![CUCURBIT[7]URIL HOST-GUEST COMPLEXES WITH DRUG MOLECULES CONTAINING ISOQUINOLINE GROUPS Julian Kwok by](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008101179_1-fa974bb5e0d463f251947f4fb85d5098-300x300.png)
Preparation of Fe-Co-Ni Ternary Alloys with Electrodeposition
... decreases gradually with the increase of pH value, while Ni content increases. Experiments showed that when the pH value was less than 2.3, the cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction was fierce; pinholes and burrs were found on the surface of the deposit, and the deposit was thin and brittle. When the ...
... decreases gradually with the increase of pH value, while Ni content increases. Experiments showed that when the pH value was less than 2.3, the cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction was fierce; pinholes and burrs were found on the surface of the deposit, and the deposit was thin and brittle. When the ...
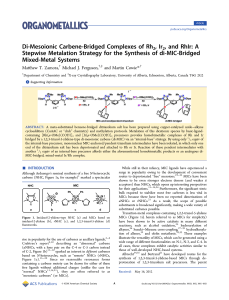
Reaction of Nitrogen Chelates with the [Rh2]4+ Core: Bis
... β-diketonates.9 In these systems, the chelates again occupy equatorial positions of the [Rh2]4+ core, and isomeric mixtures are obtained when asymmetry is present in the diketonate ligand.10 An additional group of compounds containing two nitrogen chelates bound to the [Rh2]4+ core are the Rh2(O2CR) ...
... β-diketonates.9 In these systems, the chelates again occupy equatorial positions of the [Rh2]4+ core, and isomeric mixtures are obtained when asymmetry is present in the diketonate ligand.10 An additional group of compounds containing two nitrogen chelates bound to the [Rh2]4+ core are the Rh2(O2CR) ...
here - University of Alberta
... respectively.66 Although we are unable to determine which diastereomer best describes complexes 7 and 8 through spectroscopy, it is clear from the structure of 7, shown in Figure 4, that this complex adopts the dl orientation, which is presumably a result of steric hindrance. The spectral properties ...
... respectively.66 Although we are unable to determine which diastereomer best describes complexes 7 and 8 through spectroscopy, it is clear from the structure of 7, shown in Figure 4, that this complex adopts the dl orientation, which is presumably a result of steric hindrance. The spectral properties ...
Direct Determination of Metal Cyanides by Ion
... to coelute at higher concentrations, requiring the analyst to judge where to split the peaks. The problem is less severe for nickel cyanide, the later-eluting peak. Any samples containing high levels of copper or gold cyanide should be diluted to a level where coelution does not occur. Note that bec ...
... to coelute at higher concentrations, requiring the analyst to judge where to split the peaks. The problem is less severe for nickel cyanide, the later-eluting peak. Any samples containing high levels of copper or gold cyanide should be diluted to a level where coelution does not occur. Note that bec ...
MLCT State Structure and Dynamics of a Copper(I) Diimine
... Abstract: The molecular structure and dynamics of the photoexcited metal-to-ligand-charge-transfer (MLCT) state of [CuI(dmp)2]+, where dmp is 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline, in acetonitrile have been investigated by time-domain pump-probe X-ray absorption spectroscopy, femtosecond optical transien ...
... Abstract: The molecular structure and dynamics of the photoexcited metal-to-ligand-charge-transfer (MLCT) state of [CuI(dmp)2]+, where dmp is 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline, in acetonitrile have been investigated by time-domain pump-probe X-ray absorption spectroscopy, femtosecond optical transien ...
ioan stamatin
... 1. an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering; related to thermal phenomena 2. an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data; 3. an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs; 4. an ability to function ...
... 1. an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering; related to thermal phenomena 2. an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data; 3. an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs; 4. an ability to function ...
The C=C Double Bond of Tetrafluoroethylene
... due to their ability to act as oxygen atom transfer agents and also because of the potential these reagents have as catalysts for the air oxidation of organic substrates.’V2 These complexes have been shown to oxidize a number of organic3-10 and inorganic substrates,”-I6 where the corresponding trans ...
... due to their ability to act as oxygen atom transfer agents and also because of the potential these reagents have as catalysts for the air oxidation of organic substrates.’V2 These complexes have been shown to oxidize a number of organic3-10 and inorganic substrates,”-I6 where the corresponding trans ...
2 Oxidation and Oxygen Activation by Heme Proteins
... radical is cooled to liquid-nitrogen temperature it is converted to the red Ni(III)TPP [34]. Upon warming to room temperature the Ni(II)TPP p-cation ...
... radical is cooled to liquid-nitrogen temperature it is converted to the red Ni(III)TPP [34]. Upon warming to room temperature the Ni(II)TPP p-cation ...
Wafer-Level Artificial Photosynthesis for CO2 Reduction into CH4
... bond C=O can be broken to form C-H bonds, which leads to the formation of different fuels such as methane (CH4). H2 formation is a very competitive process in CO2 photochemical and photoelectrochemical reduction. This is due to the use of water as an atomic hydrogen donor for CO2 reduction, whereby ...
... bond C=O can be broken to form C-H bonds, which leads to the formation of different fuels such as methane (CH4). H2 formation is a very competitive process in CO2 photochemical and photoelectrochemical reduction. This is due to the use of water as an atomic hydrogen donor for CO2 reduction, whereby ...
Introduction to Organometallic chemistry Prof. A. G. Samuelson
... generates a bi, a molecule which is cyclic. And it is just dimer of the cyclo butadiene. So this is a molecule that would isolate, if you are not careful enough to provide a stabilizing foresight for cyclo butadiene, which is anti aromatic and it would dimarize rapidly. Now, although cyclo butadiene ...
... generates a bi, a molecule which is cyclic. And it is just dimer of the cyclo butadiene. So this is a molecule that would isolate, if you are not careful enough to provide a stabilizing foresight for cyclo butadiene, which is anti aromatic and it would dimarize rapidly. Now, although cyclo butadiene ...
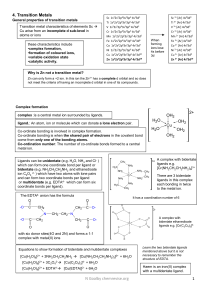
mod-5-revision-guide-4-transition-metals
... Changing a ligand or changing the coordination number will alter the energy split between the d- orbitals, changing E and hence change the frequency of light absorbed. Compounds without colour Scandium is a member of the d block. Its ion (Sc3+) hasn't got any d electrons left to move around. So the ...
... Changing a ligand or changing the coordination number will alter the energy split between the d- orbitals, changing E and hence change the frequency of light absorbed. Compounds without colour Scandium is a member of the d block. Its ion (Sc3+) hasn't got any d electrons left to move around. So the ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).


![Reaction of Nitrogen Chelates with the [Rh2]4+ Core: Bis](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109229_1-82def2167f1fa4f2a4186d949c34cb3c-300x300.png)