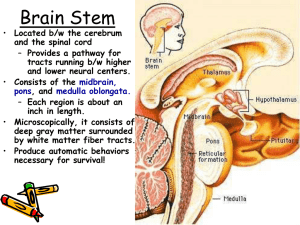
Nervous Regulation
... • Responses to both internal and external stimuli must be regulated and coordinated • These responses are controlled by the body’s nervous and endocrine systems ...
... • Responses to both internal and external stimuli must be regulated and coordinated • These responses are controlled by the body’s nervous and endocrine systems ...
Module 3 - yhernandez
... can grow about 20,000 neurons a day during the spring (learns new breeding song) – Primate and human brain researchers conclude that adult monkey and human brains are capable of growing relatively limited numbers of neurons throughout adulthood some new neurons play important role in continuin ...
... can grow about 20,000 neurons a day during the spring (learns new breeding song) – Primate and human brain researchers conclude that adult monkey and human brains are capable of growing relatively limited numbers of neurons throughout adulthood some new neurons play important role in continuin ...
the potential for abuse: addiction
... area (VTA) that connects to the limbic system through projections to the nucleus accumbens, amygdala, hippocampus, and medial prefrontal cortex (Hyman, 2005). The VTA is composed of various types of neurons that include a specific cluster of dopaminergic neurons that communicate foremost with the nu ...
... area (VTA) that connects to the limbic system through projections to the nucleus accumbens, amygdala, hippocampus, and medial prefrontal cortex (Hyman, 2005). The VTA is composed of various types of neurons that include a specific cluster of dopaminergic neurons that communicate foremost with the nu ...
BRAIN
... Neuroglia – “glial cells;” non-excitable support cells of the CNS Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – a salty solution that is continuously secreted into the ventricles of the brain Blood brain barrier – tight junctions in the brain capillaries that prevent free exchange of many substances between the blood ...
... Neuroglia – “glial cells;” non-excitable support cells of the CNS Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – a salty solution that is continuously secreted into the ventricles of the brain Blood brain barrier – tight junctions in the brain capillaries that prevent free exchange of many substances between the blood ...
Biological Bases of Human Behavior
... This text provides a comprehensive foundation for the topics discussed in class. Additional readings are assigned for each lecture and intended to provide students with current research and controversy on each topic; each article will be thoroughly critiqued, at first by the instructor and then with ...
... This text provides a comprehensive foundation for the topics discussed in class. Additional readings are assigned for each lecture and intended to provide students with current research and controversy on each topic; each article will be thoroughly critiqued, at first by the instructor and then with ...
Nourish Your Brain With a Healthful Diet
... content, but please do so under the conditions of our Creative Commons license. You may copy, distribute, transmit and adapt this work as long as you give full attribution, don’t use the work for commercial purposes and share your resulting work similarly. For more information, visit www.ag.ndsu.edu ...
... content, but please do so under the conditions of our Creative Commons license. You may copy, distribute, transmit and adapt this work as long as you give full attribution, don’t use the work for commercial purposes and share your resulting work similarly. For more information, visit www.ag.ndsu.edu ...
Neuroscience01_Introduction
... Above the midbrain, anterior means towards the front of the brain and posterior means towards the back of the brain. At and below the midbrain, anterior means toward the ventral surface of the body and posterior means toward the dorsal surface of the body. ...
... Above the midbrain, anterior means towards the front of the brain and posterior means towards the back of the brain. At and below the midbrain, anterior means toward the ventral surface of the body and posterior means toward the dorsal surface of the body. ...
Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature Regulation
... 4. Our cells use two mechanisms to capture some of the energy liberated through oxidationreduction reactions to make ATP. a. Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs when high-energy phosphate groups are transferred directly from phosphorylated substrates to ADP. b. Oxidative phosphorylation is carrie ...
... 4. Our cells use two mechanisms to capture some of the energy liberated through oxidationreduction reactions to make ATP. a. Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs when high-energy phosphate groups are transferred directly from phosphorylated substrates to ADP. b. Oxidative phosphorylation is carrie ...
fMRI of speech and language
... Returning to same/different parts of brain question: • Speech production and perception are centered in different areas, suggesting that different processes may underlie them • But Broca’s and Wernicke’s are connected to each other • Wernicke’s speech perception area is close to, but not inside ...
... Returning to same/different parts of brain question: • Speech production and perception are centered in different areas, suggesting that different processes may underlie them • But Broca’s and Wernicke’s are connected to each other • Wernicke’s speech perception area is close to, but not inside ...
Consciousness, Literature and the Arts
... philosophies that engage with the disturbances of the Modern and PostModern, in profoundly thoughtful ways, as a poetics of science as well as a science of poetics, bodies and languages in complex syntheses, as liquidities, differences, assemblages, or rhizomes. Here I might be thinking, as a single ...
... philosophies that engage with the disturbances of the Modern and PostModern, in profoundly thoughtful ways, as a poetics of science as well as a science of poetics, bodies and languages in complex syntheses, as liquidities, differences, assemblages, or rhizomes. Here I might be thinking, as a single ...
Sensation and Perception
... membranes at the top of each nostril and are absorbed by receptor cells- as many as 100 different types exist Linked to the olfactory bulb, which gathers and send the information to the brain Connects at the amygdala and then to the hippocampus instead of through the thalamus ...
... membranes at the top of each nostril and are absorbed by receptor cells- as many as 100 different types exist Linked to the olfactory bulb, which gathers and send the information to the brain Connects at the amygdala and then to the hippocampus instead of through the thalamus ...
How Psychotherapy Changes the Brain
... For example, the mechanism behind the effectiveness of cognitive therapy for patients with MDD could be through an increase in prefrontal function, which is involved in cognitive control, while antidepressant medications operate more directly on the amygdala, which is involved in the generation of n ...
... For example, the mechanism behind the effectiveness of cognitive therapy for patients with MDD could be through an increase in prefrontal function, which is involved in cognitive control, while antidepressant medications operate more directly on the amygdala, which is involved in the generation of n ...
CHAPTER 2 –OUTLINE I. Introduction: Neuroscience and Behavior
... cells in the sense organs, the skin, and the internal organs to the brain. b. Motor neurons communicate information to the muscles and glands of the body. c. Interneurons communicate information between neurons; they are the most common type of neuron found in the human nervous system. Chapter 2 Neu ...
... cells in the sense organs, the skin, and the internal organs to the brain. b. Motor neurons communicate information to the muscles and glands of the body. c. Interneurons communicate information between neurons; they are the most common type of neuron found in the human nervous system. Chapter 2 Neu ...
UNIT XI
... • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover a ...
... • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover a ...
Central Nervous System Functional Anatomy of the Brain
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
Chapter 24 Nervous Systems
... 自主神經系統 The motor nervous system - carries signals to and from skeletal muscles. - mainly responds to external stimuli. The autonomic nervous system - regulates the internal environment. - controls smooth and cardiac muscle and organs and glands of the digestive, cardiovascular, excretory, and en ...
... 自主神經系統 The motor nervous system - carries signals to and from skeletal muscles. - mainly responds to external stimuli. The autonomic nervous system - regulates the internal environment. - controls smooth and cardiac muscle and organs and glands of the digestive, cardiovascular, excretory, and en ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... for five cranial nerves (VII, IX, X, XI, and XII) ...
... for five cranial nerves (VII, IX, X, XI, and XII) ...
Biological Impact
... in the body, drugs may also help by blocking reuptake and thus increasing the amount of neurotransmitter that remains in the synapse • Prozac is an example of this sort of drug. Prozac falls in a class of drugs called SSRI’s (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) and by inhibiting reuptake of sero ...
... in the body, drugs may also help by blocking reuptake and thus increasing the amount of neurotransmitter that remains in the synapse • Prozac is an example of this sort of drug. Prozac falls in a class of drugs called SSRI’s (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor) and by inhibiting reuptake of sero ...
3 - smw15.org
... – He felt that bumps on the skull could reveal our mental abilities and character traits. – Introduced as being scientific – Although, ill-fated theory was laughed at by scientific community of that day – it may have had some validity – Localization of brain functions somehow hit the mark ...
... – He felt that bumps on the skull could reveal our mental abilities and character traits. – Introduced as being scientific – Although, ill-fated theory was laughed at by scientific community of that day – it may have had some validity – Localization of brain functions somehow hit the mark ...
BUILDING AN ARTIFICIAL BRAIN
... "Artificial Life and Robotics, Artificial Brain, Brain Computing and Brainware", North Holland. (Invited by Editor, to appear 1999), Hugo de ...
... "Artificial Life and Robotics, Artificial Brain, Brain Computing and Brainware", North Holland. (Invited by Editor, to appear 1999), Hugo de ...
An Herbalist`s View of the Nervous System
... Categories of Therapeutics Adaptogen – helps the body adapt to stress Analeptic – increases activity of the central nervous system Analgesic – relieves pain Anesthetic – produces a partial or complete loss of nerve sensation Anticholinergic – inhibits the impulses of acetylcholine Anticonvulsant – p ...
... Categories of Therapeutics Adaptogen – helps the body adapt to stress Analeptic – increases activity of the central nervous system Analgesic – relieves pain Anesthetic – produces a partial or complete loss of nerve sensation Anticholinergic – inhibits the impulses of acetylcholine Anticonvulsant – p ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by naming the parts and describing the functions of the parts of the neurons (handout). NEUROTRANSMITTERS: Here are some examples of the most commonly discussed neurotransmitters, what their function is and any problems or diseases t ...
... chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by naming the parts and describing the functions of the parts of the neurons (handout). NEUROTRANSMITTERS: Here are some examples of the most commonly discussed neurotransmitters, what their function is and any problems or diseases t ...