Lect20
... – Analysis of multi-loop circuits with batteries and resistors. – Main Feature: Currents are attained instantaneously and do not vary with time!! ...
... – Analysis of multi-loop circuits with batteries and resistors. – Main Feature: Currents are attained instantaneously and do not vary with time!! ...
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
Slide 1
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
A 10-bit 50-MS/s sample-and-hold circuit with low distortion sampling switches )
... power, high resolution and high speed ADCs are becoming more necessary. The pipeline ADC is a popular choice for high-speed data conversion because of its compact size and efficient power dissipation. Most pipeline ADCs have an onchip S/H circuit in front of the pipeline stages to buffer the input s ...
... power, high resolution and high speed ADCs are becoming more necessary. The pipeline ADC is a popular choice for high-speed data conversion because of its compact size and efficient power dissipation. Most pipeline ADCs have an onchip S/H circuit in front of the pipeline stages to buffer the input s ...
Lecture Circuits
... As soon as the circuit is complete, charge flows between a capacitor plate and a battery terminal on each side of the capacitor. This current increases the charge q on the plates and the potential difference VC (= q/C) across the capacitor. When that potential difference equals the potential differe ...
... As soon as the circuit is complete, charge flows between a capacitor plate and a battery terminal on each side of the capacitor. This current increases the charge q on the plates and the potential difference VC (= q/C) across the capacitor. When that potential difference equals the potential differe ...
Slide 1
... As soon as the circuit is complete, charge flows between a capacitor plate and a battery terminal on each side of the capacitor. This current increases the charge q on the plates and the potential difference VC (= q/C) across the capacitor. When that potential difference equals the potential differe ...
... As soon as the circuit is complete, charge flows between a capacitor plate and a battery terminal on each side of the capacitor. This current increases the charge q on the plates and the potential difference VC (= q/C) across the capacitor. When that potential difference equals the potential differe ...
... G. Current Source and Norton’s Theorem A transistor is used to illustrate a current source. You do not have to understand transistor operation to make the measurements, but remember the results because they will be helpful when you study transistors later. Set up the circuit shown in Fig. 10. Both v ...
Electrical Circuits 2 (from CPO Physics)
... 20.3 Alternating and direct current AC current is used for almost all high-power applications because it is easier to generate and to transmit over long distances. The 120 volt AC (VAC) electricity used in homes and businesses alternates between peak values of +170 V and -170 V at a frequency o ...
... 20.3 Alternating and direct current AC current is used for almost all high-power applications because it is easier to generate and to transmit over long distances. The 120 volt AC (VAC) electricity used in homes and businesses alternates between peak values of +170 V and -170 V at a frequency o ...
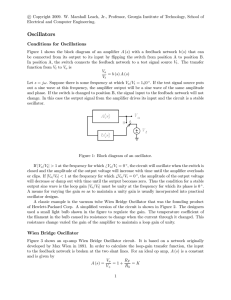
Wien-Bridge and Phase-Shift Oscillators
... ±360 ◦ ). A phase shift of +180 ◦ can be obtained by cascading two RC high-pass filters. However, at the frequency where the phase shift is exactly +180 ◦ , the gain of the filters is zero. By cascading three RC high-pass filters, there is a frequency at which the phase shift is +180 ◦ and the gain ...
... ±360 ◦ ). A phase shift of +180 ◦ can be obtained by cascading two RC high-pass filters. However, at the frequency where the phase shift is exactly +180 ◦ , the gain of the filters is zero. By cascading three RC high-pass filters, there is a frequency at which the phase shift is +180 ◦ and the gain ...
Series vs. Parallel Circuit
... ● Total voltage is same in all branches of the circuit. ● Currents in each path add to current from the battery ● Path with the least resistance gets most current ● A break in one path has no effect on the other paths. ● Fuses, resistors and switches will do nothing if they are connected in a path t ...
... ● Total voltage is same in all branches of the circuit. ● Currents in each path add to current from the battery ● Path with the least resistance gets most current ● A break in one path has no effect on the other paths. ● Fuses, resistors and switches will do nothing if they are connected in a path t ...
Ch19circuits - Mother Seton
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
... galvanometers, unless they are digital. The current in a circuit passes through the ammeter; the ammeter should have low resistance so as not to affect the current. ...
Lab 4
... While fine for ideal circuits, the rapid change at t = 0 can produce a lot of error in the calculation for actual circuits. • Solving the equation of the response using two points from the response curve. Suppose the response is of the − t /τ ...
... While fine for ideal circuits, the rapid change at t = 0 can produce a lot of error in the calculation for actual circuits. • Solving the equation of the response using two points from the response curve. Suppose the response is of the − t /τ ...
2300_QU2_All_Sects_Spring2003
... The first step in the solution is to simplify the circuit. Note that the 10[W] and 13[W] resistors are effectively in series with an open circuit, thus no current flows through them. As a result, they have no voltage across them. They can be ignored. Also, the 75[W] resistor is in parallel with a sh ...
... The first step in the solution is to simplify the circuit. Note that the 10[W] and 13[W] resistors are effectively in series with an open circuit, thus no current flows through them. As a result, they have no voltage across them. They can be ignored. Also, the 75[W] resistor is in parallel with a sh ...
quizzesf00
... This is due Tuesday Dec. 5, 2000 at the beginning of the class period. Students must work independently on this assignment, NO COLLABORATION. Any detected cheating will result in an E for the course for all involved parties. Hand in a hard copy of the circuit and tables from SPICE that clearly show ...
... This is due Tuesday Dec. 5, 2000 at the beginning of the class period. Students must work independently on this assignment, NO COLLABORATION. Any detected cheating will result in an E for the course for all involved parties. Hand in a hard copy of the circuit and tables from SPICE that clearly show ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.