Geo 1 and 2 review answers
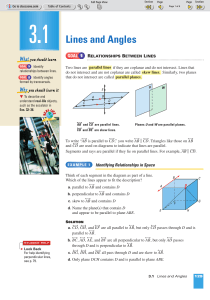
... bisect – To divide a segment or angle into two congruent parts. bisector – The line that divides the segment or angle into two congruent parts. collinear – Lying on the same line. congruent – The same size and shape. congruent angles – Angles that have the same measure. congruent segments – Segments ...
... bisect – To divide a segment or angle into two congruent parts. bisector – The line that divides the segment or angle into two congruent parts. collinear – Lying on the same line. congruent – The same size and shape. congruent angles – Angles that have the same measure. congruent segments – Segments ...
Do not write on this paper: Review work (Wednesday May 22 2013
... Lucinda wants to build a square sandbox, but has no way of measuring angles. Explain how she can make sure that the sandbox is square by only measuring length. a. Arrange four equal-length sides so the diagonals bisect each other. b. Arrange four equal-length sides so the diagonals are equal lengths ...
... Lucinda wants to build a square sandbox, but has no way of measuring angles. Explain how she can make sure that the sandbox is square by only measuring length. a. Arrange four equal-length sides so the diagonals bisect each other. b. Arrange four equal-length sides so the diagonals are equal lengths ...
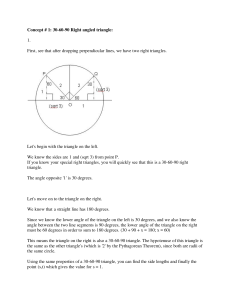
Exterior Angles
... Recall that interior means inside and that exterior means outside. So, an exterior angle is an angle on the outside of a polygon. An exterior angle is formed by extending a side of the polygon. ...
... Recall that interior means inside and that exterior means outside. So, an exterior angle is an angle on the outside of a polygon. An exterior angle is formed by extending a side of the polygon. ...
Theorems here
... In a compound event in which the first event may occur, n1 different ways, the second event may occur in n2 different ways and so on, and the k-th event may occur in nk different ways, the total number of ways the compound event may occur is n1*n2*n3 ..*nk The total number of permutations of a set o ...
... In a compound event in which the first event may occur, n1 different ways, the second event may occur in n2 different ways and so on, and the k-th event may occur in nk different ways, the total number of ways the compound event may occur is n1*n2*n3 ..*nk The total number of permutations of a set o ...