Principles of Electronics
... Voltage: is the difference in charge between two points. Current: is the rate at which charge is flowing. Resistance: is a material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge (current). ...
... Voltage: is the difference in charge between two points. Current: is the rate at which charge is flowing. Resistance: is a material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge (current). ...
Circuits and Ohm*s Law
... • If one resistor is turned off, the others still work. • The more resistors (branches) that are on, the lower the total resistance. • Each resistor has the total voltage of the power source. • Each resistor has its own circuit. ...
... • If one resistor is turned off, the others still work. • The more resistors (branches) that are on, the lower the total resistance. • Each resistor has the total voltage of the power source. • Each resistor has its own circuit. ...
Circuits and Ohm’s Law
... • If one resistor is turned off, the others still work. • The more resistors (branches) that are on, the lower the total resistance. • Each resistor has the total voltage of the power source. • Each resistor has its own circuit. ...
... • If one resistor is turned off, the others still work. • The more resistors (branches) that are on, the lower the total resistance. • Each resistor has the total voltage of the power source. • Each resistor has its own circuit. ...
Linear Circuit Elements
... As a result, we know that that there must be some linear operator that relates v t and i t in your example! LZ i t v t ...
... As a result, we know that that there must be some linear operator that relates v t and i t in your example! LZ i t v t ...
Series and Parallel Circuits • Components in a circuit can be
... Can have combinations of components switched on and off as desired All components connected in parallel will have the same voltage across them o Connecting components to the mains supply of 230 V means that all components receive the full 230 V ...
... Can have combinations of components switched on and off as desired All components connected in parallel will have the same voltage across them o Connecting components to the mains supply of 230 V means that all components receive the full 230 V ...
80VIN/80VOUT, Constant Voltage, Constant
... frequency adjust pin permits the user to program the frequency between 100kHz and 1MHz, optimizing efficiency while minimizing external component size and cost. Combined with a 5mm x 6mm QFN package, the LT3956 offers a highly compact 25 Watt LED driver solution. The LT3956 uses True Color PWM™ dimm ...
... frequency adjust pin permits the user to program the frequency between 100kHz and 1MHz, optimizing efficiency while minimizing external component size and cost. Combined with a 5mm x 6mm QFN package, the LT3956 offers a highly compact 25 Watt LED driver solution. The LT3956 uses True Color PWM™ dimm ...
Self Study Unit 1.2
... Unit 1.2 Electronic Principles: Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law is the relationship between voltage, current, and the resistance in a DC circuit. When you know any two of these values, you can calculate the third. The most basic equation for Ohm’s Law is: E = I ×R In other words, when you know the current going ...
... Unit 1.2 Electronic Principles: Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law is the relationship between voltage, current, and the resistance in a DC circuit. When you know any two of these values, you can calculate the third. The most basic equation for Ohm’s Law is: E = I ×R In other words, when you know the current going ...
R225-60-9
... the resistive component is available for the control to maintain correct voltage at the load center. If the resistive component is to be used while the negative reactance method of paralleling is used, the resistive settings of all of the regulators being paralleled should be set to the same value. ...
... the resistive component is available for the control to maintain correct voltage at the load center. If the resistive component is to be used while the negative reactance method of paralleling is used, the resistive settings of all of the regulators being paralleled should be set to the same value. ...
Datasheet - CREATIVE CHIPS GmbH
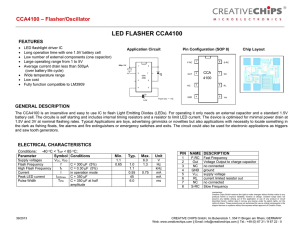
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
... The CCA4100 is an insensitive and easy to use IC to flash Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). For operating it only needs an external capacitor and a standard 1.5V battery cell. The circuite is self starting and includes internal timing resistors and a resistor to limit LED current. The device is optimise ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.