Optimizing the Heathkit HW-101, SB100-102 Transceivers
... If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too far from the filter passband, the receive and transmit signals will lack “lows” but the opposite sideband rejection will be high. If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too close to the filter center frequency, the receive and transmit signal ...
... If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too far from the filter passband, the receive and transmit signals will lack “lows” but the opposite sideband rejection will be high. If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too close to the filter center frequency, the receive and transmit signal ...
Crystal Size Reduction
... Lower frequencies are available in these small packages by using different crystal cut types that use a different resonant mode. This often comes at the expense of poorer frequency stability. The SL‐cut is an example that uses a face shear vibration mode. ...
... Lower frequencies are available in these small packages by using different crystal cut types that use a different resonant mode. This often comes at the expense of poorer frequency stability. The SL‐cut is an example that uses a face shear vibration mode. ...
Livewire - Tutorial 2
... two signals at once. Each signal (or channel) has both a positive (+) and a negative (-) pin. The oscilloscope will record the potential difference between these two pins for each channel. Wire up the first signal by connecting the + (positive) pin for the first channel (Ch.1) to the top of resistor ...
... two signals at once. Each signal (or channel) has both a positive (+) and a negative (-) pin. The oscilloscope will record the potential difference between these two pins for each channel. Wire up the first signal by connecting the + (positive) pin for the first channel (Ch.1) to the top of resistor ...
Current
... tends to decrease with age (as do many other things). It may be quite normal for a 60-year-old to hear a maximum of 16,000 Hz. We call signals in the range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz audio frequencies because the human ear can sense sounds in this range ...
... tends to decrease with age (as do many other things). It may be quite normal for a 60-year-old to hear a maximum of 16,000 Hz. We call signals in the range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz audio frequencies because the human ear can sense sounds in this range ...
24 Hour Mechanical Time Switch
... to permanent ON by sliding it to the left. This will align the arrow head to the 1 symbol, and the green flag will now be fully visible on the right. • For normal automatic mode, the main slider can be set to the middle position with the arrow head pointing at the timer symbol. • The main slider o ...
... to permanent ON by sliding it to the left. This will align the arrow head to the 1 symbol, and the green flag will now be fully visible on the right. • For normal automatic mode, the main slider can be set to the middle position with the arrow head pointing at the timer symbol. • The main slider o ...
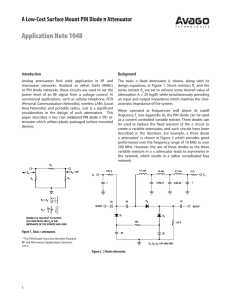
Application Note 1048 A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator Introduction Background
... diode become very complex; it will generally behave as a frequency‑dependent resistance shunted by a very large frequency and current dependent inductance or capacitance. Additionally, distortion performance will usually be very poor when operating in this frequency range. For the HSMP‑3810 series o ...
... diode become very complex; it will generally behave as a frequency‑dependent resistance shunted by a very large frequency and current dependent inductance or capacitance. Additionally, distortion performance will usually be very poor when operating in this frequency range. For the HSMP‑3810 series o ...
A CNN Implementation of a Hysteresis Chaos Generator
... proposed. The new realization consists of only RC elements and op amps. Since no inductor is used, this realization can be easily implemented in a chip. An active inductor, consisting of three resistors, one capacitor and an op amp, replaces the passive inductor. In the following sections, some back ...
... proposed. The new realization consists of only RC elements and op amps. Since no inductor is used, this realization can be easily implemented in a chip. An active inductor, consisting of three resistors, one capacitor and an op amp, replaces the passive inductor. In the following sections, some back ...
EE2301 Advanced Tutorial Problems Kirchhoff`s Current Law
... Since v3 = -50i1 = -87.5 V, no further information is required to determine its value. The 90-V source is absorbing (90)(i1) = 157.5 W of power and the dependent source is absorbing (1.8v3)(i1) = -275.6 W of power. Therefore, none of the conditions specified in (a) to (d) can be met by this circuit. ...
... Since v3 = -50i1 = -87.5 V, no further information is required to determine its value. The 90-V source is absorbing (90)(i1) = 157.5 W of power and the dependent source is absorbing (1.8v3)(i1) = -275.6 W of power. Therefore, none of the conditions specified in (a) to (d) can be met by this circuit. ...
P2.3 - School
... Pupils to then draw and write down the circuit rules for parallel and series circuits. (Resistance will be reiterated after Ohms Law). Pupils then construct series and parallel circuits using the components inc Rheostats, bulbs, and LEDS. Pupils to measure current and voltage to prove these circuit ...
... Pupils to then draw and write down the circuit rules for parallel and series circuits. (Resistance will be reiterated after Ohms Law). Pupils then construct series and parallel circuits using the components inc Rheostats, bulbs, and LEDS. Pupils to measure current and voltage to prove these circuit ...
Experiment #5 Report
... creation has pushed technology to a whole new level of electronics, one of the biggest being the computers we use today which have millions of tiny transistors placed into a very tiny area. Being able to understand how transistors work should be the goal of every electrical engineer. While engineers ...
... creation has pushed technology to a whole new level of electronics, one of the biggest being the computers we use today which have millions of tiny transistors placed into a very tiny area. Being able to understand how transistors work should be the goal of every electrical engineer. While engineers ...
SGA5286Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
... responsibility is assumed by RF Micro Devices, Inc. ("RFMD") for its use, nor for any infringement of patents, or other rights of third parties, resulting from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of RFMD. RFMD reserves the right to change comp ...
Part I: Electric Currents
... potential expressed in volts (symbol V), and R is the electrical resistance expressed in the units ohms (symbol ). Diagramming Electrical Circuits: The components in an electric circuit can be represented by symbols rather than trying to draw facsimiles of the actual objects. These symbols are used ...
... potential expressed in volts (symbol V), and R is the electrical resistance expressed in the units ohms (symbol ). Diagramming Electrical Circuits: The components in an electric circuit can be represented by symbols rather than trying to draw facsimiles of the actual objects. These symbols are used ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.