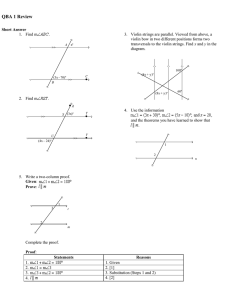
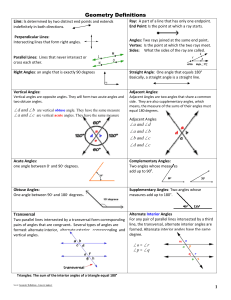
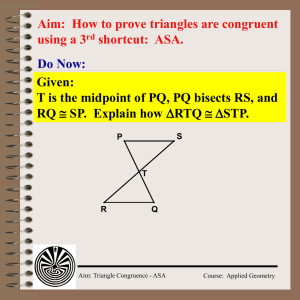
PRESENTATION NAME - Fay's Mathematics [licensed for non
... contains a point in the interior of the polygon. – Extend each side of the polygon, if no part of the extended LINE lies inside the polygon then it is convex. ...
... contains a point in the interior of the polygon. – Extend each side of the polygon, if no part of the extended LINE lies inside the polygon then it is convex. ...
Chapter 5
... An indirect proof is generally used when you need to prove something is not true. Suppose that you would like to prove two triangles are not congruent. We have plenty of methods to prove they are congruent but none so far that prove the opposite. To solve Indirectly begin by Assuming the opposite of ...
... An indirect proof is generally used when you need to prove something is not true. Suppose that you would like to prove two triangles are not congruent. We have plenty of methods to prove they are congruent but none so far that prove the opposite. To solve Indirectly begin by Assuming the opposite of ...