beat-frequency audio genera tor
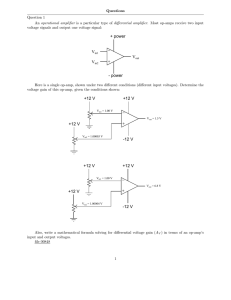
... which will lie between 0 to 20 or 20 to 40 kc, is fed to thelamplifier in· put level control through a low-pass filter, which remo•s frequency components above 40 kc. The output of the amplifier is transformercoupled to the output system. The complete schematic diagram, including power supply, is sh ...
... which will lie between 0 to 20 or 20 to 40 kc, is fed to thelamplifier in· put level control through a low-pass filter, which remo•s frequency components above 40 kc. The output of the amplifier is transformercoupled to the output system. The complete schematic diagram, including power supply, is sh ...
Document
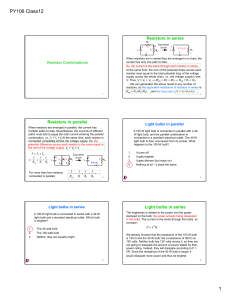
... Three identical light bulbs are connected in the circuit shown. When the power is turned on, and with the switch beside bulb C left open, how will the brightness of the bulbs compare? 1. A = B = C 2. A > B > C 3. A > B = C 4. A = B > C 5. B > A > C ...
... Three identical light bulbs are connected in the circuit shown. When the power is turned on, and with the switch beside bulb C left open, how will the brightness of the bulbs compare? 1. A = B = C 2. A > B > C 3. A > B = C 4. A = B > C 5. B > A > C ...
Jacobs University Bremen Natural Science Laboratory Fall Semester 2014
... Second-order systems are very common in nature. They are named second-order systems, as the highest power of derivative in the differential equation describing the system is two. In electrical engineering, circuits consisting of two energy storage elements, capacitors and inductors, for example RLC ...
... Second-order systems are very common in nature. They are named second-order systems, as the highest power of derivative in the differential equation describing the system is two. In electrical engineering, circuits consisting of two energy storage elements, capacitors and inductors, for example RLC ...
E-STOP relays, safety gate monitors
... Connect the base unit and the contact expander module to the supplied connector before mounting the units to the DIN rail. Installation in control cabinet The safety relay should be installed in a control cabinet with a protection type of at least IP54. Use the notch on the rear of the unit to ...
... Connect the base unit and the contact expander module to the supplied connector before mounting the units to the DIN rail. Installation in control cabinet The safety relay should be installed in a control cabinet with a protection type of at least IP54. Use the notch on the rear of the unit to ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... The reported no static power dissipation as a result of the circuits were static in nature[11]. Economist designed a netruly full adder quaternary circuit pattern 3 power provide lines and multi-Vt transistors .Ricardo has designed quaternary device (MUX) 4:1 with 4quaternary inputs and one quaterna ...
... The reported no static power dissipation as a result of the circuits were static in nature[11]. Economist designed a netruly full adder quaternary circuit pattern 3 power provide lines and multi-Vt transistors .Ricardo has designed quaternary device (MUX) 4:1 with 4quaternary inputs and one quaterna ...
Application Note AN-55 HiperLCS Family
... voltage. If VBROWNOUT is below this range, the VOV_RESTART point will be below VBULK_NOM, and the HiperLCS will not restart after a voltage swell event that triggers VOV_SHUT. For maximum hold-up time, set VBROWNOUT to 65% of VBULK_NOM. The designer may choose to use a higher VBROWNOUT voltage than ...
... voltage. If VBROWNOUT is below this range, the VOV_RESTART point will be below VBULK_NOM, and the HiperLCS will not restart after a voltage swell event that triggers VOV_SHUT. For maximum hold-up time, set VBROWNOUT to 65% of VBULK_NOM. The designer may choose to use a higher VBROWNOUT voltage than ...
Technical specification for tender cm4000specguide_02-24
... shall include frequency, temperature, current, demand current, voltage, real power, reactive power, apparent power, demand power, predicted demand power, power factor, accumulated energy, accumulated reactive energy, total harmonic distortion (THD) of each current and voltage, and K-factor of each c ...
... shall include frequency, temperature, current, demand current, voltage, real power, reactive power, apparent power, demand power, predicted demand power, power factor, accumulated energy, accumulated reactive energy, total harmonic distortion (THD) of each current and voltage, and K-factor of each c ...
UNITS, PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AND VECTORS
... EXECUTE: From Ohm’s law, the voltage drop across the 6.00 resistor is V = IR = (4.00 A)(6.00 ) = 24.0 V. The voltage drop across the 8.00 resistor is the same, since these two resistors are wired in parallel. The current through the 8.00 resistor is then I = V/R = 24.0 V/8.00 = 3.00 A. The ...
... EXECUTE: From Ohm’s law, the voltage drop across the 6.00 resistor is V = IR = (4.00 A)(6.00 ) = 24.0 V. The voltage drop across the 8.00 resistor is the same, since these two resistors are wired in parallel. The current through the 8.00 resistor is then I = V/R = 24.0 V/8.00 = 3.00 A. The ...
1-100 Transistor circuits
... Increase the voltage to the higher value and take another reading. In most cases the current will increase to double the value (or a little higher than twice the original value). If it is over 250% higher, you need to feel each of the components and see if any are getting excessively hot. If any LED ...
... Increase the voltage to the higher value and take another reading. In most cases the current will increase to double the value (or a little higher than twice the original value). If it is over 250% higher, you need to feel each of the components and see if any are getting excessively hot. If any LED ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.