Dopamine D, Receptors in the Rat Brain
... visible in the lateral septum (LS) and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (ZWT’). E (i.a. level, 8.2 mm), A more caudal level, where, besides the areas mentioned in 0, low binding densities are seen in the globus pallidus (GP). F (i.a. level, 7.2 mm), Receptors at a caudal level of the CPU. G ( ...
... visible in the lateral septum (LS) and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (ZWT’). E (i.a. level, 8.2 mm), A more caudal level, where, besides the areas mentioned in 0, low binding densities are seen in the globus pallidus (GP). F (i.a. level, 7.2 mm), Receptors at a caudal level of the CPU. G ( ...
Lower activation in the right frontoparietal network during a counting
... cocaine addiction. Patients were scanned over a maximum period of 2 months since they were recruited for the study. During this time, they were evaluated and diagnosed, and they could voluntary attend the counseling group sessions offered by the clinic. Prior to participation in the study, subjects ...
... cocaine addiction. Patients were scanned over a maximum period of 2 months since they were recruited for the study. During this time, they were evaluated and diagnosed, and they could voluntary attend the counseling group sessions offered by the clinic. Prior to participation in the study, subjects ...
The Dynamics of Functional Brain Networks
... shift toward greater inter-modular connectivity (BT) during the N-back task when compared to the resting state (FDR a < 0.05 for all 375 regions). Despite this global shift toward integration, the effect was most pronounced within frontoparietal, default mode, striatal, and thalamic regions (Figure ...
... shift toward greater inter-modular connectivity (BT) during the N-back task when compared to the resting state (FDR a < 0.05 for all 375 regions). Despite this global shift toward integration, the effect was most pronounced within frontoparietal, default mode, striatal, and thalamic regions (Figure ...
Glutamate-like immunoreactivity in axon terminals from the olfactory
... the piriform cortex is reduced following olfactory bulbectomy or transection of the lateral olfactory tract (Bradford and Richards, 1976). The present study was undertaken because to date there is no morphological information available regarding the neurotransmitter associated with this efferent pat ...
... the piriform cortex is reduced following olfactory bulbectomy or transection of the lateral olfactory tract (Bradford and Richards, 1976). The present study was undertaken because to date there is no morphological information available regarding the neurotransmitter associated with this efferent pat ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine and Dopamine
... – It is still not fully understood how memory formation occurs – However, research has shown that when a shortterm memory is converted into long-term storage in the hippocampus, neurons in the brain help to synthesize protein molecules and new connections between neurons are formed ...
... – It is still not fully understood how memory formation occurs – However, research has shown that when a shortterm memory is converted into long-term storage in the hippocampus, neurons in the brain help to synthesize protein molecules and new connections between neurons are formed ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... A postsynaptic neuron may have many different shaped receptor sites on its dendrites and may therefore be able to receive several different neurotransmitters. ...
... A postsynaptic neuron may have many different shaped receptor sites on its dendrites and may therefore be able to receive several different neurotransmitters. ...
Reticular formation
... Preterm birth induces persistent deleterious effects on arousal and sleep wake cycle and cortical mechanisms throughout development In the pontine tegmentum, there is an important center for horizontal gaze. The coordination of for lateral conjugate gaze is carried out at the pontine level by the pa ...
... Preterm birth induces persistent deleterious effects on arousal and sleep wake cycle and cortical mechanisms throughout development In the pontine tegmentum, there is an important center for horizontal gaze. The coordination of for lateral conjugate gaze is carried out at the pontine level by the pa ...
Total number and volume of Von Economo neurons in the cerebral
... bottlenose dolphin brain by Jacobs et al. (1971,1979, 1984), Morgane et al. (1980, 1982), Manger et al. (1998), and Hof et al. (2005) for the odontocetes and on the description of the structure of the cerebral cortex of the humpback whale brain by Hof and Van der Gucht (2007). Briefly, the cingulate ...
... bottlenose dolphin brain by Jacobs et al. (1971,1979, 1984), Morgane et al. (1980, 1982), Manger et al. (1998), and Hof et al. (2005) for the odontocetes and on the description of the structure of the cerebral cortex of the humpback whale brain by Hof and Van der Gucht (2007). Briefly, the cingulate ...
CDKL5 UK study
... testis-‐specific isoform and that the full-‐length, brain-‐expressed transcript remains to be identified. The study by Williamson et al. (2012) suggests that the only tissue that expresses CDKL5 ...
... testis-‐specific isoform and that the full-‐length, brain-‐expressed transcript remains to be identified. The study by Williamson et al. (2012) suggests that the only tissue that expresses CDKL5 ...
Alterations in white matter fractional anisotropy in subsyndromal perimenopausal depression Open Access
... reported significantly decreased FA in the right middle frontal gyrus, left lateral occipitotemporal gyrus, and subgyral and angular gyri of the right parietal lobe in young adults with MDD. Other DTI studies also revealed brain locations of decreased FA in MDD patients, namely the white matter fasc ...
... reported significantly decreased FA in the right middle frontal gyrus, left lateral occipitotemporal gyrus, and subgyral and angular gyri of the right parietal lobe in young adults with MDD. Other DTI studies also revealed brain locations of decreased FA in MDD patients, namely the white matter fasc ...
sms7new
... cerebellum may be viewed as key elements in two parallel reentrant systems that receive input from and return their influences to the cerebral cortex through discrete and separate portions of the ventrolateral thalamus. They also influence the brain stem and, ultimately, spinal mechanisms. ...
... cerebellum may be viewed as key elements in two parallel reentrant systems that receive input from and return their influences to the cerebral cortex through discrete and separate portions of the ventrolateral thalamus. They also influence the brain stem and, ultimately, spinal mechanisms. ...
Trends Towards Progress of Brains and Sense Organs
... the giants may be called adaptive in their geological period. But when the climate became successively warmer later on, the advantage of giant size became reduced and the disadvantage of the excessive size became more apparent, and finally selection could wipe out such a species. By such a change of ...
... the giants may be called adaptive in their geological period. But when the climate became successively warmer later on, the advantage of giant size became reduced and the disadvantage of the excessive size became more apparent, and finally selection could wipe out such a species. By such a change of ...
Study materials CNS
... reproduction, etc.) (3) Emotions and motivations Emotions – pleasure, anger, rage, fear (centre the limbic system) Motivations – reasons controlling our behaviour (motivation to learn, to have som hobby, to win in sport) (4) Instincts – set of motoric activities & behaviour, typical for one species. ...
... reproduction, etc.) (3) Emotions and motivations Emotions – pleasure, anger, rage, fear (centre the limbic system) Motivations – reasons controlling our behaviour (motivation to learn, to have som hobby, to win in sport) (4) Instincts – set of motoric activities & behaviour, typical for one species. ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM_(EEG).
... only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good memory is associated with well-regulated and efficie ...
... only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good memory is associated with well-regulated and efficie ...
Consciousness, Emotion, and Imagination: A Brain
... strategy, selects the most salient for possible execution. While the salience of the selected action falls below a given threshold it is held on veto, but as soon as its salience exceeds that threshold it is executed. The roles of the basal ganglia and amygdala analogues in the higher-order system a ...
... strategy, selects the most salient for possible execution. While the salience of the selected action falls below a given threshold it is held on veto, but as soon as its salience exceeds that threshold it is executed. The roles of the basal ganglia and amygdala analogues in the higher-order system a ...
Neurology-Extrapyramidal Disorders
... impaired ability to adjust the body's position) affecting face and axial mms first. Loss of postural reflexes. Not fatal but tremor, bradykinesia and rigidity deteriorate simultaneously affecting every aspect of the patient’s life. 50% suffer from depression, 80% develop dementia after 20 years if t ...
... impaired ability to adjust the body's position) affecting face and axial mms first. Loss of postural reflexes. Not fatal but tremor, bradykinesia and rigidity deteriorate simultaneously affecting every aspect of the patient’s life. 50% suffer from depression, 80% develop dementia after 20 years if t ...
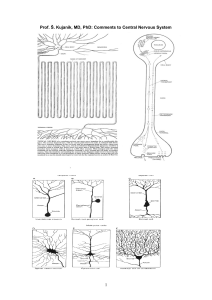
igher) order: thalamus
... No specialization Link of morphology to function or fiber type? Crudely yes Class II always associated with encapsulated mechanoreceptors Class III and IV always terminate as free endings But breaks down in detail Encapsulated endings exhibit varied morphology but all are mechanoreceptors ...
... No specialization Link of morphology to function or fiber type? Crudely yes Class II always associated with encapsulated mechanoreceptors Class III and IV always terminate as free endings But breaks down in detail Encapsulated endings exhibit varied morphology but all are mechanoreceptors ...
The Central Nervous System
... action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated ...
... action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated ...
A&P Ch 8 PowerPoint(Nervous System)
... action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated ...
... action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated ...
Project synopsis on
... EEG is relatively tolerant of subject movement, unlike most other neuroimaging techniques. There even exist methods for minimizing, and even eliminating movement artifacts in EEG data [ EEG is silent, which allows for better study of the responses to auditory stimuli. EEG does not aggravate claustro ...
... EEG is relatively tolerant of subject movement, unlike most other neuroimaging techniques. There even exist methods for minimizing, and even eliminating movement artifacts in EEG data [ EEG is silent, which allows for better study of the responses to auditory stimuli. EEG does not aggravate claustro ...
Structural divisions and functional fields in the human cerebral cortex 1
... Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex should be made on multiple criteria based on quantitative measurements of microstructural variables, such as neuron densities, neurotransmitter receptor densities, enzyme densities, etc. Because of the inter-individual variations of extent an ...
... Microstructural parcellation of the human cerebral cortex should be made on multiple criteria based on quantitative measurements of microstructural variables, such as neuron densities, neurotransmitter receptor densities, enzyme densities, etc. Because of the inter-individual variations of extent an ...
Review Inhibitory neurotransmission, plasticity and aging in the
... In accord with homeostatic plasticity, loss of sensory input results in a change in pre- and postsynaptic GABAergic and glycinergic inhibitory neurotransmission. As seen in development, age-related changes may be activity dependent. Age-related presynaptic changes in the cochlear nucleus include red ...
... In accord with homeostatic plasticity, loss of sensory input results in a change in pre- and postsynaptic GABAergic and glycinergic inhibitory neurotransmission. As seen in development, age-related changes may be activity dependent. Age-related presynaptic changes in the cochlear nucleus include red ...