The Central Nervous System
... These neurotransmitters are released from vesicles within the axon endplate and diffuse across the synapse As the neurotransmitter attaches to its receptor site, it opens sodium channels on the postsynaptic neuron This initiates an action potential in the neuron ...
... These neurotransmitters are released from vesicles within the axon endplate and diffuse across the synapse As the neurotransmitter attaches to its receptor site, it opens sodium channels on the postsynaptic neuron This initiates an action potential in the neuron ...
The Implications of Neurological Models of Memory for Learning and
... Moreover, processing and revision of knowledge were shown to be continuous and an integral part of the process of information assimilation that enables retention (Craig and Lockhart, 1972). Evidence from medical patients such as ‘HM’, for example, who, after surgical resection of the right medial te ...
... Moreover, processing and revision of knowledge were shown to be continuous and an integral part of the process of information assimilation that enables retention (Craig and Lockhart, 1972). Evidence from medical patients such as ‘HM’, for example, who, after surgical resection of the right medial te ...
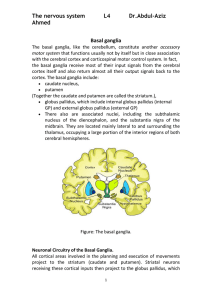
Graduate School Systems Neuroscience, MEDS 5371 2011 BASAL
... pars compacta are eliminated in Parkinson’s disease. Pars compacta has reciprocal connections with both N.subthalamicus and striatum. Pars reticulata is more ventral and in cellular composition is similar to globus pallidus. Cell types in SNr are mainly GABAergic neurons. This part projects to super ...
... pars compacta are eliminated in Parkinson’s disease. Pars compacta has reciprocal connections with both N.subthalamicus and striatum. Pars reticulata is more ventral and in cellular composition is similar to globus pallidus. Cell types in SNr are mainly GABAergic neurons. This part projects to super ...
A Brief History of Memory and Aging
... In the above quote Confucius explains that he uses previously-existing knowledge to bind meaningful information together in order to remember it. This is perhaps the first written description of how structure and organization can aid memory. Contrary to Socrates’ dismissal of the art of writing, Con ...
... In the above quote Confucius explains that he uses previously-existing knowledge to bind meaningful information together in order to remember it. This is perhaps the first written description of how structure and organization can aid memory. Contrary to Socrates’ dismissal of the art of writing, Con ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... depending on whether the brain is doing social or nonsocial tasks. • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity ...
... depending on whether the brain is doing social or nonsocial tasks. • “Default brain network” involves a large-scale brain network (cingulate cortex, mPFC, lateral PC), shows low activity for goal-related actions; it is active in social and emotional processing, mindwandering, daydreaming. • Activity ...
Jeopardy - Zion-Benton Township High School
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
... Brain & Addiction B: The limbic system is involved in emotions, learning and memory, and other functions necessary for survival. The reward circuit is part of the limbic system and is activated by pleasurable activities, such as hanging out with friends and by drugs of abuse. ...
1.In the direct pathway
... of the substantia nigra (the pars compacta) that sends dopaminesecreting nerve fibers to the caudate nucleus and putamen. The disease is characterized by (1) rigidity of much of the musculature of the body, (2) involuntary tremor of the involved areas even when the person is resting at a fixed rate ...
... of the substantia nigra (the pars compacta) that sends dopaminesecreting nerve fibers to the caudate nucleus and putamen. The disease is characterized by (1) rigidity of much of the musculature of the body, (2) involuntary tremor of the involved areas even when the person is resting at a fixed rate ...
structure and function of the neurologic system
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
... – Neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron • Signals opening of nearby Na+ channels • Membrane potential changes in the postsynaptic neuron • Generation of action potential • Action potential travels through postsynaptic neuron’s dendrite, cell body and axon to axon ending ...
presentation5
... Article focused on predicted area (motor), but the expertise effect activated other areas, some related to emotional experience Ventromedial frontal lobe Responds to pleasurable/rewarding stimuli & social judgement Parahippocampal gyrus Responds to meaningful rather than meaningless actions ...
... Article focused on predicted area (motor), but the expertise effect activated other areas, some related to emotional experience Ventromedial frontal lobe Responds to pleasurable/rewarding stimuli & social judgement Parahippocampal gyrus Responds to meaningful rather than meaningless actions ...
chapter two - Description
... Explain the role of neurotransmitters and their involvement in abnormal behavior. Identify the functions of different brain regions and their role in psychopathology. Compare and contrast the behavioral and cognitive theories and how they are used to explain the origins of mental illness. Explain th ...
... Explain the role of neurotransmitters and their involvement in abnormal behavior. Identify the functions of different brain regions and their role in psychopathology. Compare and contrast the behavioral and cognitive theories and how they are used to explain the origins of mental illness. Explain th ...
Another Efferent (outgoing) System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... Limbic Memory Regions • The limbic system also includes the inner most regions of the cortex (immediately surrounding the brainstem and subcortical structures). This inner most cortex (or “paleocortex”) is evolutionarily more ancient than the neocortex we see on the surface of the brain. Some anatom ...
... Limbic Memory Regions • The limbic system also includes the inner most regions of the cortex (immediately surrounding the brainstem and subcortical structures). This inner most cortex (or “paleocortex”) is evolutionarily more ancient than the neocortex we see on the surface of the brain. Some anatom ...
What changes in the brain when we learn?
... creation of this ever-changing brain-album is made possible because of the amazing tendency of the neuronal substrate to constantly change following new experiences. These physical changes undergo progressive stabilization in the brain, sometimes forming long-term memories. What are the physical cha ...
... creation of this ever-changing brain-album is made possible because of the amazing tendency of the neuronal substrate to constantly change following new experiences. These physical changes undergo progressive stabilization in the brain, sometimes forming long-term memories. What are the physical cha ...
Food for Thought: Essential Fatty Acid Protects
... and BAD → disinhibition of caspases → actin degradation → destabilization of postsynaptic proteins and dendrites. Although the investigators have not yet proved that each step in this cascade is necessary and sufficient for the next, the proposed cascade provides a thoughtprovoking framework of test ...
... and BAD → disinhibition of caspases → actin degradation → destabilization of postsynaptic proteins and dendrites. Although the investigators have not yet proved that each step in this cascade is necessary and sufficient for the next, the proposed cascade provides a thoughtprovoking framework of test ...
Nervous System - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... Receive information from adjoining cells or receptors and pass the information along the neuron Cell Body: Contains organelles and processes the input from dendrites Axon: Extension of the cytoplasm through which nerve impulses move ...
... Receive information from adjoining cells or receptors and pass the information along the neuron Cell Body: Contains organelles and processes the input from dendrites Axon: Extension of the cytoplasm through which nerve impulses move ...
human genome - American Federation for Aging Research
... entering what is called a senescent phase. Of course, there are also non-genetic influences on cellular aging. For example, free radicals, byproducts of the body’s natural metabolism of oxygen, are involved in a process called oxidation. Exposure to radiation is another example. ...
... entering what is called a senescent phase. Of course, there are also non-genetic influences on cellular aging. For example, free radicals, byproducts of the body’s natural metabolism of oxygen, are involved in a process called oxidation. Exposure to radiation is another example. ...
human genome - American Federation for Aging Research
... entering what is called a senescent phase. Of course, there are also non-genetic influences on cellular aging. For example, free radicals, byproducts of the body’s natural metabolism of oxygen, are involved in a process called oxidation. Exposure to radiation is another example. ...
... entering what is called a senescent phase. Of course, there are also non-genetic influences on cellular aging. For example, free radicals, byproducts of the body’s natural metabolism of oxygen, are involved in a process called oxidation. Exposure to radiation is another example. ...
diencephalon - ugur baran kasirga web pages
... Functions of the Diencephalon • The diencephalon ("interbrain") is the region of the vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. • In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon , the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube that later forms both the di ...
... Functions of the Diencephalon • The diencephalon ("interbrain") is the region of the vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. • In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon , the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube that later forms both the di ...
The changing impact of genes and environment on brain
... One approach to disentangling these complex interactions is to use stepping stones such as brain structure to help bridge the gap between genetic and environmental risk factors and behavior (Figure 1). Genes do not code for behaviors, but for the building blocks of the cells whose interactions event ...
... One approach to disentangling these complex interactions is to use stepping stones such as brain structure to help bridge the gap between genetic and environmental risk factors and behavior (Figure 1). Genes do not code for behaviors, but for the building blocks of the cells whose interactions event ...
Ch. 49 Nervous system-2012
... information about touch, pain, pressure, temperature, and the position of muscles and limbs • The thalamus directs different types of input to distinct locations Essential knowledge 3.E.2: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and ...
... information about touch, pain, pressure, temperature, and the position of muscles and limbs • The thalamus directs different types of input to distinct locations Essential knowledge 3.E.2: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and ...
Chapter 2 ciccarelli
... neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles. • Enzyme - a complex protein that is manufactured by cells. • One type specifically breaks up acetylcholine because muscle activity needs to happen rapidly, so reuptake ...
... neurotransmitters are taken back into the synaptic vesicles. • Enzyme - a complex protein that is manufactured by cells. • One type specifically breaks up acetylcholine because muscle activity needs to happen rapidly, so reuptake ...