Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... 3: Hypothalamus: Involved in eating, drinking, and sexual behavior. It also controls the endocrine (hormonal system) via the pituitary gland. It is sometimes referred to as "the pleasure center" of the brain. Cerebral Cortex: The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebr ...
... 3: Hypothalamus: Involved in eating, drinking, and sexual behavior. It also controls the endocrine (hormonal system) via the pituitary gland. It is sometimes referred to as "the pleasure center" of the brain. Cerebral Cortex: The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebr ...
Brain Facts
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you’re born, all brain cells in place ...
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you’re born, all brain cells in place ...
AP Psychology
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
... 7. What are the two examples of poison that affect Ach transmission and what does each do? 8. What are the opiate receptors that we naturally produce and what is their purpose? 9. Give two examples of how drugs and other chemicals alter neurotransmission. 10. What are agonists and antagonists? 11. W ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... What is done to the brain in a split-brain procedure and why? ...
... What is done to the brain in a split-brain procedure and why? ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... a slowing of voluntary movements and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1 ...
... a slowing of voluntary movements and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1 ...
Development of the Brain
... • Survivors of brain damage show subtle to significant behavioral recovery. • Some of the mechanisms of recovery include those similar to the mechanisms of brain development such as the new branching of axons and dendrites. ...
... • Survivors of brain damage show subtle to significant behavioral recovery. • Some of the mechanisms of recovery include those similar to the mechanisms of brain development such as the new branching of axons and dendrites. ...
The Nervous System
... HAMMER, ANVIL, and STIRRUP. These create pressure waves in the fluid of the COCHLEA, which contains tiny hairs that wave back and forth. The motion of these hairs produce the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain ...
... HAMMER, ANVIL, and STIRRUP. These create pressure waves in the fluid of the COCHLEA, which contains tiny hairs that wave back and forth. The motion of these hairs produce the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
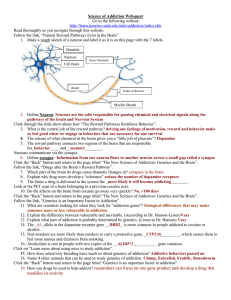
... Follow the link, “Natural Reward Pathways Exist in the Brain” 1. Make a rough sketch of a neuron and label it as it is on this page with the 7 labels. Dendrite s Nucleus ...
... Follow the link, “Natural Reward Pathways Exist in the Brain” 1. Make a rough sketch of a neuron and label it as it is on this page with the 7 labels. Dendrite s Nucleus ...
Brain Chips - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... Brain chips can enhance memory of human beings, help paralyzed patients and are intended for military purposes. Develop direct interface between brain and computers. Its likely that implantable computer chips acting as sensors may soon assist failing memory, but even provide fluency in a new languag ...
... Brain chips can enhance memory of human beings, help paralyzed patients and are intended for military purposes. Develop direct interface between brain and computers. Its likely that implantable computer chips acting as sensors may soon assist failing memory, but even provide fluency in a new languag ...
Unit N Notes #1 – The Central Nervous System - Mr. Lesiuk
... Unit N Notes #1 – The Central Nervous System - The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of both the brain and spinal cord. Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord ...
... Unit N Notes #1 – The Central Nervous System - The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of both the brain and spinal cord. Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord ...
The Nervous System
... either too stiff or too floppy. Cerebral palsy can’t be cured, but treatment will often improve a child's capabilities. ...
... either too stiff or too floppy. Cerebral palsy can’t be cured, but treatment will often improve a child's capabilities. ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... Sympathetic( speeds up heart rate) Parasympathetic (slows down heart rate) ...
... Sympathetic( speeds up heart rate) Parasympathetic (slows down heart rate) ...
Neuroanatomy - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Quantum states believed to be too sensitive and fragile to disruption by thermal energy (environmental decoherence) to affect the macroscopic nature of proteins and other macromolecular ...
... Quantum states believed to be too sensitive and fragile to disruption by thermal energy (environmental decoherence) to affect the macroscopic nature of proteins and other macromolecular ...
File
... Like all vertebrate brains, the human brain develops from three sections known as the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Each of these contains fluid-filled cavities called ventricles. The forebrain develops into the cerebrum and underlying structures; the midbrain becomes part of the brainstem; an ...
... Like all vertebrate brains, the human brain develops from three sections known as the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Each of these contains fluid-filled cavities called ventricles. The forebrain develops into the cerebrum and underlying structures; the midbrain becomes part of the brainstem; an ...
Texts - mistergui
... complex, lasting ways that Rhodes’s team was studying. “They loved the toys,” Rhodes says, and the mice rarely ventured into the empty, quieter portions of their cages. But unless they also exercised, they did not become smarter. Why would exercise build brainpower in ways that thinking might not? T ...
... complex, lasting ways that Rhodes’s team was studying. “They loved the toys,” Rhodes says, and the mice rarely ventured into the empty, quieter portions of their cages. But unless they also exercised, they did not become smarter. Why would exercise build brainpower in ways that thinking might not? T ...
Relating too much information without enough time to
... distracted, and unfocused. Source: Judy Willis, Research-based strategies to ignite student learning. ...
... distracted, and unfocused. Source: Judy Willis, Research-based strategies to ignite student learning. ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... Etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease ...
... Etiopathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease ...
B6 – Brain and Mind Go to the BBC Bitesize website from the school
... 44. What is changing our behaviour due to new experiences called? _______________________ 45. What happens to the new connection if that experience is repeated? ___________________ 46. So why does repetition help us learn new skills? ____________________________________ 47. Why does learning benefit ...
... 44. What is changing our behaviour due to new experiences called? _______________________ 45. What happens to the new connection if that experience is repeated? ___________________ 46. So why does repetition help us learn new skills? ____________________________________ 47. Why does learning benefit ...
Right Brain/Left Brain: Different Qualities and an Uneasy Alliance?
... Masses of white matter that belong to the descending tracts are called the EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM (includes parts of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and pons). The extrapyramidal system controls BODY MOVEMENT AND POSTURE. The extrapyramidal system passes into the basal nuclei (masses of grey matter that li ...
... Masses of white matter that belong to the descending tracts are called the EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM (includes parts of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and pons). The extrapyramidal system controls BODY MOVEMENT AND POSTURE. The extrapyramidal system passes into the basal nuclei (masses of grey matter that li ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... the result of damage to the brain before, during , or just after birth or in early childhood. ...
... the result of damage to the brain before, during , or just after birth or in early childhood. ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... informatics analysis tools are integrated to provide a searchable digital atlas of gene expression. Together, these resources present a comprehensive online platform for exploration of the brain at the cellular and molecular level. In particular, this project investigates the gene expression of sero ...
... informatics analysis tools are integrated to provide a searchable digital atlas of gene expression. Together, these resources present a comprehensive online platform for exploration of the brain at the cellular and molecular level. In particular, this project investigates the gene expression of sero ...
Unit_2_-_Biological_Bases_of_Behavior
... The skull of Phineas and rogue tamping iron, displayed proudly at Harvard University’s medical school! For real! ...
... The skull of Phineas and rogue tamping iron, displayed proudly at Harvard University’s medical school! For real! ...
48.5, .6, .7
... – Thalamus: main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum and the main output center for motor information leaing the cerebrum; information from all senses is sorted in the thalamus – Hypothalamus: source of posterior pituitary and releasing hormones that on the anterior pituitary ...
... – Thalamus: main input center for sensory information going to the cerebrum and the main output center for motor information leaing the cerebrum; information from all senses is sorted in the thalamus – Hypothalamus: source of posterior pituitary and releasing hormones that on the anterior pituitary ...