Power Inverters - Personal WWW Pages
... First 5 ms on-period when vL = 340 V and initially iL = 0 A iL = 34 - 34 e-200t and at 5ms, iL = 21.5A First 5 ms zero-period when vL = 0 V iL = 21.5 e-200t and at 5ms, iL =7.9A Second 5 ms on-period when vL = -340 V iL = -34 + (34+7.9) e-200t with iL = 0 at 1 ms and ending with iL = -18.6 A Second ...
... First 5 ms on-period when vL = 340 V and initially iL = 0 A iL = 34 - 34 e-200t and at 5ms, iL = 21.5A First 5 ms zero-period when vL = 0 V iL = 21.5 e-200t and at 5ms, iL =7.9A Second 5 ms on-period when vL = -340 V iL = -34 + (34+7.9) e-200t with iL = 0 at 1 ms and ending with iL = -18.6 A Second ...
Introduction to Short Circuit Analysis
... To select the appropriate fuse and breaker/relay settings, it's necessary to perform a short circuit and coordination analysis for the electrical system. The process begins with developing a single line diagram for the electrical distribution system. Equipment and conductor impedances, operating vol ...
... To select the appropriate fuse and breaker/relay settings, it's necessary to perform a short circuit and coordination analysis for the electrical system. The process begins with developing a single line diagram for the electrical distribution system. Equipment and conductor impedances, operating vol ...
ec1009 electron devices lab laboratory manual
... late more than 15 minutes more than once) will receive 10 point reductions in their grades for each occurrence following the first. 7. Reports Due Dates: Reports are due one week after completion of the corresponding lab. 8. Systems of Tests: Regular laboratory class work over the full semester will ...
... late more than 15 minutes more than once) will receive 10 point reductions in their grades for each occurrence following the first. 7. Reports Due Dates: Reports are due one week after completion of the corresponding lab. 8. Systems of Tests: Regular laboratory class work over the full semester will ...
Servay 7th Edition_Chapter33
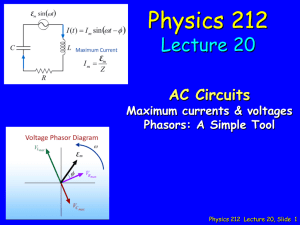
... called the positive direction. Between points a and b, the current is decreasing in magnitude but is still in the positive direction. At point b, the current is momentarily zero; it then begins to increase in the negative direction between points b and c. At point c, the current has reached its maxi ...
... called the positive direction. Between points a and b, the current is decreasing in magnitude but is still in the positive direction. At point b, the current is momentarily zero; it then begins to increase in the negative direction between points b and c. At point c, the current has reached its maxi ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... in which magnitude and angle are fixed. Since voltage and current signal of a power system are expressed using a phasor, accuracy of an algorithm using a phasor depends on accuracy of phasor estimation. Discrete Fourier, Walsh, Harr, Least Square or Kalman filtering have been used for phasor estimat ...
... in which magnitude and angle are fixed. Since voltage and current signal of a power system are expressed using a phasor, accuracy of an algorithm using a phasor depends on accuracy of phasor estimation. Discrete Fourier, Walsh, Harr, Least Square or Kalman filtering have been used for phasor estimat ...
Standing wave ratio

In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line.The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced ""viswar""). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 denotes an AC voltage due to standing waves along the transmission line reaching a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line. The SWR can as well be defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength, or the magnetic field strength. Neglecting transmission line loss, these ratios are identical.The power standing wave ratio (PSWR) is defined as the square of the VSWR, however this terminology has no physical relation to actual powers involved in transmission.The SWR can be measured with an instrument called an SWR meter. Since SWR is defined relative to the transmission line's characteristic impedance, the SWR meter must be constructed for that impedance; in practice most transmission lines used in these applications are coaxial cables with an impedance of either 50 or 75 ohms. Checking the SWR is a standard procedure in a radio station, for instance, to verify impedance matching of the antenna to the transmission line (and transmitter). Unlike connecting an impedance analyzer (or ""impedance bridge"") directly to the antenna (or other load), the SWR does not measure the actual impedance of the load, but quantifies the magnitude of the impedance mismatch just performing a measurement on the transmitter side of the transmission line.