What Are Emotional States, and Why Do We
... noxious stimuli. 4. Communication. Monkeys, for example, may communicate their emotional state to others, for instance by making face expressions (such as an open-mouth threat to indicate the extent to which they are willing to compete for resources), and this may influence the behaviour of other a ...
... noxious stimuli. 4. Communication. Monkeys, for example, may communicate their emotional state to others, for instance by making face expressions (such as an open-mouth threat to indicate the extent to which they are willing to compete for resources), and this may influence the behaviour of other a ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... Conscious: reach cerebral cortex Unconscious: do not reach cerebral cortex Sensations from body reach the opposite side of the brain ...
... Conscious: reach cerebral cortex Unconscious: do not reach cerebral cortex Sensations from body reach the opposite side of the brain ...
12 - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... • Conscious perception of sensation • Voluntary initiation and control of movement • Capabilities associated with higher mental processing (memory, logic, judgment, etc.) • Loss of consciousness signal that brain function impaired – Fainting or syncopy – brief – Coma – extended period © 2013 Pearson ...
... • Conscious perception of sensation • Voluntary initiation and control of movement • Capabilities associated with higher mental processing (memory, logic, judgment, etc.) • Loss of consciousness signal that brain function impaired – Fainting or syncopy – brief – Coma – extended period © 2013 Pearson ...
pdf, 1 MiB - Infoscience
... a key place in establishing the structural basis of the human connectome. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been introduced to document and measure in vivo anatomical connectivity between regions (Jbabdi and Johansen-Berg, 2011). DTI offers an overall view of brain anatomy, including the pattern an ...
... a key place in establishing the structural basis of the human connectome. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been introduced to document and measure in vivo anatomical connectivity between regions (Jbabdi and Johansen-Berg, 2011). DTI offers an overall view of brain anatomy, including the pattern an ...
Sensory5
... PAG (in midbrain) raphe n. (in medulla) – uses 5-HT projections to dorsal horn (in SC). 5-HT suppresses pain transmission in dorsal horn by: i. Inhibiting ascending AL system pain projection neurons. ii. Exciting inhibitory (enkephalin-producing) interneurons in dorsal horn. F. Thalamic Nuclei and ...
... PAG (in midbrain) raphe n. (in medulla) – uses 5-HT projections to dorsal horn (in SC). 5-HT suppresses pain transmission in dorsal horn by: i. Inhibiting ascending AL system pain projection neurons. ii. Exciting inhibitory (enkephalin-producing) interneurons in dorsal horn. F. Thalamic Nuclei and ...
Presentation
... What fraction of regenerated serotonin axons survive long-term and do they attain normal morphology and spatial distribution? ~90% of the regenerated axons survive for 6 months after PCA treatment: They survive at the same rate as uninjured serotonin axons. Furthermore, their distribution and shape ...
... What fraction of regenerated serotonin axons survive long-term and do they attain normal morphology and spatial distribution? ~90% of the regenerated axons survive for 6 months after PCA treatment: They survive at the same rate as uninjured serotonin axons. Furthermore, their distribution and shape ...
48nervous
... cycle, their wheel-turning activity (indicated by the dark bars) occurred at roughly the same time every day. However, when they were kept in constant darkness, their activity phase began about 21 minutes later each day. ...
... cycle, their wheel-turning activity (indicated by the dark bars) occurred at roughly the same time every day. However, when they were kept in constant darkness, their activity phase began about 21 minutes later each day. ...
The limbic system. A maze on the essentials: memory, learning and
... thalamus, through the cingulate gyrus. (Figure 2) Today, the limbic system is considered a set of structures interconnected among themselves and with other areas, in the brain and in the body. It is located in the medial faces of both cerebral hemispheres and their functions are multiple and complex ...
... thalamus, through the cingulate gyrus. (Figure 2) Today, the limbic system is considered a set of structures interconnected among themselves and with other areas, in the brain and in the body. It is located in the medial faces of both cerebral hemispheres and their functions are multiple and complex ...
Mircea Steriade
... activity and conditioned reflexes. He bitterly questioned such a possibility, arguing that Ivan Pavlov had taught us that the cerebral cortex governs subcortical structures and not the other way around. If this man were aware of my present views according to which, indeed, the cortex exerts a powerf ...
... activity and conditioned reflexes. He bitterly questioned such a possibility, arguing that Ivan Pavlov had taught us that the cerebral cortex governs subcortical structures and not the other way around. If this man were aware of my present views according to which, indeed, the cortex exerts a powerf ...
CNS - Algonquin College
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
Unit 22.1: The Nervous System
... drug. Over time, a drug user may need more of the drug to get the desired effect. This can lead to drug overdose and death. Disorders of the Nervous System There are several different types of problems that can affect the nervous system. • Vascular disorders involve problems with blood flow. For exa ...
... drug. Over time, a drug user may need more of the drug to get the desired effect. This can lead to drug overdose and death. Disorders of the Nervous System There are several different types of problems that can affect the nervous system. • Vascular disorders involve problems with blood flow. For exa ...
Neural Mechanisms of Subclinical Depressive
... change from baseline. The same high-pass filtering applied to the functional data was applied to the GLM. Group-wise activation images were calculated by a mixed effects analysis using Bayesian estimation techniques, FMRIB Local Analysis of Mixed Effects [FILM, 41]. Group-level models, with mean-cen ...
... change from baseline. The same high-pass filtering applied to the functional data was applied to the GLM. Group-wise activation images were calculated by a mixed effects analysis using Bayesian estimation techniques, FMRIB Local Analysis of Mixed Effects [FILM, 41]. Group-level models, with mean-cen ...
Nervous System - Lakeridge Health
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
... medulla, more commonly referred to as white matter. This is an area of myelinated axons that interconnect neurons both within the nervous system and with other body parts. The surface of the cerebral cortex is marked by ridges and grooves (gyri) and is divided into lobes by spaces called sulci. Ther ...
Topographic Maps are Fundamental to Sensory
... Biologically important information often results from an assessment of how input coming in from one focus of receptors is different from that coming in from adjoining sets of receptors. As Hartline [33] and Kuffler [52] first demonstrated, the center-surround organization of receptive fields occurs ...
... Biologically important information often results from an assessment of how input coming in from one focus of receptors is different from that coming in from adjoining sets of receptors. As Hartline [33] and Kuffler [52] first demonstrated, the center-surround organization of receptive fields occurs ...
Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance
... particular object was significantly greater than that for other objects (p <0.01, t-test). Seventeen cells (31%) were moderately selective, in the sense that two or three objects were equally effective, but ten cells (18%) were nonselective. In contrast, selectivity in position was rarely observed i ...
... particular object was significantly greater than that for other objects (p <0.01, t-test). Seventeen cells (31%) were moderately selective, in the sense that two or three objects were equally effective, but ten cells (18%) were nonselective. In contrast, selectivity in position was rarely observed i ...
Connection Patterns Distinguish 3 Regions of Human Parietal Cortex
... area Opt, and some transitional opercular regions in the most ventral part of the IPL are also recognized. Distinct functional and anatomical regions, MIP and PE, occupy the medial bank of the IPS and the superior parietal lobule (SPL). The functional specializations of these regions have been inves ...
... area Opt, and some transitional opercular regions in the most ventral part of the IPL are also recognized. Distinct functional and anatomical regions, MIP and PE, occupy the medial bank of the IPS and the superior parietal lobule (SPL). The functional specializations of these regions have been inves ...
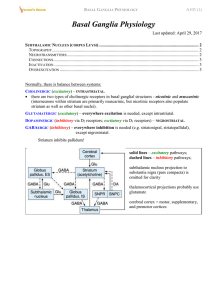
A103 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Normally, there is balance between systems: CHOLINERGIC (excitatory) – INTRASTRIATAL. there are two types of cholinergic receptors in basal ganglial structures - nicotinic and muscarinic (interneurons within striatum are primarily muscarinic, but nicotinic receptors also populate striatum as well ...
... Normally, there is balance between systems: CHOLINERGIC (excitatory) – INTRASTRIATAL. there are two types of cholinergic receptors in basal ganglial structures - nicotinic and muscarinic (interneurons within striatum are primarily muscarinic, but nicotinic receptors also populate striatum as well ...
Ventromedial frontal cortex mediates affective shifting in
... lesions of the ventromedial frontal (VMF) cortex. An early study of this kind of stimulus±reward learning in brain-damaged humansÐand the most informative to dateÐwas carried out by Rolls and colleagues (Rolls et al., 1994). They examined the relationship between changes in day-to-day behaviour and ...
... lesions of the ventromedial frontal (VMF) cortex. An early study of this kind of stimulus±reward learning in brain-damaged humansÐand the most informative to dateÐwas carried out by Rolls and colleagues (Rolls et al., 1994). They examined the relationship between changes in day-to-day behaviour and ...
Brain Facts: A Primer On The Brain And Nervous System
... with nonidentical siblings of getting the same disease; however, if ...
... with nonidentical siblings of getting the same disease; however, if ...
Attention - Biology Courses Server
... consciousness (NCC) • Challenges of interpreting NCC study data – What is “minimal” brain activity sufficient for conscious experience? – Is the neural activity a prerequisite for conscious experience or consequence of the experience but not NCC? – Can attention be confounded with awareness? • The “ ...
... consciousness (NCC) • Challenges of interpreting NCC study data – What is “minimal” brain activity sufficient for conscious experience? – Is the neural activity a prerequisite for conscious experience or consequence of the experience but not NCC? – Can attention be confounded with awareness? • The “ ...
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
... • The outer layer, or cortex, secretes cortical steroids. • Cortical steroids increase resistance to stress, promote muscle development, and make the liver release stored sugar to provide ...
... • The outer layer, or cortex, secretes cortical steroids. • Cortical steroids increase resistance to stress, promote muscle development, and make the liver release stored sugar to provide ...
Lecoq J, Savall J, Vucinic D, Grewe BF, Kim H, Li
... anesthetized mice expressing the red fluorophore TdTomato 10 in parvalbumin interneurons. To illustrate flexibility of usage, we examined a pair of neocortical areas (motor area M1 and somatosensory area S1) separated by ~3.5 mm (Fig. 2a), and another pair (visual areas V1 and LM) that were adjacent ...
... anesthetized mice expressing the red fluorophore TdTomato 10 in parvalbumin interneurons. To illustrate flexibility of usage, we examined a pair of neocortical areas (motor area M1 and somatosensory area S1) separated by ~3.5 mm (Fig. 2a), and another pair (visual areas V1 and LM) that were adjacent ...
Cortical and basal ganglia contributions to habit learning and
... time, patience and resources than studies of initial learnCorresponding author: Ashby, F.G. ([email protected]). ...
... time, patience and resources than studies of initial learnCorresponding author: Ashby, F.G. ([email protected]). ...
Author`s personal copy
... range of functional capacities than mere ‘association’, including transforming sensory information into motor plans [19,20]. Closer scrutiny reveals that these principles may not hold in these areas. In this review, we explore the extent to which these organizational principles generalize (or fail t ...
... range of functional capacities than mere ‘association’, including transforming sensory information into motor plans [19,20]. Closer scrutiny reveals that these principles may not hold in these areas. In this review, we explore the extent to which these organizational principles generalize (or fail t ...