Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Einstein’s brain was removed within seven and a half hours of his death and was preserved for scientific studies. Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared t ...
... Einstein’s brain was removed within seven and a half hours of his death and was preserved for scientific studies. Einstein's brain weighed only 1,230 grams, which is less than the average adult male brain (about 1,400 grams). One of the differences that were found between Einstein’s brain compared t ...
Ch 2 Cognition & the Brain
... (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? • Single cell recording ...
... (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? • Single cell recording ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... events or objects in its environment and uses that knowledge for comprehension and problem-solving. CORPUS CALLOSUM - The large bundle of nerve fibers linking the left and right cerebral hemispheres. DENDRITE - A treelike extension of the neuron cell body. The dendrite is the primary site for receiv ...
... events or objects in its environment and uses that knowledge for comprehension and problem-solving. CORPUS CALLOSUM - The large bundle of nerve fibers linking the left and right cerebral hemispheres. DENDRITE - A treelike extension of the neuron cell body. The dendrite is the primary site for receiv ...
The Prefix extra: A Cognitive Linguistic Approach
... of prefixes classified as prefixes of degree and size. The prefix analyzed combines with different word classes and its semantics might seem chaotic due to different meaning extensions. The prototype theory, along with the theory of conceptual metaphor and metonymy can make sense of the semantics of ...
... of prefixes classified as prefixes of degree and size. The prefix analyzed combines with different word classes and its semantics might seem chaotic due to different meaning extensions. The prototype theory, along with the theory of conceptual metaphor and metonymy can make sense of the semantics of ...
Project 4: Quadratic programming of tuning curves: a theory for
... Firing rate tuning curves come in many shapes and sizes, from bumpshaped to sigmoidal, from sharply peaked to broad. What are the functional roles of these many shapes? This question has been central to neuroscience since the first firing rate recordings of Lord Adrian in 1928. In this project, we w ...
... Firing rate tuning curves come in many shapes and sizes, from bumpshaped to sigmoidal, from sharply peaked to broad. What are the functional roles of these many shapes? This question has been central to neuroscience since the first firing rate recordings of Lord Adrian in 1928. In this project, we w ...
slides - NYU Computation and Cognition Lab
... The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons Cell assemblies may be the emergent consequence of Hebbian learning in cortex which can support multiple forms of ...
... The likely mechanism for memory is the changes at the synapses in the form of LTP, dendritic growth, etc.. Circuits represent the collective action of interconnected networks of neurons Cell assemblies may be the emergent consequence of Hebbian learning in cortex which can support multiple forms of ...
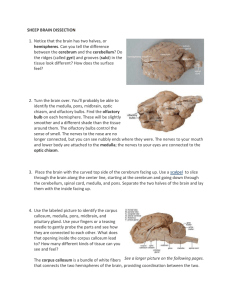
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
Chapter 51 Disorders of Brain Function
... • The brain floats freely in the CSF. Blunt force to the head accelerates the brain within the skull, and then the brain decelerates abruptly upon hitting the inner skull surfaces. • Coup: direct contusion of the brain at the site of external force • Contrecoup: rebound injury on the opposite side o ...
... • The brain floats freely in the CSF. Blunt force to the head accelerates the brain within the skull, and then the brain decelerates abruptly upon hitting the inner skull surfaces. • Coup: direct contusion of the brain at the site of external force • Contrecoup: rebound injury on the opposite side o ...
Systems Neuroscience - College of William and Mary
... and continues without lapse for the entire lifespan of the animal, which in humans can last up to, or exceed, 100 years. Diseases that affect the neural control of breathing can strike at any age, but newborns and premature babies are particularly susceptible to various forms of apnea and SIDS. We a ...
... and continues without lapse for the entire lifespan of the animal, which in humans can last up to, or exceed, 100 years. Diseases that affect the neural control of breathing can strike at any age, but newborns and premature babies are particularly susceptible to various forms of apnea and SIDS. We a ...
consciousness
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... decides how to react. Your eyes may take in light, but your brain interprets what you see. ...
... decides how to react. Your eyes may take in light, but your brain interprets what you see. ...
History of Psychology
... AP Psychology Exam Study Guide History and Approaches History of Psychology ...
... AP Psychology Exam Study Guide History and Approaches History of Psychology ...
$doc.title
... There are different definitions of mindfulness. These differences exist within Buddhism, and are reflected in its secular reincarnation as a clinical intervention and as an area of scientific research. Furthermo ...
... There are different definitions of mindfulness. These differences exist within Buddhism, and are reflected in its secular reincarnation as a clinical intervention and as an area of scientific research. Furthermo ...
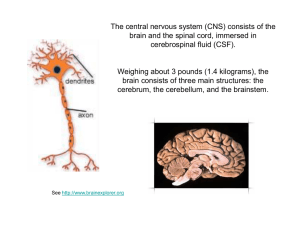
Nervous System
... Interesting Facts about the Neuron • Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose The nerve fibers of newborns are unmyelinated - ...
... Interesting Facts about the Neuron • Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose The nerve fibers of newborns are unmyelinated - ...
working memory
... Older adults show working memory deficiencies and slowing due to selection of irrelevant information into the contents of working memory, along with inefficient deletion of working memory contents that are no longer relevant to task performance (filtering or inhibitory ...
... Older adults show working memory deficiencies and slowing due to selection of irrelevant information into the contents of working memory, along with inefficient deletion of working memory contents that are no longer relevant to task performance (filtering or inhibitory ...
The Nervous System
... Is a result of disruption to blood supply (i.e. ischaemia) to part of the brain ...
... Is a result of disruption to blood supply (i.e. ischaemia) to part of the brain ...
Biological Check-list
... Topic 3: Biological psychology Topic overview Students must show understanding that biological psychology makes a direct link between the normal functioning of the body (physiology) and its effect on behaviour. Here we explain the role of genes, hormones and how the brain works, relating them to agg ...
... Topic 3: Biological psychology Topic overview Students must show understanding that biological psychology makes a direct link between the normal functioning of the body (physiology) and its effect on behaviour. Here we explain the role of genes, hormones and how the brain works, relating them to agg ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... A. The nervous system controls and regulates the body’s activities. It is the body's information gatherer, storage center and control system. It can respond to stimuli, transmit nerve impulses, and activate muscles. It collects information about the external conditions in relation to the body's exte ...
... A. The nervous system controls and regulates the body’s activities. It is the body's information gatherer, storage center and control system. It can respond to stimuli, transmit nerve impulses, and activate muscles. It collects information about the external conditions in relation to the body's exte ...
presentation source - Arkansas Tech Faculty Web Sites
... with age. The number of spaces increases by one unit every other year beginning at age three. Juan Pascual-Leon, 1970 The m-space capacity of individuals increases at about this rate but can vary up or down by up to two units for each age group. ...
... with age. The number of spaces increases by one unit every other year beginning at age three. Juan Pascual-Leon, 1970 The m-space capacity of individuals increases at about this rate but can vary up or down by up to two units for each age group. ...
Permeability, Osmosis, and Edema
... Dr. Drummond’s teaching point is that in the periphery, any reduction in colloid has a significant osmotic effect, because only the colloid is impermeant. The other solutes, small molecules such as electrolytes, pass freely through the membranes and therefore do not have an osmotic effect. In the br ...
... Dr. Drummond’s teaching point is that in the periphery, any reduction in colloid has a significant osmotic effect, because only the colloid is impermeant. The other solutes, small molecules such as electrolytes, pass freely through the membranes and therefore do not have an osmotic effect. In the br ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
... • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
Exercises and Tests
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
optional biology 1 study packet the brain
... The brain may be divided into many parts, but for the purpose of this unit, four main parts will be defined. They are referred to as the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. Even though they are part of one organ, they function differently and work together to control body activities. ...
... The brain may be divided into many parts, but for the purpose of this unit, four main parts will be defined. They are referred to as the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. Even though they are part of one organ, they function differently and work together to control body activities. ...