Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... Low spin due to the NO2- ion being strong field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [Fe(NO2)6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six NO2- ions carries a charge of –1 and the charge on the entire complex is 4-. Fe is in Group 8 (it has eight valence electrons). Fe2+ has si ...
... Low spin due to the NO2- ion being strong field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [Fe(NO2)6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six NO2- ions carries a charge of –1 and the charge on the entire complex is 4-. Fe is in Group 8 (it has eight valence electrons). Fe2+ has si ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #1
... occupied d-orbitals. Repulsions between ligand electrons and the d-electrons of a metal cation removes some of the degeneracy of the d-orbitals. An electron can absorb a visible photon and move to a higher energy d-orbital from a lower energy d-orbital.. The energy gap between the d-orbitals is affe ...
... occupied d-orbitals. Repulsions between ligand electrons and the d-electrons of a metal cation removes some of the degeneracy of the d-orbitals. An electron can absorb a visible photon and move to a higher energy d-orbital from a lower energy d-orbital.. The energy gap between the d-orbitals is affe ...
Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Ln(III) complexes with 4
... The cation coordination sites are provided by six oxygens from three different crotonato units attached in a chelating mode, one of which acts also in a bridging mode linking to a near Ln neighbour and thus providing a seventh site. The independent bpy nitrogen and the aqua oxygen complete the ninefo ...
... The cation coordination sites are provided by six oxygens from three different crotonato units attached in a chelating mode, one of which acts also in a bridging mode linking to a near Ln neighbour and thus providing a seventh site. The independent bpy nitrogen and the aqua oxygen complete the ninefo ...
LENGTH
... iron is +4, then the splitting is large, and the molecule is most likely lowspin. This means that the molecule has two unpaired electrons. If the molecules were to be high spin, it would have four unpaired electrons. The experiment therefore to test for low-spin or high-spin is to test for the degre ...
... iron is +4, then the splitting is large, and the molecule is most likely lowspin. This means that the molecule has two unpaired electrons. If the molecules were to be high spin, it would have four unpaired electrons. The experiment therefore to test for low-spin or high-spin is to test for the degre ...
1 - University of North Texas
... there is more than one allowed transition, list them in order of increasing energy. ( 16 points) complex ground state term excited state term(s) [Fe(CN)6]4[Co(H2O)6]3+ [RhF6]3[CoF6]3– 4. The low energy of d-d transitions gives most coordination compounds their intense visible colors. However, the fo ...
... there is more than one allowed transition, list them in order of increasing energy. ( 16 points) complex ground state term excited state term(s) [Fe(CN)6]4[Co(H2O)6]3+ [RhF6]3[CoF6]3– 4. The low energy of d-d transitions gives most coordination compounds their intense visible colors. However, the fo ...
Studying of transition metal complexes containing
... This material was extensively investigated To its wide applications in photochemical studies ,actinometery ,sensors and magnetic materials (3-5). The complexation of metals with ligands can drastically change the physico–chemical and biological properties of the metal species(6). Metal ions play an ...
... This material was extensively investigated To its wide applications in photochemical studies ,actinometery ,sensors and magnetic materials (3-5). The complexation of metals with ligands can drastically change the physico–chemical and biological properties of the metal species(6). Metal ions play an ...
Electronic Selection Rules (II)
... (note that the ground state 3T1g is curved in the Orgel diagram but linear in the Tanabe-Sugano diagram) o the axes are in units of B or the Racah parameter which and represents the extent of repulsion between electrons in dAOs. The vertical axis is energy E/B and the horizontal axis is Δoct/B • a f ...
... (note that the ground state 3T1g is curved in the Orgel diagram but linear in the Tanabe-Sugano diagram) o the axes are in units of B or the Racah parameter which and represents the extent of repulsion between electrons in dAOs. The vertical axis is energy E/B and the horizontal axis is Δoct/B • a f ...
The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the
... “For several years before 1970 my research group had been investigating transition metal complexes of heterocyclic ligands, particularly from the viewpoint of their possible use as analytical reagents. As so often happens, although this aspect proved to be disappointing another area became of intere ...
... “For several years before 1970 my research group had been investigating transition metal complexes of heterocyclic ligands, particularly from the viewpoint of their possible use as analytical reagents. As so often happens, although this aspect proved to be disappointing another area became of intere ...
Chapter 7
... trigonal-prismatic.) There are a couple of important types of isomerism, and a number of lesser significance. All are relevant only to complexes which are kinetically inert, that is, not subject to ligand exchange processes which will thwart attempts to physically separate the isomers. Geometrical I ...
... trigonal-prismatic.) There are a couple of important types of isomerism, and a number of lesser significance. All are relevant only to complexes which are kinetically inert, that is, not subject to ligand exchange processes which will thwart attempts to physically separate the isomers. Geometrical I ...
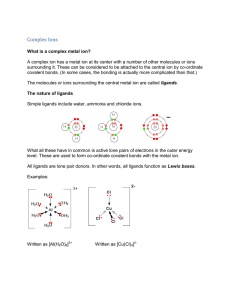
Complex Ions - Frankie Guglieri
... Complex Ions What is a complex metal ion? A complex ion has a metal ion at its center with a number of other molecules or ions surrounding it. These can be considered to be attached to the central ion by co-ordinate covalent bonds. (In some cases, the bonding is actually more complicated than that.) ...
... Complex Ions What is a complex metal ion? A complex ion has a metal ion at its center with a number of other molecules or ions surrounding it. These can be considered to be attached to the central ion by co-ordinate covalent bonds. (In some cases, the bonding is actually more complicated than that.) ...
Electronic Structures of Metal Hexacarbonyls
... Preparation of Compounds. Cr(COh, MO(CO)~, and W(CO)6. Samples of these complexes were obtained from the Ethyl Corp. and the Climax Molybdenum Co. and purified by sublimation. [n-BuaN][v(cO)~]. An aqueous solution of [rz-BuaN]Br was deaerated with nitrogen. Alpha grade [Na(diglyme)r][V(CO)s] was add ...
... Preparation of Compounds. Cr(COh, MO(CO)~, and W(CO)6. Samples of these complexes were obtained from the Ethyl Corp. and the Climax Molybdenum Co. and purified by sublimation. [n-BuaN][v(cO)~]. An aqueous solution of [rz-BuaN]Br was deaerated with nitrogen. Alpha grade [Na(diglyme)r][V(CO)s] was add ...
Document
... There is no combination of ligand σ orbitals with the symmetry of the metal T2g orbitals, so these do not participate in σ bonding. ...
... There is no combination of ligand σ orbitals with the symmetry of the metal T2g orbitals, so these do not participate in σ bonding. ...
Exam_3
... c). Give the region of the electromagnetic spectrum in which the photon will be found. ...
... c). Give the region of the electromagnetic spectrum in which the photon will be found. ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).