ESR spectrum of the Ti(II1) ion in Nafion is readily observable at room temperature, the configuration of ligands around Ti(II1) in Nafion clearly deviates from a species with perfect octahedral symmetry, which is ESR-inactive due to very rapi ...
... width of 16 G at room temperature (Figure 1A). Since the ESR spectrum of the Ti(II1) ion in Nafion is readily observable at room temperature, the configuration of ligands around Ti(II1) in Nafion clearly deviates from a species with perfect octahedral symmetry, which is ESR-inactive due to very rapi ...
Chapter 2 - University of Amsterdam
... monoligated [Rh(H)(CO)31a] with the phosphorus ligand in the equatorial position; an hydride signal centred at -11.01 ppm is observed with a small PH coupling typical of such cis-[Rh(H)(CO)31a] complex. Much to our surprise, in the presence of two equivalent of porphyrin 2, this signal disappears an ...
... monoligated [Rh(H)(CO)31a] with the phosphorus ligand in the equatorial position; an hydride signal centred at -11.01 ppm is observed with a small PH coupling typical of such cis-[Rh(H)(CO)31a] complex. Much to our surprise, in the presence of two equivalent of porphyrin 2, this signal disappears an ...
Spin transport of electrons and holes in a metal and in a
... Conventionally, the spin transport in a conductor is described by the model of spin-up/spin-down bands [1]. This model assumes that all electrons of an electron gas can be divided into two independent groups: a group of electrons with the spin-up spin projections and a group of electrons with the sp ...
... Conventionally, the spin transport in a conductor is described by the model of spin-up/spin-down bands [1]. This model assumes that all electrons of an electron gas can be divided into two independent groups: a group of electrons with the spin-up spin projections and a group of electrons with the sp ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).