The Nervous System
... uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episodes of uncontrolled electrical impulses in the brain (seizures) Cerebral Palsy – non-progressiv ...
... uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episodes of uncontrolled electrical impulses in the brain (seizures) Cerebral Palsy – non-progressiv ...
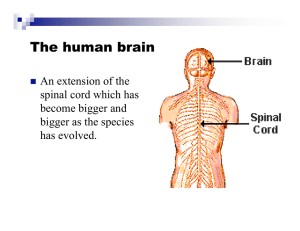
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi a ...
... Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere only resulted in speech impairment. Korbinian Brodmann (18681918) defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi a ...
THE BRAIN - Dublin City Schools
... Weighs about 3 pounds Different centers which control different things Despite being 90-95 percent of its adult size by age six, the brain is still “under construction” until age 18. ...
... Weighs about 3 pounds Different centers which control different things Despite being 90-95 percent of its adult size by age six, the brain is still “under construction” until age 18. ...
Neuro-transmitters
... 1. MATERIALISTS: view the brain as a machine in which the consciousness was irrelevant to its functioning. 2. DUALISTS: consider the mind to exist independently of the brain, but could exact some control over it. Mind and body are separate but interactive. 3. IDENTITY POSITION: the mind is viewed as ...
... 1. MATERIALISTS: view the brain as a machine in which the consciousness was irrelevant to its functioning. 2. DUALISTS: consider the mind to exist independently of the brain, but could exact some control over it. Mind and body are separate but interactive. 3. IDENTITY POSITION: the mind is viewed as ...
Aotearoa Neuroscience Postdoctoral Fellow Projects
... development and continues to impact on normal brain function as well as being a major drug target for known neuroactive pharmaceuticals and in novel drug design. How the inhibitory system works in the normal brain, and how it is altered in brain diseases, is well studied but poorly understood. In th ...
... development and continues to impact on normal brain function as well as being a major drug target for known neuroactive pharmaceuticals and in novel drug design. How the inhibitory system works in the normal brain, and how it is altered in brain diseases, is well studied but poorly understood. In th ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
General PLTW Document
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
... and hearing. Senses such as sight and smell are processed by the brain after signals are sent through specialized nerves such as the optic nerve. Alternately, sensory neurons in the skin send signals through the spinal cord in order for the brain to interpret sensations of touch, pain, heat, and col ...
AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology
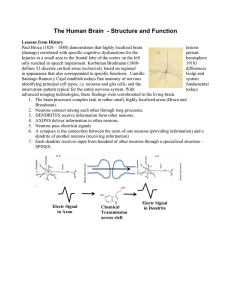
... a. Dendrites- bushy fibers that receive information b. Axon- fibers that pass message along to other neurons, muscles or glands. c. Myelin Sheath- fatty tissue insulates axon to speed info. d. Axon terminals- form junctions with other cells ...
... a. Dendrites- bushy fibers that receive information b. Axon- fibers that pass message along to other neurons, muscles or glands. c. Myelin Sheath- fatty tissue insulates axon to speed info. d. Axon terminals- form junctions with other cells ...
biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... 1. How do neuroscientists explore the connection among, brain, mind and behavior? 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cort ...
... 1. How do neuroscientists explore the connection among, brain, mind and behavior? 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cort ...
Neurofeedback
... • Virtual Reality – Enhance neurofeedback in a couple ways • The total immersion and totality of the feedback allows the patient to focus completely on his physiology without distraction • More engaging and motivating for the client ...
... • Virtual Reality – Enhance neurofeedback in a couple ways • The total immersion and totality of the feedback allows the patient to focus completely on his physiology without distraction • More engaging and motivating for the client ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... occupies only a small region in humans (it is relatively much larger in "lower" vertebrates ...
... occupies only a small region in humans (it is relatively much larger in "lower" vertebrates ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic forces and radio-frequency (RF) waves to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. D ...
... A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic forces and radio-frequency (RF) waves to make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. D ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... • Nerve cell which transmits electrical and chemical information (via neurotransmitters) throughout the body. Each nerve cell is separate from another and is called a Neuron – a string of these is a nerve cell. • Learning takes place by new dendrites actually sprouting to make connection with other ...
... • Nerve cell which transmits electrical and chemical information (via neurotransmitters) throughout the body. Each nerve cell is separate from another and is called a Neuron – a string of these is a nerve cell. • Learning takes place by new dendrites actually sprouting to make connection with other ...
Study Shows Practice May Have Potential to Change Brain`s
... of the brain but involve large-scale networks that include the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes and the anterior corpus callosum, as well as limbic structures and the brain stem. "Our results suggest that long-term meditators have white-matter fibers that are either more numerous, mor ...
... of the brain but involve large-scale networks that include the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes and the anterior corpus callosum, as well as limbic structures and the brain stem. "Our results suggest that long-term meditators have white-matter fibers that are either more numerous, mor ...








![AP_Chapter_2[1] - HopewellPsychology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008569681_1-9cf3b4caa50d34e12653d8840c008c05-300x300.png)