Ch9-12
... A pair of differential signals can be generated, among other ways, by a transformer. Differential signals have the property that they share the same average value to ground and are equal in magnitude but opposite in phase. CH 10 Differential Amplifiers ...
... A pair of differential signals can be generated, among other ways, by a transformer. Differential signals have the property that they share the same average value to ground and are equal in magnitude but opposite in phase. CH 10 Differential Amplifiers ...
Automatic Transfer Switch Protection
... New considerations for ATSs requirements of UL 1008. Courtesy: Cooper came to the forefront with the Bussmann, division of Cooper Industries plc addition of selective coordination requirements for emergency systems, time ratings are limited and also usulegally required standby systems, and ally carr ...
... New considerations for ATSs requirements of UL 1008. Courtesy: Cooper came to the forefront with the Bussmann, division of Cooper Industries plc addition of selective coordination requirements for emergency systems, time ratings are limited and also usulegally required standby systems, and ally carr ...
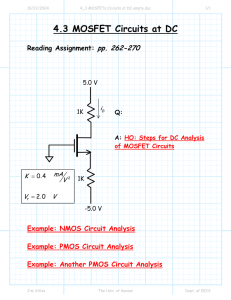
Chapter 2. PV ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 2.1 I
... A comparison of the effect of shunt resistance on modeled I-V behavior is illustrated in Figures 9 and 10 for a typical module, at irradiance levels of 1030 W/m2 and 125 W/m2. At 1030 W/m2, the differences between the two I-V curves are barely perceptible. One curve assumes infinite shunt resistance ...
... A comparison of the effect of shunt resistance on modeled I-V behavior is illustrated in Figures 9 and 10 for a typical module, at irradiance levels of 1030 W/m2 and 125 W/m2. At 1030 W/m2, the differences between the two I-V curves are barely perceptible. One curve assumes infinite shunt resistance ...
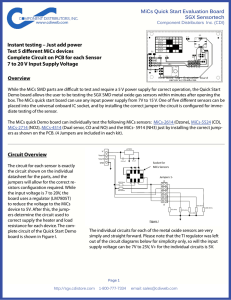
TD-5 Timing Relay
... linear function of the rheostat setting, since RP gives a parallel resistive path. This has the effect of expanding the scale for short times and thereby permitting more accurate settings. ...
... linear function of the rheostat setting, since RP gives a parallel resistive path. This has the effect of expanding the scale for short times and thereby permitting more accurate settings. ...
The SR560 (manual - Stanford Research Systems
... range from 0.03 Hz to 1 MHz, and the slope of the rolloff is shown by one of the four ROLLOFF LED’s. When the filter section is configured as band-pass (iii), the cutoff frequencies are illuminated by two LED’s. The frequency setting on the left marks the cutoff for the high-pass filter, and the set ...
... range from 0.03 Hz to 1 MHz, and the slope of the rolloff is shown by one of the four ROLLOFF LED’s. When the filter section is configured as band-pass (iii), the cutoff frequencies are illuminated by two LED’s. The frequency setting on the left marks the cutoff for the high-pass filter, and the set ...
Variation-Aware Supply Voltage Assignment for Minimizing Circuit Degradation and Leakage Xiaoming Chen
... designers. And the growing process variations can no longer be ignored. Meanwhile, reducing leakage power remains to be one of the design goals. In this paper, we first present a platform for NBTI-aware statistical timing and leakage power analysis. A variation-aware supply voltage assignment (SVA) ...
... designers. And the growing process variations can no longer be ignored. Meanwhile, reducing leakage power remains to be one of the design goals. In this paper, we first present a platform for NBTI-aware statistical timing and leakage power analysis. A variation-aware supply voltage assignment (SVA) ...
Thevenin and Norton Theorem
... must be zero. There is no “juice” in the circuit so there cannot be any open circuit voltage except zero. This is always true when the circuit is made up of only dependent sources and ...
... must be zero. There is no “juice” in the circuit so there cannot be any open circuit voltage except zero. This is always true when the circuit is made up of only dependent sources and ...
Stepping Circuits
... slow to operate feature ensures that the relay is well fluxed before it operates, so making the slow to release feature reliable as soon as the relay is operated. This means that the momentary "dis" that appears in its holding path when the CD3 contact change over will not cause the release of relay ...
... slow to operate feature ensures that the relay is well fluxed before it operates, so making the slow to release feature reliable as soon as the relay is operated. This means that the momentary "dis" that appears in its holding path when the CD3 contact change over will not cause the release of relay ...
Chapter 4
... constant dc voltages (voltage regulators) application of the diode in the design of rectifier circuits, which convert ac voltages to dc as needed for powering electronic equipment a number of other practical and important applications Oxford University Publishing Microelectronic Circuits by Adel ...
... constant dc voltages (voltage regulators) application of the diode in the design of rectifier circuits, which convert ac voltages to dc as needed for powering electronic equipment a number of other practical and important applications Oxford University Publishing Microelectronic Circuits by Adel ...
kcs problem and solution for microelectronic circuit
... constant dc voltages (voltage regulators) application of the diode in the design of rectifier circuits, which convert ac voltages to dc as needed for powering electronic equipment a number of other practical and important applications Oxford University Publishing Microelectronic Circuits by Adel ...
... constant dc voltages (voltage regulators) application of the diode in the design of rectifier circuits, which convert ac voltages to dc as needed for powering electronic equipment a number of other practical and important applications Oxford University Publishing Microelectronic Circuits by Adel ...
Circuits in “Real life”
... Power We previously used the result that the power (joules per second) dissipated across a resistor was I 2 R. Let’s take that a step further. Change in electric potential energy, ∆U, required to change the electric potential a charge q experiences is = q∆V If this is done in a time ∆t, then the pow ...
... Power We previously used the result that the power (joules per second) dissipated across a resistor was I 2 R. Let’s take that a step further. Change in electric potential energy, ∆U, required to change the electric potential a charge q experiences is = q∆V If this is done in a time ∆t, then the pow ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.