mRNA
... Translation occurs in the cell's cytoplasm, where the large and small subunits of the ribosome are located, and bind to the ...
... Translation occurs in the cell's cytoplasm, where the large and small subunits of the ribosome are located, and bind to the ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Messenger RNA: (mRNA) Codon - carry messages from the DNA to the rest of the cell. • Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) found in the ribosomes where proteins are assembled • Transfer RNA: (tRNA) Anticodon - transfers each amino acid to the ribosomes as it is needed ...
... • Messenger RNA: (mRNA) Codon - carry messages from the DNA to the rest of the cell. • Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) found in the ribosomes where proteins are assembled • Transfer RNA: (tRNA) Anticodon - transfers each amino acid to the ribosomes as it is needed ...
Fragmenting genomic DNA for cloning
... a contiguous sequence (contig) • Genes whose general location is known (by genetic mapping), but whose function is not known, can be found by starting with the genetic marker clone and “walking” away from it ...
... a contiguous sequence (contig) • Genes whose general location is known (by genetic mapping), but whose function is not known, can be found by starting with the genetic marker clone and “walking” away from it ...
Lecture 2a – Origin of Life and the transition from the RNA world to
... From RNA to DNA/protein Although RNA can function both as an information carrier (template for replication) and as a catalyst (replicase), it is not very good at either. This means that both e and ln s are unfavorable – a lot of errors are made in copying RNA (even using modern RNA polymerases) and ...
... From RNA to DNA/protein Although RNA can function both as an information carrier (template for replication) and as a catalyst (replicase), it is not very good at either. This means that both e and ln s are unfavorable – a lot of errors are made in copying RNA (even using modern RNA polymerases) and ...
LECTURE 5: DNA, RNA & PROTEINS
... • Transcription occurs in the _________ • mRNA carries the message about what type of protein to make from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome • The nucleotide sequences of RNA and DNA are the same (except in RNA _______ is used instead of thymine) • mRNA is synthesized from DNA using base pairin ...
... • Transcription occurs in the _________ • mRNA carries the message about what type of protein to make from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome • The nucleotide sequences of RNA and DNA are the same (except in RNA _______ is used instead of thymine) • mRNA is synthesized from DNA using base pairin ...
DNA Review (study guide)
... 2. In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the __________________ of the next group. 3. Base pairing rule states that the DNA of any species contains equal amounts of __________________ & ____________ and also equal amounts of __________________ & ____________________ 4. Wilkins and ...
... 2. In a single strand of DNA, the phosphate group binds to the __________________ of the next group. 3. Base pairing rule states that the DNA of any species contains equal amounts of __________________ & ____________ and also equal amounts of __________________ & ____________________ 4. Wilkins and ...
RNA interference was popularized by work in C
... RNA interference was popularized by work in C.elegans. When long double-stranded RNAs were injected into a worm’s gonad, a standard way of introducing transgenes into worms, they blocked the expression of endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are ...
... RNA interference was popularized by work in C.elegans. When long double-stranded RNAs were injected into a worm’s gonad, a standard way of introducing transgenes into worms, they blocked the expression of endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are ...
Gene Section FHL2 (four and a half LIM domains 2)
... FHL2 belongs to the four-and-a-half-LIM-only protein family, which includes FHL1, FHL2, FHL3, FHL4 and FHL5 (ACT). Human FHL2 amino acid sequence is 48.2% identical with FHL1, 53.4% with FHL3, 48.4% with mouse FHL4, and 59.1% with FHL5. Orthologs of human FHL2 are found in macaque, mouse, rat, bovin ...
... FHL2 belongs to the four-and-a-half-LIM-only protein family, which includes FHL1, FHL2, FHL3, FHL4 and FHL5 (ACT). Human FHL2 amino acid sequence is 48.2% identical with FHL1, 53.4% with FHL3, 48.4% with mouse FHL4, and 59.1% with FHL5. Orthologs of human FHL2 are found in macaque, mouse, rat, bovin ...
Biology_Review-final
... The 5’ untranslated region (yellow). A UTR is a non-coding sequence of bases in the mRNA. The 5’ UTR contains the ribosome binding site. The coding sequence—CDS (green), which begins with the sequence AUG, the start codon. Codons are sequences three bases long and code for one amino acid. The start ...
... The 5’ untranslated region (yellow). A UTR is a non-coding sequence of bases in the mRNA. The 5’ UTR contains the ribosome binding site. The coding sequence—CDS (green), which begins with the sequence AUG, the start codon. Codons are sequences three bases long and code for one amino acid. The start ...
Document
... • Control of transcription initiation can be: – positive control – increases transcription when activators bind DNA – negative control – reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory regions called operators ...
... • Control of transcription initiation can be: – positive control – increases transcription when activators bind DNA – negative control – reduces transcription when repressors bind to DNA regulatory regions called operators ...
Fen-1 Nuclease in Genome Stability
... metal affinity chromatography). This method is based on the principle that nickel beads in the Ni-NTA(nickel-nitrotriacetic acid) complex can bind effectively to the histidine tags located on the surface of a protein, which also immobilize the protein. We specifically constructed these six consecuti ...
... metal affinity chromatography). This method is based on the principle that nickel beads in the Ni-NTA(nickel-nitrotriacetic acid) complex can bind effectively to the histidine tags located on the surface of a protein, which also immobilize the protein. We specifically constructed these six consecuti ...
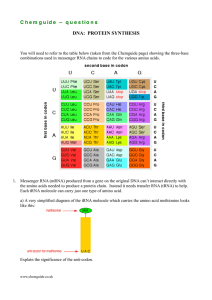
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Transcription and Translation
... Transcription Termination • At end of gene DNA has a “terminator” • Sequence that signals end of transcription • RNA polymerase disassociates from DNA • ss mRNA floats away ...
... Transcription Termination • At end of gene DNA has a “terminator” • Sequence that signals end of transcription • RNA polymerase disassociates from DNA • ss mRNA floats away ...
交通大學特色研究計畫邀請 - 國立交通大學生物資訊研究所
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
No Slide Title
... repressors & corepressors from genes for galactose catabolism •Speeds induction of GAL genes ...
... repressors & corepressors from genes for galactose catabolism •Speeds induction of GAL genes ...
Hoku`s Slides
... Several coupled DNA and protein libraries are constructed, randomizing 3 base pairs and 5 contacting amino acids for each NNNGGAGGTTTCTCTGTAAA TGANNNGGTTTCTCTGTAAA ...
... Several coupled DNA and protein libraries are constructed, randomizing 3 base pairs and 5 contacting amino acids for each NNNGGAGGTTTCTCTGTAAA TGANNNGGTTTCTCTGTAAA ...
DNA_Technology_part2
... bacteria containing the plasmid • Only about 0.001% of bacterial cells take up any DNA/Plasmids when the two are mixed together. • Firstly, we must identify the bacteria containing the plasmids – we do this by growing the bacteria on a medium containing an antibiotic. • The antibiotic resistant gene ...
... bacteria containing the plasmid • Only about 0.001% of bacterial cells take up any DNA/Plasmids when the two are mixed together. • Firstly, we must identify the bacteria containing the plasmids – we do this by growing the bacteria on a medium containing an antibiotic. • The antibiotic resistant gene ...
The Future of Human Gene Editing
... contained the replacement genetic material. “If you want to do it in normal embryos, you need to be close to 100%,” Huang says. “That’s why we stopped. We still think it’s too immature.” Additionally, his team also found a surprising number of ‘off-target’ mutations, assumed to be introduced by the ...
... contained the replacement genetic material. “If you want to do it in normal embryos, you need to be close to 100%,” Huang says. “That’s why we stopped. We still think it’s too immature.” Additionally, his team also found a surprising number of ‘off-target’ mutations, assumed to be introduced by the ...
Chapter 1
... Insertions can revert by deletion of the inserted material, but deletions cannot revert. Suppression occurs when a mutation in a second gene bypasses the effect of mutation in the first gene. ...
... Insertions can revert by deletion of the inserted material, but deletions cannot revert. Suppression occurs when a mutation in a second gene bypasses the effect of mutation in the first gene. ...