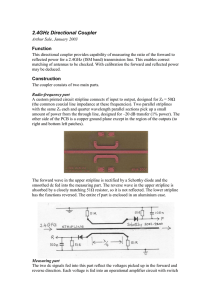
Mar 2003 Triple and Quad RGB Amplifiers Deliver Full Performance on 3.3V
... for driving RGB and component video cables. These voltage feedback amplifiers drive either 50Ω or 75Ω double terminated cables and are preconfigured for a fixed gain of two, thus eliminating six or eight external gain setting resistors. The industry trend of using lower supply voltages increases the ...
... for driving RGB and component video cables. These voltage feedback amplifiers drive either 50Ω or 75Ω double terminated cables and are preconfigured for a fixed gain of two, thus eliminating six or eight external gain setting resistors. The industry trend of using lower supply voltages increases the ...
Ohm`s law report Sogi_Fuentes
... The voltage across each resistor changes. 2. What can you say about the sum of the current through the resistor in circuit 2? The current across each resistor changes and the current stays the same. 3. Construct a graph for each circuit plotting every V(I) point. Look for obvious linear relationship ...
... The voltage across each resistor changes. 2. What can you say about the sum of the current through the resistor in circuit 2? The current across each resistor changes and the current stays the same. 3. Construct a graph for each circuit plotting every V(I) point. Look for obvious linear relationship ...
Power Dissipated in Resistors - Purdue Physics
... Power Dissipation - the Technology Underlying Fuses and Circuit Breakers •In a fuse, current passes through a thin metal strip – The strip acts as a resistor with a small resistance – If a fault causes the current to become large, the increased power melts the strip to melt and the current stops – ...
... Power Dissipation - the Technology Underlying Fuses and Circuit Breakers •In a fuse, current passes through a thin metal strip – The strip acts as a resistor with a small resistance – If a fault causes the current to become large, the increased power melts the strip to melt and the current stops – ...
855
... When a resistor is traversed in the direction of the current, the potential difference DV across the resistor is 2IR. When a resistor is traversed in the direction opposite the current, DV 5 1IR. When a source of emf is traversed in the direction of the emf (negative terminal to positive terminal), ...
... When a resistor is traversed in the direction of the current, the potential difference DV across the resistor is 2IR. When a resistor is traversed in the direction opposite the current, DV 5 1IR. When a source of emf is traversed in the direction of the emf (negative terminal to positive terminal), ...
Model Answer
... The voltage at the positive terminal of the op-amp vp and the voltage at the negative terminal is vn ...
... The voltage at the positive terminal of the op-amp vp and the voltage at the negative terminal is vn ...
BJT Amplifiers Lecture Slides
... C3 are large coupling capacitors or dc blocking capacitors, their reactance (XC = |ZC| = 1/wC) at signal frequency is negligible. They are effective open circuits for the circuit when DC bias is considered. • AC coupling through capacitors is used to inject an ac input signal and extract the ac outp ...
... C3 are large coupling capacitors or dc blocking capacitors, their reactance (XC = |ZC| = 1/wC) at signal frequency is negligible. They are effective open circuits for the circuit when DC bias is considered. • AC coupling through capacitors is used to inject an ac input signal and extract the ac outp ...
Analog-to-Digital Converter and Multivibrators
... • A multi-vibrator is an electronic circuit that can exist in a number of “states” (voltage and/or current outputs) • A flip-flop is a bi-stable multi-vibrator, bistable means it has two stable states • A state is stable if it is robust against the fluctuations (noise) that are always occurring ...
... • A multi-vibrator is an electronic circuit that can exist in a number of “states” (voltage and/or current outputs) • A flip-flop is a bi-stable multi-vibrator, bistable means it has two stable states • A state is stable if it is robust against the fluctuations (noise) that are always occurring ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... The open circuit voltage is the Thévenin equivalent voltage. Now we need to find the impedance ZTH. The circuit has only independent power supplies. We can turn off the power supplies then find the equivalent impedance ZTH. To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to m ...
... The open circuit voltage is the Thévenin equivalent voltage. Now we need to find the impedance ZTH. The circuit has only independent power supplies. We can turn off the power supplies then find the equivalent impedance ZTH. To turn off the current source, we make the current equal to 0. We need to m ...
How to Create Square Waves in MATLAB
... applied across a series circuit (OUTPUT a Signal) Use the DAQ as a voltmeter to measure the voltage across a resistor (INPUT the measurements) The DAQ will send these measurements back into MATLAB so we can easily plot the voltage vs. time ...
... applied across a series circuit (OUTPUT a Signal) Use the DAQ as a voltmeter to measure the voltage across a resistor (INPUT the measurements) The DAQ will send these measurements back into MATLAB so we can easily plot the voltage vs. time ...
Electric Circuits
... electrical circuit caused when the wire touches another hot wire or touches a neutral wire. It can also be caused if there is a break in a wire or connection. ...
... electrical circuit caused when the wire touches another hot wire or touches a neutral wire. It can also be caused if there is a break in a wire or connection. ...
Electromagnetism G. L. Pollack and D. R. Stump Four stepped exercises.
... similarly. Consider next what happens at the junction (0, 1, 1): Two b equal currents bjI/6 and kI/6 flow into it so that current biI/3 must flow out from (0, 1, 1) to (1, 1, 1). The cube with all currents is shown in Fig 1(b). Finally then for the path (0, 0, 0) → (0, 0, 1) → (0, 1, 1) → (1, 1, 1) ...
... similarly. Consider next what happens at the junction (0, 1, 1): Two b equal currents bjI/6 and kI/6 flow into it so that current biI/3 must flow out from (0, 1, 1) to (1, 1, 1). The cube with all currents is shown in Fig 1(b). Finally then for the path (0, 0, 0) → (0, 0, 1) → (0, 1, 1) → (1, 1, 1) ...
Bipolar Junction Transistor
... the PNP and NPN bipola r transistor are given above with the arrow in the circuit symbol always showing the direction of “conventional current flow” between the base terminal and its emitter terminal. The direction of the arrow always points from the positive P-type region to the negative N-type reg ...
... the PNP and NPN bipola r transistor are given above with the arrow in the circuit symbol always showing the direction of “conventional current flow” between the base terminal and its emitter terminal. The direction of the arrow always points from the positive P-type region to the negative N-type reg ...
REVIEW SHEET – ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
... b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...
... b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? ...
Lecture 7-3 Phasor Domain Analysis
... Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS rights reserved. Do notby copythe or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Press, Used withAllPermission Publisher ...
... Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS rights reserved. Do notby copythe or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Press, Used withAllPermission Publisher ...
Transformer problems (Due Tuesday 25th March (PAYDAY
... Directions: Everyone must complete #1 on the circuit problems below. Be sure to diagram the circuit, label the appropriate parts, and show all work on calculations. Once complete, choose any additional 2 problems to complete. 1. A circuit is set up with two parallel resistors, each of a resistance o ...
... Directions: Everyone must complete #1 on the circuit problems below. Be sure to diagram the circuit, label the appropriate parts, and show all work on calculations. Once complete, choose any additional 2 problems to complete. 1. A circuit is set up with two parallel resistors, each of a resistance o ...