Resist. - SharpSchool
... resistance, voltage, and amperage. • A written description of the TWO ways in which the amperage can be raised and the TWO ways amperage can be lowered. ...
... resistance, voltage, and amperage. • A written description of the TWO ways in which the amperage can be raised and the TWO ways amperage can be lowered. ...
12.6 Electrical Circuits
... Electricity effectively travels at the speed of light in a conductor (186,000 miles/second) but slower in an insulating material. An electric current is a flow of charge carried by tiny particles known as electrons. Movement of charge is caused by the force from a voltage supply such as a battery or ...
... Electricity effectively travels at the speed of light in a conductor (186,000 miles/second) but slower in an insulating material. An electric current is a flow of charge carried by tiny particles known as electrons. Movement of charge is caused by the force from a voltage supply such as a battery or ...
18-6 Resistors in Parallel
... Answer to Essential Question 18.5: Each bulb has a potential difference less than the 120 V the bulb is designed for, so the bulbs are dimmer than usual. This reduces the filament temperature, lowering its resistance, which decreases the equivalent resistance of the circuit. This increases the curre ...
... Answer to Essential Question 18.5: Each bulb has a potential difference less than the 120 V the bulb is designed for, so the bulbs are dimmer than usual. This reduces the filament temperature, lowering its resistance, which decreases the equivalent resistance of the circuit. This increases the curre ...
Experiment - TerpConnect
... you have extracted the fit parameters. Ideally, you would choose meter scales that will give you the best resolution for your measurements, but you might want to consider whether the systematic errors will be easier to handle if you use the same scale for all readings. Add your fitted result to your ...
... you have extracted the fit parameters. Ideally, you would choose meter scales that will give you the best resolution for your measurements, but you might want to consider whether the systematic errors will be easier to handle if you use the same scale for all readings. Add your fitted result to your ...
the Note
... A difference in electric potential energy between two points in a circuit is the potential difference across that point. The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is the energy transferred (work must be done) when 1 coulomb charge moves from the one point to the other. Poten ...
... A difference in electric potential energy between two points in a circuit is the potential difference across that point. The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is the energy transferred (work must be done) when 1 coulomb charge moves from the one point to the other. Poten ...
Lab7-diode
... is made of two different types of semiconducting materials. On one side is n-type material which is doped (impurities implanted) with an element which causes it to have free conduction electrons. The other side is p-type material which has holes into which electrons may fit. When a voltage is placed ...
... is made of two different types of semiconducting materials. On one side is n-type material which is doped (impurities implanted) with an element which causes it to have free conduction electrons. The other side is p-type material which has holes into which electrons may fit. When a voltage is placed ...
Experiment 1-4
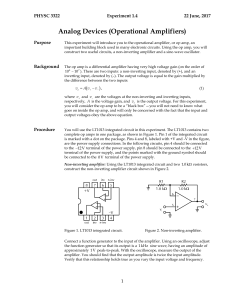
... that R 4 is a potentiometer, not a resistor. The combination of R 3 and R 4 provide negative feedback, as in the amplifier circuit. The two RC networks provide positive feedback at a frequency determined by the RC time constants. When the positive and negative feedback are precisely in balance, the ...
... that R 4 is a potentiometer, not a resistor. The combination of R 3 and R 4 provide negative feedback, as in the amplifier circuit. The two RC networks provide positive feedback at a frequency determined by the RC time constants. When the positive and negative feedback are precisely in balance, the ...
Experiment 3 ~ Ohm`s Law, Measurement of Voltage
... the standard symbols for showing a battery and a resistor in a circuit. Remember that current flows from positive to negative, representing the flow of positive charge in the wire. (Remember also that it is really the negatively charged electrons that actually do the moving!) In reality, any ...
... the standard symbols for showing a battery and a resistor in a circuit. Remember that current flows from positive to negative, representing the flow of positive charge in the wire. (Remember also that it is really the negatively charged electrons that actually do the moving!) In reality, any ...
Notes Ch 17 – Current and Resistance
... charge from a lower potential to a higher potential in order to maintain a constant potential difference (voltage) in a circuit. The maximum potential difference (voltage) of a battery is the emf of the battery. In a closed circuit, the battery creates an electric field within and parallel to the wi ...
... charge from a lower potential to a higher potential in order to maintain a constant potential difference (voltage) in a circuit. The maximum potential difference (voltage) of a battery is the emf of the battery. In a closed circuit, the battery creates an electric field within and parallel to the wi ...
Ohms Law and Basic Circuit Theory
... As you can see the basic equation associated with Ohm’s Law is V = IR. V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance. The circuit that we apply this to is a DC circuit. That is a circuit that is carrying current in only one direction as is produced by a battery. Q1) On your worksheet sk ...
... As you can see the basic equation associated with Ohm’s Law is V = IR. V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance. The circuit that we apply this to is a DC circuit. That is a circuit that is carrying current in only one direction as is produced by a battery. Q1) On your worksheet sk ...
Ohm`s Law and Resistance
... are protected by either fuses or circuit breakers which will disconnect the flow of electricity if too much demand is placed on that system. The purpose is to protect the component parts from damage from overloading. If too many electrons pass through the wiring inside the wall, or through a jumper, ...
... are protected by either fuses or circuit breakers which will disconnect the flow of electricity if too much demand is placed on that system. The purpose is to protect the component parts from damage from overloading. If too many electrons pass through the wiring inside the wall, or through a jumper, ...