Electronics
... the potential difference between the collector and emitter. The current gain for this transistor is ...
... the potential difference between the collector and emitter. The current gain for this transistor is ...
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS DARTMOUTH
... resistance from the series resistance necessary to obtain Q = 5. For both the capacitor and resistor, use the standard component value that is closest to your calculated value. 2. Once you have designed your circuit, construct it in MultiSim and run a simulation using the Bode Plotter. Measure the r ...
... resistance from the series resistance necessary to obtain Q = 5. For both the capacitor and resistor, use the standard component value that is closest to your calculated value. 2. Once you have designed your circuit, construct it in MultiSim and run a simulation using the Bode Plotter. Measure the r ...
Superposition Analysis LectureNotes
... current I flows through all of them. Now, using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law we get the following equation: -5V + VR1 + VR2 = 0 Now we can use Ohm’s Law, V=IR, to define the voltages across the two resistors. -5V + I*R1 + I*R2 = 0 Rearranging to solve for I, we get: I = 5V/(R1+R2) = 1/6 A Now we can use ...
... current I flows through all of them. Now, using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law we get the following equation: -5V + VR1 + VR2 = 0 Now we can use Ohm’s Law, V=IR, to define the voltages across the two resistors. -5V + I*R1 + I*R2 = 0 Rearranging to solve for I, we get: I = 5V/(R1+R2) = 1/6 A Now we can use ...
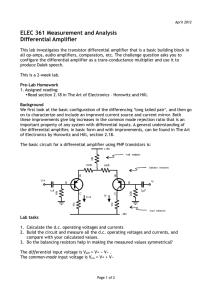
ELEC 361 Measurement and Analysis Differential Amplifier
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
EE 221 Review 1
... The algebraic sum of the currents entering any node is zero. iA + iB - iC - iD = 0 ...
... The algebraic sum of the currents entering any node is zero. iA + iB - iC - iD = 0 ...
25._ElectricCircuits
... A camera flash gets its energy from a 150-F capacitor & requires 170 V to fire. If the capacitor is charged by a 200-V source through an 18-k resistor, how long must the photographer wait between flashes? Assume the capacitor is fully charged at each flash. ...
... A camera flash gets its energy from a 150-F capacitor & requires 170 V to fire. If the capacitor is charged by a 200-V source through an 18-k resistor, how long must the photographer wait between flashes? Assume the capacitor is fully charged at each flash. ...
Document
... series circuit has a time constant of 600 μs, and the maximum current is 300 mA. What’s the value of the inductance? 3. Calculate the resistance in an RL circuit in which L = 2.50 H and the current increases to 90.0% of its final value in 3.00 s. 4. How much energy is stored in a 70 mH inductor at a ...
... series circuit has a time constant of 600 μs, and the maximum current is 300 mA. What’s the value of the inductance? 3. Calculate the resistance in an RL circuit in which L = 2.50 H and the current increases to 90.0% of its final value in 3.00 s. 4. How much energy is stored in a 70 mH inductor at a ...
Network analysis (electrical circuits)

A network, in the context of electronics, is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, every component in the network. There are many different techniques for calculating these values. However, for the most part, the applied technique assumes that the components of the network are all linear.The methods described in this article are only applicable to linear network analysis, except where explicitly stated.