Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
Minireview: Global Regulation and Dynamics of Ribonucleic Acid
... 18, 20). For example, in the case of hormonal responses, one can imagine how rapidly responding changes at the level of RNA stability provide an advantage to multicellular systems (48). An important feature of RNA networks is that a significant proportion of cellular proteins encode RBPs that in tur ...
... 18, 20). For example, in the case of hormonal responses, one can imagine how rapidly responding changes at the level of RNA stability provide an advantage to multicellular systems (48). An important feature of RNA networks is that a significant proportion of cellular proteins encode RBPs that in tur ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... environmental change for achieving defined substrate specificity. Substitution, deletion and insertion are the available mechanisms for the purpose of evolution of which the former is comparable among different domains as it happens at locus specific positions. In these study six orthologous sets of ...
... environmental change for achieving defined substrate specificity. Substitution, deletion and insertion are the available mechanisms for the purpose of evolution of which the former is comparable among different domains as it happens at locus specific positions. In these study six orthologous sets of ...
Text S1 Y2H Interactome Mapping The literature was curated to
... therefore included in our collection. However, further study suggests that they are likely to be essential in vitro [41,42]. They were probably not identified in the Sassetti study for technical ...
... therefore included in our collection. However, further study suggests that they are likely to be essential in vitro [41,42]. They were probably not identified in the Sassetti study for technical ...
The Structure of Proteins
... such as the following. One hexamethylenetetra- fa~tors;2~12~ mine molecule and one pentaerythritol molecule the oxygens of certain of the triazine rings, (2) contain the same bonds as four cyclized glycine the multiple paths of linkage between atoms in the residues and three methane molecules; hence ...
... such as the following. One hexamethylenetetra- fa~tors;2~12~ mine molecule and one pentaerythritol molecule the oxygens of certain of the triazine rings, (2) contain the same bonds as four cyclized glycine the multiple paths of linkage between atoms in the residues and three methane molecules; hence ...
Assembly and function of cell surface structures of the
... Ligated RNA-reverse transcriptase PCR (LRRT-PCR, Mandl et al., 1991) was performed with total A. ambivalens RNA in order to confirm the transcription start site independently, to map the transcriptional terminators, to demonstrate that the internal transcription terminator is active, and to show tha ...
... Ligated RNA-reverse transcriptase PCR (LRRT-PCR, Mandl et al., 1991) was performed with total A. ambivalens RNA in order to confirm the transcription start site independently, to map the transcriptional terminators, to demonstrate that the internal transcription terminator is active, and to show tha ...
Detection of RNA-protein complex in vaccinia virus core in vitro
... with vaccinia virus, the prototype of the family, have contributed to our understanding of the strategies used by these viruses to replicate and express their genome. The infection of tissue culture cells with vaccinia virus results in profound cytopathic effects, such as changes in membrane permeab ...
... with vaccinia virus, the prototype of the family, have contributed to our understanding of the strategies used by these viruses to replicate and express their genome. The infection of tissue culture cells with vaccinia virus results in profound cytopathic effects, such as changes in membrane permeab ...
Passage 36
... Protein synthesis begins when the gene encoding a protein is activated. The gene’s sequence of nucleotides is transcribed into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA), which reproduces the information contained in that (5) sequence. Transported outside the nucleus to the cytoplasm, the mRNA is translated ...
... Protein synthesis begins when the gene encoding a protein is activated. The gene’s sequence of nucleotides is transcribed into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA), which reproduces the information contained in that (5) sequence. Transported outside the nucleus to the cytoplasm, the mRNA is translated ...
Teaching old NCATs new tricks: using non
... Although local synthesis of a number of candidate proteins has been described in neurons [24], FUNCAT can be applied to study global protein synthesis in specific subcellular compartments, such as dendrites and axonal growth cones. In the first demonstration of FUNCAT in neurons, Dieterich et al. sh ...
... Although local synthesis of a number of candidate proteins has been described in neurons [24], FUNCAT can be applied to study global protein synthesis in specific subcellular compartments, such as dendrites and axonal growth cones. In the first demonstration of FUNCAT in neurons, Dieterich et al. sh ...
The PRA1 Gene Family in Arabidopsis1[W]
... AtPRA1 Proteins Can Dimerize in Accordance with Their Phylogenetic Distribution ...
... AtPRA1 Proteins Can Dimerize in Accordance with Their Phylogenetic Distribution ...
Astrobiology
... – A differential selection process. What is this known as? • Natural Selection – more replicators are made each generation than can survive. The best adapted, to their environment, replicators are typically those that survive. ...
... – A differential selection process. What is this known as? • Natural Selection – more replicators are made each generation than can survive. The best adapted, to their environment, replicators are typically those that survive. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... Summary 28.3 Regulation of Gene expression in Eukaryotes Hormones affect the regulation of gene expression in one of two ways. Steroid hormones interact directly with intracellular receptors that are DNA-binding regulatory proteins; binding of the hormone has either positive or negative effects o ...
... Summary 28.3 Regulation of Gene expression in Eukaryotes Hormones affect the regulation of gene expression in one of two ways. Steroid hormones interact directly with intracellular receptors that are DNA-binding regulatory proteins; binding of the hormone has either positive or negative effects o ...
Short review - BioPublisher
... outside a cell - including cell wall, extracellular matrix and extracellular space - in an organism. Recently many efforts have been made to identify secretomes as these proteins have both potential applications in environmental industry and biomedicine (Lum and Min, 2011; Makridakis and Vlahou, 201 ...
... outside a cell - including cell wall, extracellular matrix and extracellular space - in an organism. Recently many efforts have been made to identify secretomes as these proteins have both potential applications in environmental industry and biomedicine (Lum and Min, 2011; Makridakis and Vlahou, 201 ...
Glucose transport proteins
... These transport proteins mediate facilitated transport, that is, they can only transport glucose (or fructose) from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. The sugar is bound by the protein, a flip-flop mechanism reverses the membrane direction of the sugar-protein complex, the ...
... These transport proteins mediate facilitated transport, that is, they can only transport glucose (or fructose) from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. The sugar is bound by the protein, a flip-flop mechanism reverses the membrane direction of the sugar-protein complex, the ...
没有幻灯片标题
... 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The b ...
... 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The b ...
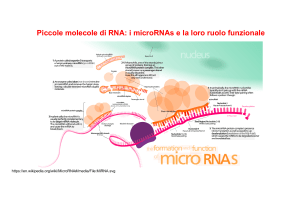
Types of RNA
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information about a protein sequence to the ribosomes, the protein synthesis factories in the cell. It is coded so that every three nucleotides (a codon) correspond o one amino acid. In eukaryotic cells, once precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) has been transcribed from DNA, it is ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information about a protein sequence to the ribosomes, the protein synthesis factories in the cell. It is coded so that every three nucleotides (a codon) correspond o one amino acid. In eukaryotic cells, once precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) has been transcribed from DNA, it is ...
Protein thermal stability: insights from atomic displacement
... possess better packed interiors than their mesophilic counterparts, leading to lesser overall flexibility and a corresponding reduction in surface-to-volume ratio. These observations prompted an analysis of B values reported in high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of mesophilic and thermophilic ...
... possess better packed interiors than their mesophilic counterparts, leading to lesser overall flexibility and a corresponding reduction in surface-to-volume ratio. These observations prompted an analysis of B values reported in high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of mesophilic and thermophilic ...
Genetic Analysis of the Large Subunit of Yeast Transcription Factor
... and TFA1-391540 (described above), and cloned into the BamHI-HindIII backbone of pZM41, an integrating vector with a URA3 selectable marker. The PCR-amplified TFA1 fragment contains a BamHI restriction site just upstream of the TFA1 ATG, a BglII restriction site 183 bp downstream of the ATG, and a H ...
... and TFA1-391540 (described above), and cloned into the BamHI-HindIII backbone of pZM41, an integrating vector with a URA3 selectable marker. The PCR-amplified TFA1 fragment contains a BamHI restriction site just upstream of the TFA1 ATG, a BglII restriction site 183 bp downstream of the ATG, and a H ...
Adding Protein Context to the Human Protein-Protein
... We associated an interaction with a tissue when both interactors are expressed in the same tissue (e.g. ‘‘lung’’). Given a term of a functional ontology, we associated an interaction with this function when both interactors are annotated with either the given functional term or with children of it i ...
... We associated an interaction with a tissue when both interactors are expressed in the same tissue (e.g. ‘‘lung’’). Given a term of a functional ontology, we associated an interaction with this function when both interactors are annotated with either the given functional term or with children of it i ...
RACC BIO transcription and translation
... o Are additions or losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene that are not in multiples of three • These change the reading frame and are called Frameshift mutations • All nucleotides downstream from the mutation will be improperly grouped. The codons are not read properly and create extensive missense an ...
... o Are additions or losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene that are not in multiples of three • These change the reading frame and are called Frameshift mutations • All nucleotides downstream from the mutation will be improperly grouped. The codons are not read properly and create extensive missense an ...
New insight into plant intramembrane proteases
... number of transmembrane segments but also consensus sequences of evolutionarily conserved motifs resulted in proposition of subdivision of the rhomboid family to six different phylogenetic clades: PARL, secretase-A, secretase-B, mixed secretases, iRhoms and mixed inactive homologs. According to this ...
... number of transmembrane segments but also consensus sequences of evolutionarily conserved motifs resulted in proposition of subdivision of the rhomboid family to six different phylogenetic clades: PARL, secretase-A, secretase-B, mixed secretases, iRhoms and mixed inactive homologs. According to this ...
ppt file
... acceptors be hydrogen bonded to something, be it solvent, protein backbone, or protein side chains. Alan Fersht has called this concept “hydrogen bond inventory”. This is important when trying to understand the effect of mutations that impact hydrogen bonding, because removal of one partner of a hyd ...
... acceptors be hydrogen bonded to something, be it solvent, protein backbone, or protein side chains. Alan Fersht has called this concept “hydrogen bond inventory”. This is important when trying to understand the effect of mutations that impact hydrogen bonding, because removal of one partner of a hyd ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.










![The PRA1 Gene Family in Arabidopsis1[W]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007975965_1-68ff328dd33afa57eaf37e2f089459b4-300x300.png)